![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
65 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Accommodiation
|
adaptation of the eye for near vision by increasing the curvature of the lens
|
|
|
Anisocoria
|
unequal pupil size
|
|
|
Arcus senilis
|
gray-white arc or circle around the limbus of the iris that is common with aging
|
|
|
Argyll Robertson pupil
|
pupil does not react to light; does constrict with accommodation
|
|
|
Astigmatism
|
refractive error of vision due to differences in curvature in refractive surfaces of the eye (cornea and lens)
|
|
|
A-V crossing
|
crossing paths of an artery and vein in the ocular fundus
|
|
|
Bitemporal hemianopsia
|
loss of both temporal visual fields
|
|
|
Blepharitis
|
inflammation of the glands and eyelash follicles along the margin of the eyelids
|
|
|
Cataract
|
opacity of the lens of the eye that develops slowly with aging and gradually obstructs vision
|
|
|
Chalazion
|
infection or retention cyst of a meibomian gland, showing as a beady nodule on the eyelid
|
|
|
Conjunctivitis
|
infection of the conjunctiva, “pinkeye”
|
|
|
Cotton-wool area
|
abnormal soft exudates visible as gray-white areas on the ocular fundus
|
|
|
Cup-disc ratio
|
ratio of the width of the physiologic cup to the width of the optic disc, normally half or less
|
|
|
Diopter
|
unit of strength of the lens settings on the ophthalmoscope that changes focus on the eye structures
|
|
|
Diplopia
|
double vision
|
|
|
Drusen
|
benign deposits on the ocular fundus that show as round yellow dots and occur commonly with aging
|
|
|
Ectropion
|
lower eyelid loose and rolling outward
|
|
|
Entropion
|
lower eyelid rolling inward
|
|
|
Exophthalmos
|
protruding eyeballs
|
|
|
Fovea
|
area of keenest vision at the center of the macula on the ocular fundus
|
|
|
Glaucoma
|
a group of eye diseases characterized by increased intraocular pressure
|
|
|
Hordeolum
|
(stye) red, painful pustule that is a localized infection of hair follicle at eyelid margin
|
|
|
Lid lag
|
the abnormal white rim of sclera visible between the upper eyelid and the iris when a person moves the eyes downward
|
|
|
Macula
|
round, darker area of the ocular fundus that mediates vision only from the central visual field
|
|
|
Microaneurysm
|
abnormal finding of round red dots on the ocular fundus that are localized dilations of small vessels
|
|
|
Miosis
|
constricted pupils
|
|
|
Mydriasis
|
dilated pupils
|
|
|
Myopia
|
“nearsighted”; refractive error in which near vision is better than far vision
|
|
|
