![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
18 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Fibrous Joint |
Joins fibrous tissue, no joint cavity present, synarthrotic |
|
|
Sutures |
Type of Fibrous joint; irregular edges of bone interlocking connected by short connective tissue fibers; found in the skull |
|
|
Syndesmoses |
Fibrous joint; articulating bones by short ligaments by dense fibrous tissue; don't interlock; found at the distal ends of the tibia and fibula. |
|
|
Cartilaginous Joints |
Contains cartilage; no joint cavity; amphiarthrotic- somewhat movable. |
|
|
Synchondrosis |
Bony portions united by hyaline cartilage; found at the costal cartilages and epiphyseal plate. |
|
|
Symphysis |
Means growing together; bones are connected by broad, flat disc of fibrocartilage; intervertebral joints and pubic symphysis |
|
|
Synovial Joints |
Found in articulating bone ends; separated by a joint cavity containing synovial fluid; diarthrotic; Composed of articular capsule- Double layered sleeve of connective tissue which encloses the joint surfaces and forms the cavity, articular cartilage, bursae- fluid filled sacs helps reduce friction, articular discs- pads of fibrocartilage aka miniscus. |
|
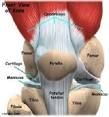
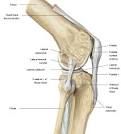
Knee Joint |
Quadriceps tendon, patellar ligament, lateral meniscus, medial meniscus, anterior cruciate ligament, posterior cruciate ligament, fibular collateral ligament, tibial collateral ligament. |
|
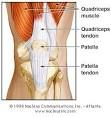
Anterior |
Quadriceps tendon- Superior to patella; Patellar Ligament- Inferior to patella |
|
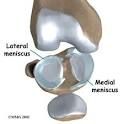
|
Lateral Meniscus- Pad of cartilage at the ends of the Femur and Tibia. Medial Meniscus- pad of fibrocartilage; AKA articular discs. |
|
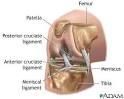
|
Anterior Cruciate Ligament- Inside the capsule; Posterior Cruciate Ligament- outside the capsule; both help prevent over flexion and hypertension in the knee. |
|
|
Fibular Collateral Ligament- Outside articular capsule, lateral side; Tibial Collateral Ligament- Outside articular capsule, medial side; both prevent rotation. |
|
|
Flexion- Decreases angles of joint |
Extension- Increasing in angle of the joint |
|
|
Abduction- away from the midline of the body |
Adduction- towards the midline of the body; adding to the body |
|
|
Rotation- movement along an axis; Lateral rotation and Medial rotation |
|
|
|
Pronation- palms facing down |
Supination- palms facing up |
|
|
Inversion- medially pointing of the foot |
Eversion- Outward facing feet. |
|
|
Dorsiflextion- toes up toward the knee |
Plantar Flexion- planting toes down; pointing the feet. |

