![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
50 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What nursing is: |
health promotion; infection prevention; communication; continuity of care; teamwork; system error; relationship-based care; thinking in action; serving leader |
|
|
What nursing is not: |
your pin; hat; cute scrubs; wiping asses |
|
|
The Boomer Challenge |
A generation that has dominated American life for a half-century will have an enormous impact on health care as it ages. A big unknown is how well medicare will digest the 75 million baby boomers. |
|
|
Individual Mandate (Patient Protection & Affordable Care Act) |
Individuals not covered by Medicare or Medicaid will be required to have health insurance or pay a penalty (play or pay). |
|
|
Affordable Coverage (Patient Protection & Affordable Care Act) |
Lower-income individuals and families, together with some middle-income individuals and families, will receive financial assistance to help pay for health insurance. |
|
|
Employer Mandate (Patient Protection & Affordable Care Act) |
With the exception of small businesses, employers that do not provide qualifying health insurance coverage will be subject to an additional tax. |
|
|
Cover Preventative Health Services (Patient Protection & Affordable Care Act) |
New group health insurance plans, as well as individual health insurance policies, will have to provide "first dollar" coverage for certain preventive services and immunizations |
|
|
Transforming the Health Care Delivery System (Patient Protection & Affordable Care Act) |
Provides for research and demonstration projects to test payment and service delivery models designed to reduce health care costs and improve the quality of care provided. |
|
|
Coverage Gap |
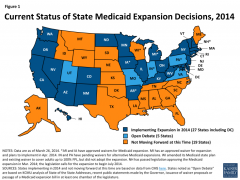
Uninsured poor adults in states that do not expand medicaid |
|
|
Novice nurse (Benner’s Stages of Clinical Competence) |
Only feels responsible to follow the rules. |
|
|
Advanced Beginner nurse (Benner’s Stages of Clinical Competence) |
Still does not experience personal responsibility. |
|
|
Competent nurse (Benner’s Stages of Clinical Competence) |
Sense of responsibility arises from actively making decisions. |
|
|
Proficient nurse (Benner’s Stages of Clinical Competence) |
Sense of responsibility increases with experience. |
|
|
Expert nurse (Benner’s Stages of Clinical Competence) |
Responsibility extends to others and the environment. |
|
|
"caring" in nursing practice |
1. providing presence 2. touch 3. listening 4. knowing the patient 5. spiritual caring 6. relieving pain and suffering 7. family-centered care |
|
|
non-verbal behaviors to develop trust |
providing presence, touch, listening |
|
|
3 types of touch that demonstrate caring |
1. Task-oriented touch (skillful, gentle care) 2. Caring touch (enhances comfort, security,self-esteem, mental well-being) 3. Protective touch (prevents injury to patient or insulates nurse from emotional pain—withdrawal) |
|
|
listening |
1. Active listening: - Taking in - Interpreting/understanding (meanings) - Responding (verbal, nonverbal) |
|
|
the patient's story |
Every patient has a “story” to tell, and needs a listener |
|
|
knowing the patient |
the core of clinical decision-making and a foundation to patient-centered care |
|
|
4 Healing relationships |
- Mobilize hope - Promote understanding/meanings of illness, symptoms, emotions - Assist in use of social, emotional, spiritual resources - Recognition that caring relationships connect us human-to-human, spirit-to-spirit |
|
|
5 factors in assessing and treating pain |
- Understand meaning of pain - Cultural/individual differences - Pharmacologic/nonpharmacologic - Therapeutic touch - Caring presence |
|
|
patient outcomes impacted by family involvement and support |
- Sharing of information, history - Acceptance, understanding of treatment - Plan workable in daily lives? - Delivery of therapy/care |
|
|
internal variables that influence health and health beliefs and practice |
1. Developmental stage - Fear, anxiety common among ill children - Emotional development (teens vs adults) 2. Intellectual background - Knowledge, educational background - Cognitive skills 3. Perception of functioning - Fatigue, SOB, pain (subjective) - B/P, height, lung sounds (objective) 4. Emotional factors - Degree of stress, depression, fear vs. patient who is generally calm 5. Spiritual factors - How patient lives life - Lived values & beliefs - Relationship with family, friends - Ability to find hope, meaning in life |
|
|
socioeconomic factors influencing health and health practices |
