![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
63 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the fat soluble vitamins? |
A, D, E, and K
|
|
|
What do the fat soluble vitamins (A, D, E, K) depend on for absorption?
|
Depend on gut (ileum) and pancreas
|
|
|
What can cause fat soluble vitamin deficiencies?
|
- Malabsorption syndromes (eg, steatorrhea), such as cystic fibrosis and sprue
- Mineral oil intake |
|
|
What are the water soluble vitamins?
|
- B1 (Thiamine: TPP)
- B2 (Riboflavin: FAD, FMN) - B3 (Niacin: NAD+) - B5 (Pantothenic acid: CoA) - B6 (Pyridoxine: PLP) - B7 (Biotin) - B9 (Folate) - B12 (Cobalamin) - C (Ascorbic Acid) |
|
|
Are fat or water soluble vitamins more likely to cause toxicity? Why?
|
- Fat soluble vitamins are more likely to cause toxicity because they can accumulate in the fat
- By contrast, water soluble vitamins wash out easily from body (except B12 and B9 - folate, which are stored in liver) |
|
|
What do B-complex deficiencies often cause?
|
- Dermatitis
- Glossitis - Diarrhea |
|
|
What are the functions of Vitamin A? Uses?
|
Functions:
- Antioxidant - Constituent of visual pigments (retinal) - Essential for normal differentiation of epithelial cells into specialized tissue (pancreatic cells, mucus-secreting cells) - prevents squamous metaplasia Uses: - Treat measles - Treat AML, subtype 3 - Topically for wrinkles and acne |
|
|
What are the sources of Vitamin A? What can a deficiency cause?
|
Sources:
- Liver - Leafy vegetables Deficiency: - Night blindness - Dry skin |
|
|
What can excess Vitamin A cause?
|
- Arthralgias
- Fatigue - Headaches - Skin changes - Sore throat - Teratogenic (cleft palate, cardiac abnormalities) - must rule out pregnancy before prescribing |
|
|
What are the functions of Vitamin B1 (Thiamine)?
|
In Thiamine Pyrophosphate (TPP) form, it is a cofactor for several enzymes in decarboxylation reactions:
- α-Ketoglutarate Dehydrogenase (TCA cycle) - Transketolase (HMP shunt) - Pyruvate dehydrogenase (links glycolysis to TCA cycle) (think ATP synthesis) - Branched-chain amino acid dehydrogenase |
|
|
What can a deficiency of Vitamin B1 (Thiamine) cause?
|
- Impaired glucose breakdown → ATP depletion worsened by glucose infusion
- Highly aerobic tissues (brain and heart) affected first - Causes Wernicke-Korsakoff Syndrome and Beriberi - Seen in malnutrition as well as alcoholism (2° to malnutrition and malabsorption) |
|
|
What is the cause of Wernicke-Korsakoff Syndrome? Symptoms?
|
- Vitamin B1 (thiamine) deficiency, 2° to malnutrition as well as alcoholism
Causes: Classic Triad: - Confusion - Ophthalmoplegia - Ataxia Other - Confabulation - Personality change - Memory loss (permanent) *Damage to medial dorsal nucleus of thalamus and mamillary bodies |
|
|
What is the cause of Beriberi? Symptoms?
|
Beriberi, think Ber1-Ber1 (B1) = Thiamine
Dry: - Polyneuritis - Symmetrical muscle wasting Wet: - High-output cardiac failure (dilated cardiomyopathy) - Edema |
|
|
What are the functions of Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin)?
|
Cofactor in oxidation and reduction (eg, FADH2)
|
|
|
What can a deficiency of Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin) cause?
|
"2 C's of B2"
- Cheilosis (inflammation of lips, scaling and fissures at the corners of the mouth) - Corneal vascularization |
|
|
What are the functions of Vitamin B3 (Niacin)?
|
Constituent of NAD+, NADP+ (used in redox reactions)
|
|
|
What is Vitamin B3 (Niacin) derived from? What does synthesis require?
