![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
33 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
The retina is the light-sensitive layer of tissue at the back of the inner eye. It acts like the film in a camera -- images come through the eye's lens and are focused on the retina. The retina then converts these images to electric signals and sends them via the optic nerve to the brain.
|
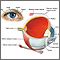
what is the retina
|
|
|
what is hyperopia
|
problems reading
|
|
|
what is myopia
|
problems driving
|
|
|
what is accommodation
|
adaptation of the eyes for near vision by increasing the curvature of the lens
|
|
|
what is anisocoria
|
unequal pupil size
|
|
|
what is arcus senilis
|
gray-white arc or circle around the limbus of the iris that is common with aging
|
|
|
what is argyll Robertson pupil
|
when the pupil does not react to light; does not constrict with accommodation
|
|
|
what is Astigmatism
|
a refractive error of vision due to differences in curvature in refractive surfaces of the eye (cornea and lens)
|
|
|
what is A-V crossing
|
the crossing paths of an artery and vein in the ocular fundus
|
|
|
what is bitemporal hemianopsia
|
loss of both temporal visual fields
|
|
|
what is blepharitis
|
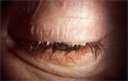
inflammation of the glands and eyelash follicles along the margin to the eyelids
|
|
|
an opacity of the lens of the eye that develops slowly with aging and gradually obstucts vision
|
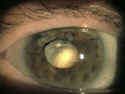
what is a cataract
|
|
|
Chalazion
|
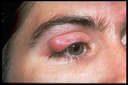
infection or retention cyst of a meibomian gland, showing as a beady nodule on the eyelid
|
|
|
strabismus
|

describe this eye
|
|
|
abnormal soft exudates visible as gray-white areas on the ocular fundus
|
cotton-wool area
|
|
|
diopter
|
unit of strength of the lens settings on the ophthalmoscope that changes focus on the eye structures.
|
|
|
diplopia
|
double vision
|
|
|
benign deposits on the ocular fundus that show as round yellow dots and occur commonly with aging
|
drusen
|
|
|
lower eyelid loose and rolling owtward
|
ectropion
|
|
|
lower eyelid rolling inward
|
entropion
|
|
|
protruding eyeballs
|
exopthalmos
|
|
|
what is glaucoma
|
a group of eye diseases characterized by incread intraocular pressure
|
|
|
what is hordeolum
|
red, painful pustule that is a localized infection of hair follicle at eyelid margin
|
|
|
what is a microaneurysm
|
the abnormal finding of round red dots on the ocular fundus that are localized dilatations of small vessels
|
|
|
describe the lacrimal system
|
the lacriminal apparatus provides constant irrigation to keep the conjunctiva and cornea moist and lubricated.
|
|
|
what is pupillary light reflex
|
the normal constriction of trhe pupils when bright light shines on the retina.
|
|
|
what is fixation
|
a reflex direction of the eye toward an object attracting the person's attn.
|
|
|
occurs when you shine a light directly into the pupil and that pupil constricts
|
direct light reflex
|
|
|
occurs when you shine a light inot one pupil and the opposite pupil constricts
|
consensual light reflex
|
|
|
true or false. peripheral vision is not intact in the newborn
|
false, it is intact at birth
|
|
|
what are the three common causes of decreased visual functions in the elderly
|
1. macular degeneration: loss of central vision, the area of clearest vision, most common cause of blindness.
2. Glaucoma or increased ocular pressure 3. Cataract formation |
|
|
when testing for accommodation, at near distance you would expect the pupils to.....
|
constrict
|
|
|
yellowish elevated nodules that are due to thickning of the bulbar conjunctiva from prolonged exposure to sun, wind, and dust
|
pinguecula
|