- Stability of key relationship - Lifestyle habits - Occupational environment - Social networks/desire for approval & support - Economic variables influence when the pt accesses care and whether he complies with care (affordability of care,Rx, foods) - May try to decrease costs by taking meds every other day, or water down infant formula |
|
|
Healthcare Continuum |
- Is a concept describing the comprehensive array of health needs and services a patient may access, spanning all levels and intensity of care - The Continuum of Care covers the delivery of healthcare over a period of time (acute or chronic illness) and may also refer to care provided from birth to the end of life. |
|
|
nurses role in discharge planning |
- CMS Definition: “Discharge planning is a process used to decide what a patient needs for a smooth move from one level of care to another." - The discharge plan is developed by the healthcare team, and includes the patient. - The nurse typically reviews the plan with the patient/family prior to discharge, and provides a written copy to the patient/family |
|
|
Elements of the Discharge Plan: |
- Evaluation of the patient by qualified personnel - Discussion with the patient or his representative - Planning for homecoming or transfer to another care facility - Determining if caregiver training or other support is needed - Referrals to home care agency and/or appropriate support organizations in the community - Arranging for follow-up appointments or tests |
|
|
Healthy People 2020 Goals |
- Attain high-quality, longer lives free of preventable disease, disability, injury, and premature death - Achieve health equity, eliminate disparities, and improve the health of all groups - Create social and physical environments that promote good health for all - Promote quality of life, healthy development and healthy behaviors across all lifestages |
|
|
Public Health Services provided in Kansas |
- Health screening (100%) - Laboratory services (100%) - Immunizations (100%) - WIC (100%) - Childcare provider licensing (100%) - Disease investigation/follow-up (100%) - Pre and postnatal services (97%) - Health education (90%) - Limited dental services (86%) - Car seats (59%) - Foot care (59%) - Preparedness (99%) - School health services (74%) - Healthy Start Home Visitors (76%) |
|
|
Focal Nursing Practice: Meeting the Patient as a Person |
- being with the patient - bearing witness to the patient’s plight - preserving patient dignity in the face of injury, illness, meds |
|
|
Focal Nursing Practice: Preserving Personhood |
- provision of care that preserves the dignity and worth of the elderly - recognizing the need all human beings have to create, be productive, be independent, to be loved, to be in community with others who understand them - recognizing the need to share and hear life stories |
|
|
Focal Nursing Practice: Patient Advocacy at the Bedside |
- Nurses must be vigilant—they must advocate even when multiple demands are being placed on them - Giving the silent patient a voice - Ensuring medical treatments are manageable and do not conflict with patient concerns and intentions - confronting substandard care in hospital settings - it’s foundation is being able to empathize with the patient |
|
|
Family assessments: Family Forms |
- Nuclear - Extended - Single-parent - Blended - Alternative (multi-adult,“skip-generation, communal, non-families, cohabitating partners, homosexual couples) |
|
|
Family assessments: threats facing the family |
1.Changing economic status (declining income and lack of access to health care) 2.Homelessness 3.Family violence 4.Presence of acute or chronic illnesses (including trauma, end-of-life care) |
|
|
Family assessments: Family stage of development |
- Unattached young adult - Joining of families through marriage - Family with young children - Launching children and moving on - Family in later life |
|
|
Family Centered Nursing Care |
1. Dignity and Respect - As an interprofessional healthcare team, we listen to and honor the perspective, wishes and choices of our patients and their families. The knowledge, values, beliefs and culture of our patients and their family members are incorporated into their plan and delivery of care. 2. Information Sharing - We openly communicate and share timely, complete and accurate information with our patients to help them understand,and we encourage them to participate in decisions about their care. 3. Participation - We encourage and support patients and their families to participate in and make decisions about their care. 4. Collaboration - We work together with patients and families to design, implement and deliver the best care possible. This philosophy goes into everything we do, from providing care to program planning. |
|
|
Nursing Quality Indicators |
