![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
38 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Rate of reaction
|
The change in concentration of a reactant OR product over time
|
|
|
Order
|
The power to which the concentration of the reactant is raised in the rate equation
|
|
|
Rate constant
|
k. The constant that links the rate of reaction with the concentrations of the reactants raised to the power of their orders in the rate equation!
|
|
|
Half-life
|
The time taken for the concentration of a reactant to reduce by half
|
|
|
Rate-determining step
|
The slowest step in the reaction mechanism of a multi-step reaction
|
|
|
The half-life of a first-order reaction is ___________ of the concentration
|
independent
|
|
|
Two factors about zero order conc-time graphs
|
Conc decreases at a constant rate
Half-life decreases with time |
|
|
Two factors about first order conc-time graphs
|
Concentration halves in equal time intervals
Half-life is CONSTANT |
|
|
Two factors about second order conc-time graphs
|
Concetration decreases rapidly, but rate of decrease then slows down
Half-life INCREASES with time |
|
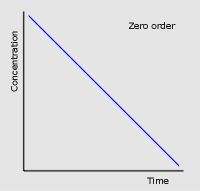
|
Zero order
|
|
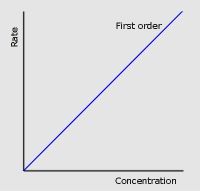
|
First order
|
|
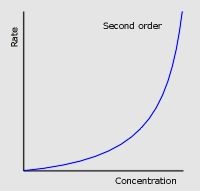
|
Second order
|
|
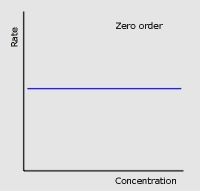
|
Zero order
|
|
|
k =
|
rate/[A]ⁿⁿ[B]ⁿ
|
|
|
How is k affected by an increase in temperature?
|
Increase in temperature = Increase in k and hence there is a faster rate of reaction
|
|
|
Kc =
|
[C]^c[D]^d/[A]^a[B]^b
|
|
|
For an exothermic reaction, an increase on temperature _________ Kc
|
decreases
|
|
|
For an endothermic reaction, an increase in temperature _________ Kc
|
increases
|
|
|
How does concentration/pressure/a catalyst affect Kc?
|
None of them do!
|
|
|
What is an acid?
|
A species that can DONATE a proton
|
|
|
What is a base?
|
A species that can ACCEPT a proton
|
|
|
What is an acid-base pair?
|
A pair of two species that TRANSFORM INTO EACH OTHER by gain or loss of a PROTON
|
|
|
What is a conjugate acid?
|
A species formed when a proton is added to a base
|
|
|
What is a conjugate base?
|
A species formed when a proton is added to an acid
|
|
|
Strong acid
|
An acid that completely dissociates in solution
|
|
|
Weak acid
|
An acid that partially dissociates in solution
|
|
|
What does acid dissociation constant show?
|
The extent of acid dissociation
|
|
|
pH =
|
-log[H⁺]
|
|
|
[H⁺] =
|
10^-pH
|
|
|
Kw =
|
[H⁺][OH⁻]
At 25*C - Kw = 1.00 x 10^-14 |
|
|
Strong acid, [H⁺] =
|
[HA]
|
|
|
Weak acid, [H⁺] =
|
sqrt(Ka * [HA])
|
|
|
Strong base, [H⁺] =
|
Kw/[OH⁻]
|
|
|
Buffer solution
|
A system that minimises pH changes on addition of small amounts of an acid or a base
|
|
|
How can a buffer solution be made?
|
From a weak acid and a salt of the weak acid
|
|
|
Buffer, [H⁺] =
|
Ka * [Acid]/[Salt]
|
|
|
What is carbonic acid-hydrogencarbonate used for?
|
A buffer in the control of blood pH
|
|
|
Enthalpy change of neutralisation
|
The energy change that accompanies the neutralisation of an aqueous acid by an aqueous base to form one mole of water under standard conditions
|

