![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
38 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Homeostatsis
|
internal balance of the human organism
|
|
|
Feedback Systems
|
Maintains homeostasis.
|
|
|
Normal blood sugar
|
80 - 120mg/ml
|
|
|
Sagittal Plane
|
veritically (from head to toes)
divides body into left and right portions. |
|
|
Parasagittal plane
|
Any sagittal plane that passes through the body to the left or right of the midline and divides the body into unequal left and right portions.
|
|
|
Frontal Coronal Plane
|
Vertical plane that divides the body into front (anterior) and back (posterior) portions.
|
|
|
Transverse plane
|
Horizontal (perpendicular) plane that divides body into top (superior) and bottom (inferior) portions.
|
|
|
Another name for Anterior
|
Ventral
|
|
|
Another name for Posterior
|
Dorsal
|
|
|
Medial
|
Toward the midline
|
|
|
Proximal
|
Closer to midline or point of attachment of a limb.
|
|
|
Distal
|
Farther away from the midline or point of attachment of a limb.
|
|
|
Superficial
|
Closer to the surface of the body.
|
|
|
Deep
|
Farther from the body surface.
|
|
|
Axial region
|
Area of body closest to midline or axis. (head, neck, and trunk)
|
|
|
9 abdominal regions
|
1. Right hypochondriac region
2. Epigastric region 3. Left hypochondriac region 4. Right lateral (lumbar) region 5. Umbilical region 6. Left lateral (lumbar) region 7. Right inguinal (iliac) region 8. Hyprogastric region 9. Left inguinal (iliac) region |
|
|
Right hypochondriac region
|
Liver, Gall bladder
|
|
|
Epigastric region
|
Liver, Stomach, Pancreas
|
|
|
Left hypochrondriac region
|
Stomach, Spleen
|
|
|
Right lateral (lumbar) region
|
Ascending colon, gall bladder
|
|
|
Umbilical region
|
Stomach, transverse colon, small intestine, pancreas
|
|
|
Left lateral (lumbar) region
|
Small intestine, descending colon
|
|
|
Right inguinal (iliac) region
|
Cecum, small intestine
|
|
|
Hyprogastric region
|
Small intestine, rectum, urinary bladder, reproductive organs
|
|
|
Left inguinal (iliac) region
|
Small intestine, sigmoid colon
|
|
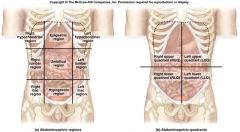
Abdomnopelvic region
|
Abdominopelvic region
|
|
|
Dorsal cavity
|
Cranial cavity
Vertebral or spinal cavity |
|
|
Ventral cavity
|
Thoracic cavity
Abdominopelvic cavity |
|
|
6 characteristic of living organisms
|
Metabolism, growth, differentiation, movement, responsiveness, reproduction
|
|
|
Negative feedback does what?
|
The body senses a change in a variable and activates mechanisms that reverse that change.
|
|
|
Positive feeback system does what?
|
Produces a self amplifying affect to orginal stimulus.
|
|
|
Chloride is the only
|
Anion
|
|
|
Chloride is the only
|
Anion
|
|
|
Free radicals
|
Charged groups of atoms with an odd number of electrons. Produced by some normal metabolic reactions of the body as well as by radiation. They are unstable and combine quickly with fats, proteins, and DNA. They destroy nearby molecules.
|
|
|
The higher the H+ ions, the more ____ the blood.
|
Acidic
|
|
|
Anabolism
|
Energy requiring reactions where small molecules are joined together to form large ones. (synthesis or endergentic reactions)
|
|
|
Catabolism
|
Energy releasing reactions where large molecules are broken down into smaller ones Idecomposition, or exergonic reactions)
|
|
|
Glycolysis
|
First stage of glucose oxidation.
Literally means "sugar splitting" 2 molecules of ATP is produced at this stage Splits glucose into 2 molecules of pyruvic acid. |