Nystagmus
|
involuntary, rapid, rhythmic movement of the eyeball
|
|
|
OD
|
oculus dexter, or right eye
|
|
|
Optic atrophy
|
pallor of the optic disc due to partial or complete death of optic nerve
|
|
|
Optic disc
|
area of ocular fundus in which blood vessels exit and enter
|
|
|
OS
|
oculus sinister, or left eye
|
|
|
Papilledema
|
stasis of blood flow out of the ocular fundus; sign of increased intracranial pressure
|
|
|
Presbyopia
|
decrease in power of accommodation that occurs with aging
|
|
|
Pterygium
|
triangular opaque tissue on the nasal side of the conjunctiva that grows toward the center of the cornea
|
|
|
Ptosis
|
drooping of upper eyelid over the iris and possibly covering pupil
|
|
|
Red reflex
|
red glow that appears to fill the person's pupil when first visualized through the ophthalmoscope
|
|
|
Strabismus
|
(squint, crossed eye) disparity of the eye axes
|
|
|
Xanthelasma
|
soft, raised yellow plaques occurring on the skin at the inner corners of the eyes
|
|
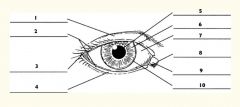
1
|
Upper eyelid
|
|
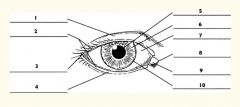
2
|
Palpebral fissure
|
|
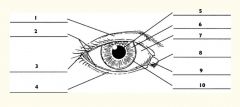
3
|
Lateral canthus
|
|
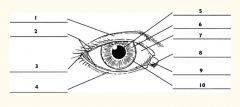
4
|
Lower eyelid
|
|
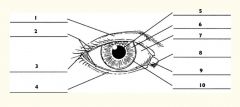
5
|
Pupil
|
|
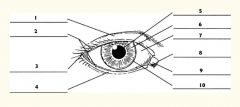
6
|
Iris
|
|
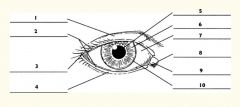
7
|
Sclera
|
|
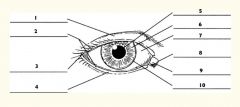
8
|
Medial canthus
|
|
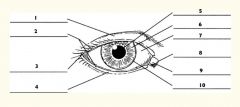
9
|
Caruncle
|
|
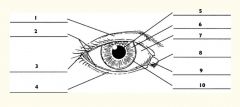
10
|
Limbus (border between cornea and sclera)
|
|
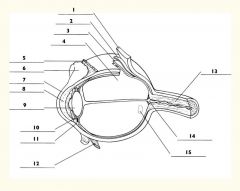
1
|
Sclera
|
|
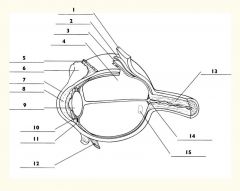
2
|
Choroid
|
|
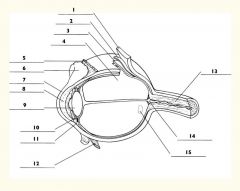
3
|
Retina
|
|
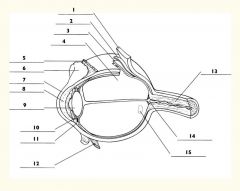
4
|
Vitreous body
|
|
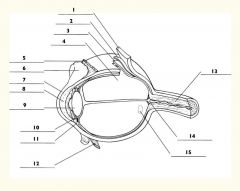
5
|
Superior rectus m.
|
|
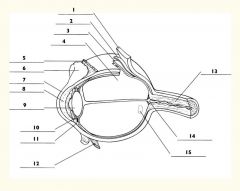
6
|
Conjunctiva
|
|
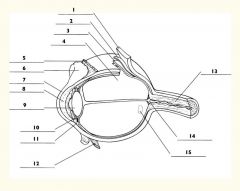
7
|
Cornea
|
|
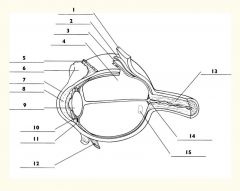
8
|
Anterior chamber
|
|
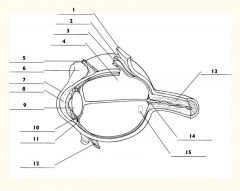
9
|
Lens
|
|
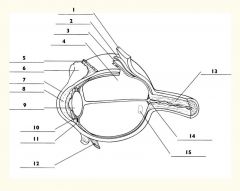
10
|
Posterior chamber
|
|
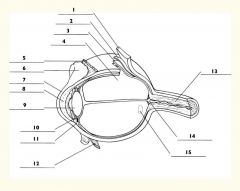
11
|
Ciliary body
|
|
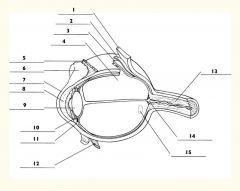
12
|
Inferior rectus m.
|
|
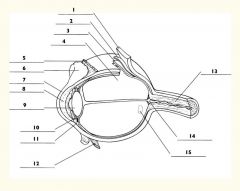
13
|
Optic nerve
|
|
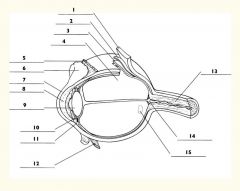
14
|
Optic disc
|
|
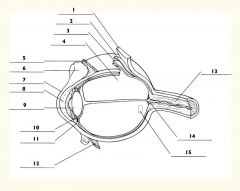
15
|
Macula
|

