![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
32 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
anagen |
period of growth in the hair cycle; averaging 3 to 5 years
|
|
|
association |
a link between an unknown sample and known evidence |
|
|
catagen
|
intermediate period of hair growth; lasting about three weeks |
|
|
cortex |
middle layer of the hair shaft that provides strength; comprises most of the hair mass |
|
|
cortical fusi |
little sacs of air contained within the cortex; comes in different sizes and shapes |
|
|
cuticle |
the clear outside covering of the hair shaft; made up of tough, overlapping scales |
|
|
exemplar |
term used to describe a sample of known origin |
|
|
follicle |
a tubelike organ in the sublayer of skin that hair grows from |
|
|
keratin |
a tough protein polymer made of about 20 amino acids; accounts for distinctive smell of burning hair |
|
|
medulla |
the spongy interior core of hair that gives it flexibility; appears as a canal |
|
|
medullary index |
measure of the relative thickness; calculation: (diameter of medulla)/(diameter of hair) x100. |
|
|
melanin |
a natural pigment found in skin; also, pigment granulates that give hair colour |
|
|
polymer |
a molecule consisting of many identical repeating units; can be synthetic or natural |
|
|
telogen |
final phase of hair growth; resulting in the loss of hair over three months |
|
|
coronal (cuticle) |
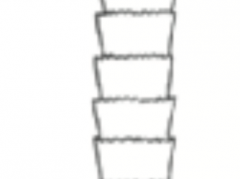
|
|
|
spinous (cuticle) |
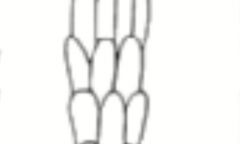
|
|
|
imbricate (cuticle) |
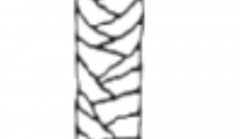
|
|
|
undulation |

|
|
|
twisted |
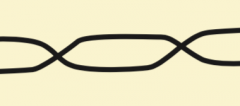
|
|
|
fragmented (human) |
|
|
|
interrupted (human) |

|
|
|
continuous (human) |

|
|
|
continuous (animal) |

|
|
|
stacked (animal) |

|
|
|
fabric |
a cloth material made up of fibers woven or bonded together in a distinctive manner |
|
|
fibers |
made up of filaments bonded together to form a thread or yarn |
|
|
filaments |
single strands of material, usually twisted with other filaments to make thread or fiber |
|
|
inorganic |
substances not composed primarily of hydrocarbons |
|
|
natural fibers |
animal, plant, or inorganic; wool, cotton, fiber glass, hemp, silk, cashmere, etc. |
|
|
synthetic fibers |
synthesized or created from altered natural sources; rayon, nylon, acetate, polyester, spandex, acrylic, etc. |
|
|
cellulose/plant based fibers |
fibers made with ether or esters of cellulose, which can be obtained from the bark, wood or leaves of plants, or from a plant-based material |
|
|
protein/animal based fibers |
natural fibers that consist largely of particular proteins; silk, hair/fur (including wool) and feathers |

