![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
26 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is a wave? |
A wave is a way by which energy is transferred from place to place.
|
|
|
What is a transverse wave? |
It is the vibration of particles that are parallel to the direction of travel. |
|
|
What is a longitudinal wave? |
It is the direction of vibration that is perpendicular to the direction of travel. |
|
|
What are the types of transverse waves? |
Water wave String wave Light wave |
|
|
What is the type of longitudinal wave? |
Sound waves |
|
|
What are the properties of a wave? |
Crest Trough Wavelength Amplitude Frequency Period of time The speed of wave |
|
|
Crest |
Is the highest point of a wave |
|
|
Trough |
Is the lowest point of a wave from rest position |
|
|
Wavelength |
Is the length of a full cycle of wave from one point to the other same point. E.g: from crest to crest from trough to trough |
|
|
Amplitude |
Is the measure of energy and it is the size of a wave that is measured from the rest position to the crest or the trough. |
|
|
Frequency |
Is the number of one complete wave in a certain point per unit time |
|
|
The period of time |
Is the time taken for one compete wave to pass a certain point |
|
|
The speed of wave |
Speed of wave= frequency* wavelength |
|
|
Visible light |
Is a form of energy that we can detect with our eyes |
|
|
Luminous source |
Are objects that produce their own light. For example : television, glow worms and others. |
|
|
Illuminated |
Are objects that reflection there own light. For example: moon the pages and others. |
|
|
How does light travel |
Light travels in a straight line it also can travel in the space (vacuum) |
|
|
Light travels in a distance of |
Light is ver fast. It travels 300,000,000 m/s |
|
|
Ray |
Ray is a narrow beam of light. |
|
|
Shadows |
It is when rays of light stays traveling in a straight line while other rays are blocked by an object |
|
|
Shadows due to small source |
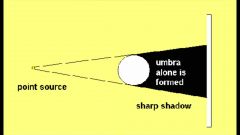
It causes sharp edges called umbra. |
|
|
Shadow due to large source |
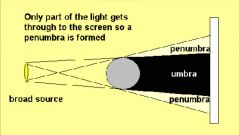
It forms a blurred edge. The penumbra and the umbra. |
|
|
Eclipse |
Occur because the moon and the earth cast a large shadow. |
|
|
Solar eclipse |
Is when the moon comes between the sun and the earth. |
|
|
Lunar eclipse |
When the moon moves into the earths shadows. |
|
|
Properties of pinhole camera. |
1. It is laterally inverted. ( left side becomes right and vice versa). 2. It is real image. ( it can be collected on a screen 3.the image produced is an upside down image. 4. When the image is close to the hole the image produced is very large. When the image is very far to the the hole the image produce is very small. |