|
- Derived from tryptophan
- Synthesis requires Vitamin B6 |
|
|
What can a deficiency of Vitamin B3 (Niacin) cause?
|
- Glossitis
- Severe deficiency can cause "3 D's of B3": pellagra (dermatitis, diarrhea, and dementia) |
|
|
What can cause pellagra? Symptoms?
|
Vitamin B3 (Niacin) Deficiency can be caused by:
- Hartnup Disease (↓ tryptophan absorption) - Malignant carcinoid syndrome (↑ tryptophan metabolism) - INH (↓ Vitamin B6) Symptoms: 3 D's of B3 - Diarrhea - Dementia - Dermatitis |
|
|
What can an excess of Vitamin B3 (Niacin) cause?
|
Facial flushing (d/t pharmacologic doses for treatment of hyperlipidemia)
|
|
|
What are the functions of Vitamin B5 (Pantothenic Acid)?
|
Essential component of CoA (a cofactor for acyl transfers) and fatty acid synthase
|
|
|
What can a deficiency of Vitamin B5 (Pantothenic Acid) cause?
|
- Dermatitis
- Enteritis - Alopecia - Adrenal insufficiency |
|
|
What are the functions of Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine)?
|
- Converted to pyridoxal phosphate (cofactor for transamination - eg, ALT and AST)
- Decarboxylation reactions - Glycogen phosphorylase - Synthesis of cystathionine, heme, niacin, histamine, and NTs including serotonin, epi, NE, and GABA |
|
|
What can a deficiency of Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine) cause?
|
- Convulsions
- Hyperirritability - Peripheral neuropathy (deficiency inducible by INH and oral contraceptives) - Sideroblastic anemias d/t impaired hemoglobin synthesis and iron excess |
|
|
What are the functions of Vitamin B7 (Biotin)?
|
Cofactor for carboxylation enzymes (which add 1C group)
- Pyruvate carboxylase: Pyruvate (3C) → Oxaloacetate (4C) - Acetyl-CoA carboxylase: Acetyl-CoA (2C) → Malonyl-CoA (3C) - Propionyl-CoA carboxylase: Propionyl-CoA (3C) → Methylmalonyl-CoA (4C) |
|
|
What can a deficiency of Vitamin B7 (Biotin) cause? What can cause a deficiency?
|
Symptoms:
- Dermatitis - Alopecia - Enteritis Causes of deficiency: - Antibiotic use - Excessive ingestion of raw eggs: "AVIDin in egg whites AVIDly binds Biotin" |
|
|
What are the functions of Vitamin B9 (Folic Acid)?
|
- Converted to THF, a coenzyme for 1C transfer/methylation reactions
- Important for synthesis of nitrogenous bases in DNA and RNA |
|
|
What are the sources of Vitamin B9 (Folic Acid)? What can a deficiency cause?
|
Sources:
- Found in leafy green vegetables: FOLate from FOLiage - Small reserve pool stored primarily in the liver Deficiency: - Macrocytic, megaloblastic anemia - NO NEURO SX (as opposed to B12 deficiency) |
|
|
What is the most common vitamin deficiency in US? Common presentation?
|
- Vitamin B9 (Folic Acid): most common vitamin deficiency in US
- Common in alcoholism and pregnancy (supplemental folic acid in early pregnancy is important to reduce neural tube defects) |
|
|
What can cause a deficiency of Vitamin B9 (Folic Acid)? Symptoms?
|
Causes:
- Several drugs (eg, Phenytoin, Sulfonamides, MTX) - Inadequate intake Symptoms: - Macrocytic, megaloblastic anemia - NO NEURO SX (as opposed to B12 deficiency) - Neural tube defects early in pregnancy |
|
|
What are the functions of Vitamin B12 (Cobalamin)?
|
Cofactor for homocysteine methyltransferase (transfers CH3 groups as methylcobalamin) and methylmalonyl-CoA mutase
|
|
|
What are the sources of Vitamin B12 (Cobalamin)? What can a deficiency cause?