1. Patient falls 2. Patient falls with injury 3. Pressure ulcers: - community acquired - hospital acquired - unit acquired 4. Staff mix 5. Nursing hours per patient day 6. Registered nurse (RN) surveys on job satisfaction and practice environment scale 7. RN education and certification 8. Pediatric pain assessment cycle 9. Pediatric intravenous infiltration rate 10. Psychiatric patient assault rate 11. Restraint prevalence 12. Nurse turnover 13. Hospital-acquired infections: - ventilator-associated pneumonia - central line-associated bloodstream infection - catheter-associated urinary tract infection |
|
|
The health care game changer: "Crossing the Quality Chasm" |
Level A: The experience of patients Level B: The functioning of small units of care delivery (“microsystems”) Level C: The functioning of the larger system(s) that support the microsystems Level D: The environment of policy, payment, regulation, accreditation and other factors |
|
|
How Level A: the experience of patients is impacted by levels B, C, and D |
The quality of actions at levels B, C,& D are defined by the effects of those actions at Level A—the experience/outcomes of patients |
|
|
National Patient Safety Goals: Identifying the Patient Correctly |
Use at least two ways to identify patients. For example, use the patient’s name and date of birth. This is done to make sure that each patient gets the correct medicine and treatment. Make sure that the correct patient gets the correct blood when they get a blood transfusion. |
|
|
Who is measuring patient care satisfaction? |
Organization Based Hospital Compare; Physician Compare HCAHPS |
|
|
What are they measuring? |
SAMPLE QUESTION: - During this hospital stay, how often did nurses treat you with courtesy and respect? - During this hospital stay, how often did nurses listen carefully to you? - During this hospital stay, how often did doctors treat you with courtesy and respect? - During this hospital stay, how often were your room and bathroom kept clean? - How often did you get help in getting to the bathroom or in using a bedpan as soon as you wanted? - During this hospital stay, how often was your pain well controlled? - Before giving you any new medicine, how often did hospital staff tell you what the medicine was for? - Using any number from 0 to 10, where 0 is the worst hospital possible and 10 is the best hospital possible, what number would you use to rate this hospital during your stay? - Would you recommend this hospital to your friends and family? |
|
|
Why do we care? - patient outcome - value based purchasing |
What is Value Based Purchasing? 1. The Hospital Value-Based Purchasing (VBP) Program is a Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) initiative that rewards acute-care hospitals with incentive payments for the quality of care they provide to people with Medicare 2. How Are Hospitals Rewarded? The Hospital VBP Program is funded by a percentage with held from participating hospitals’ Diagnosis-Related Group (DRG) payments. Those hospitals not meeting process, experience and outcome goals lose CMS reimbursement; those meeting goals are rewarded |
|
|
5 of the 10 characteristics of an effective leader: |
1. effective communicator 2. participatory approach in decision-making 3. displays caring, understanding, empathy 4. motivates others 5. proactive, flexible |
|
|
SBAR-format communication |
SBAR A technique for communicating critical information that requires immediate attention and action concerning a patient's condition. Situation - What is going on with the patient? "I am calling about Mrs. Joseph in room 251. Chief complaint is shortness of breath of new onset." Background - What is the clinical background or context? "Patient is a 62-year-old female post-op day one from abdominal surgery. No prior history of cardiac or lung disease." Assessment - What do I think the problem is? "Breath sounds are decreased on the right side with acknowledgment of pain. Would like to rule out pneumothorax." Recommendation and Request - What would I do to correct it? "I feel strongly the patient should be assessed now. Can you come to room 251 now?" |
|
|
Delegation |
Transfer of responsibility for the performance of an activity or task while retaining accountability for the outcome |
|
|
5 Rights for Delegation |
1. Right Task 2. Right Circumstances 3. Right Person 4. Right Direction/Communication 5. Right Supervision/Evaluation |
|
|
What a nurse can delegate: |
1. The RN decides when to delegate (tasks, not patients) 2. Task delegation is based upon: - Nurse Practice Act guidelines - Institutional policy - Patient assessment - Job description and characteristics of the delegatee (LPN or unlicensed assistive personel—nurse aid) |
|
|
What a nurse can NEVER delegate: |
The nurse NEVER delegates any of the steps of the Nursing Process—these responsibilities require a nursing license |