|
Sources:
- Found in animal products - Synthesized only by microorganisms - Very large reserve pool (several years) primarily in the liver Deficiency symptoms: - Macrocytic, megaloblastic anemia - Hypersegmented PMNs - Neurologic symptoms (paresthesias, subacute combined degeneration) d/t abnormal myelin - Prolonged deficiency leads to irreversible neurological damage |
|
|
What can cause a deficiency of Vitamin B12 (Cobalamin)? Symptoms?
|
Causes of deficiency:
- Malabosrption (sprue, enteritis, Diphyllobothrium latum) - Lack of intrinsic factor (pernicious anemia, gastric bypass surgery) - Absence of terminal ileum (Crohn's disease) Symptoms: - Macrocytic, megaloblastic anemia - Hypersegmented PMNs - Neurologic symptoms (paresthesias, subacute combined degeneration) d/t abnormal myelin - Prolonged deficiency leads to irreversible neurological damage |
|
|
How can you determine the etiology of the Vitamin B12 deficiency?
|
Schilling test
|
|
|
How do Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine), Vitamin B9 (Folate), and Vitamin B12 (Cobalamin) relate in terms of metabolism?
|
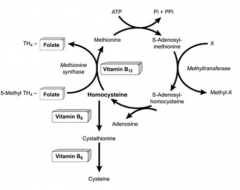
Vitamin B6:
- Cofactor for conversion of homocysteine → cysteine - Cofactor for Succinyl-CoA → Hemoglobin Vitamin B9: - Coenzyme for 1C transfer, important for conversion of homocysteine → methionine Vitamin B12: - Cofactor for conversion of homocysteine → methionine - Cofactor for Methylmalonyl-Coa → Succinyl-CoA |
|
|
What is S-adenosyl-methionine formed from? Function?
|
- ATP + Methionine → SAM (S-Adenosyl-Methionine)
- Regeneration of Methionine is dependent on B12 and B9 (Folate) - SAM transfers methyl units (SAM the methyl donor man) - Required for the conversion of NE to Epi |
|
|
What is necessary to convert Dopamine to NE?
|
Vitamin C (Ascorbic Acid)
|
|
|
What is necessary to convert NE to Epinephrine?
|
SAM (methyl donation)
- Dependent on formation of methionine which requires Vitamin B12 and Vitamin B9 (Folate) |
|
|
What are the functions of Vitamin C (Ascorbic Acid)?
|
- Antioxidant
- Facilitates iron absorption by keeping iron in reduced Fe2+ state - Necessary for hydroxylation of proline and lysine in collagen synthesis - Necessary for dopamine β-hydroxylase, which converts dopamine to NE |
|
|
What are the sources of Vitamin C? What can a deficiency cause?
|
Sources:
- Found in fruits and vegetables Deficiency symptoms: - Scurvy: swollen gums, bruising, hemarthrosis, anemia, poor wound healing (Collagen synthesis defect) - Weakened immune response |
|
|
What can excess Vitamin C cause?
|
- Nausea
- Vomiting - Diarrhea - Fatigue - Sleep problems - Can ↑ risk of iron toxicity in predisposed individuals (eg, those with transfusions or hereditary hemochromatosis) |
|
|
What are the forms of Vitamin D? Sources?
|
- D2: Ergocalciferol - ingested from plants
- D3: Cholecalciferol - consumed in milk, formed in sun-exposed skin - 25-OH D3: storage form - 1,25-(OH)2 D3 (Calcitriol): active form |
|
|
What are the functions of Vitamin D?
|
- ↑ intestinal absorption of Ca2+ and phosphate
- ↑ bone mineralization |
|
|
What can a deficiency of Vitamin D cause?
|
- Rickets in children (bone pain and deformity)
- Osteomalacia in adults (bone pain and muscle weakness) - Hypocalcemic tetany - Breast milk has ↓ Vitamin D (supplement in dark-skinned patients) |
|
|
What can an excess of Vitamin D cause? When is this seen?
|
Excess:
- Hypercalcemia - Hypercalciuria - Loss of appetite - Stupor Seen in: - Sarcoidosis (↑ activation of vitamin D by epithelioid macrophages) |
|
|
What are the functions of Vitamin E?
|
Antioxidant (protects erythrocytes and membranes from free-radical damage)
|
|
|
What can a deficiency of Vitamin E cause?
|
- ↑ Fragility of erythrocytes → hemolytic anemia (E is for erythrocytes)
- Muscle weakness - Posterior column and spinocerebellar tract demyelination |
|
|
What are the functions of Vitamin K? Source?
|
Function:
- Catalyzes γ-carboxylation of glutamic acid residues on various proteins concerned with blood clotting - Necessary for synthesis of clotting factors II, VII, IX, X, and proteins C and S Source: synthesized by intestinal flora |
|
|
What drug is a vitamin K antagonist?
|
Warfarin
|
|
|
What can a deficiency of Vitamin K cause?
|
- Neonatal hemorrhage w/ ↑ PT and ↑ aPTT but normal bleeding time (neonates have sterile intestines and are unable to synthesize vitamin K)
- Can also occur after prolonged use of broad-spectrum antibiotics |
|
|
How do neonates get Vitamin K?
|
- Neonates have a sterile intestine and are unable to synthesize vitamin K (normally vitamin K is synthesized by intestinal flora)
- Vitamin K is not found in breast milk - Neonates must receive an injection of Vitamin K at birth to prevent hemorrhage |
|
|
What are the functions of Zinc? Source?
|
- Essential for activity of 100+ enzymes
- Important in the formation of zinc fingers (transcription factor motif) |
|
|
What can a deficiency of Zinc cause?
|
- Delayed wound healing
- Hypogonadism - ↓ Adult hair (axillary, facial, pubic) - Dysgeusia - Anosmia - May predispose to alcoholic cirrhosis |
|
|
How is alcohol metabolized? Enzymes? Location?
|
1. Alcohol → Acetaldehyde by Alcohol Dehydrogenase
(NAD+ → NADH) Cytosol 2. Acetaldehyde → Acetate by Acetaldehyde Dehydrogenase (NAD+ → NADH) Mitochondria |
|
|
Which drugs can affect alcohol metabolism?
|
- Fomepizole
- Disulfiram (Antabuse) |
|
|
What is the mechanism of Fomepizole? Use?
|
- Inhibits alcohol dehydrogenase
- Antidote for methanol or ethylene glycol poisoning |
|
|
What is the mechanism of Disulfiram (Antabuse)? Use?
|
- Inhibits acetaldehyde dehydrogenase
- Acetaldehyde accumulates contributing to hangover symptoms (making patient not want to drink alcohol) |
|
|
What is the limiting factor of alcohol metabolism?
|
NAD+ is the limiting reagent
|
|
|
What is the effect of alcohol metabolism on NADH/NAD+ ratio? Implications?
|
Ethanol metabolism ↑ NADH/NAD+ ratio in liver
- Causes diversion of pyruvate to lactate and OAA to malate - Inhibits gluconeogenesis and stimulates FA synthesis - Leads to hypoglycemia and hepatic fatty liver change (hepatocellular steatosis) - Overproduction of lactate → acidosis - Depletion of OAA shuts down TCA cycle, shunting acetyl-CoA into ketone production - Breakdown of excess malate ↑NADPH and fatty acid synthesis |
|
|
What are the two types of malnutrition?
|
- Kwashiorkor
- Marasmus |
|
|
What causes Kwashiorkor and Marasmus?
|
- Kwashiorkor: protein malnutrition
- Marasmus: energy malnutrition |
|
|
What are the symptoms of Kwashiorkor? Cause?
|
Results from a protein-deficient MEAL:
- Malnutrition - Edema - Anemia - Liver malfunction (fatty change d/t ↓ apolipoprotein synthesis) Also - Skin lesions *Small child with swollen belly* |
|
|
What are the symptoms of Marasmus? Cause?
|
Energy / calorie malnutrition results in:
- Tissue and muscle wasting - Loss of subcutaneous fat - Variable edema (Marasmus causes Muscle wasting) |

