![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
28 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
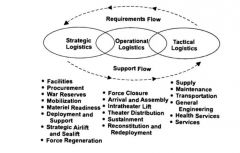
Doctrinal Definition of Logistics |
Logistics ecompasses all actions required to move and maintain forces. |
|
|
Definition of Combat Service Support |
Combat service support is the activity which actually provides services and supplies to the combat forces. |
|
|
Describe |
|
|
Principles of Logistics |
Triple "S" FEAR -Simplicity- Fosters efficiency in both the planning and execution of logistics operations through establishment of priorities and standardized procedures and use of mission-type orders. -Sustainability - The ability to maintain logistics support to all users throughout the area of operations for the duration of the operations. -Survivability - The capacity of the organization to protect its forces and resources -Flexibility - The ability to adapt logistics structure and procedures to changing situations, missions, and concepts of operation. Includes the concepts of alternative planning, anticipation, reserve assets, redundancy, forward support of phased logistics and centralized control with decentralized operations. -Economy - Fosters efficiency in both the planning and execution of logistics operations through establishment of priorities and standardized procedures and use of mission-type orders. -Attainability - The ability to provide the minimum, essential supplies and services required to begin combat operations. -Responsiveness - is the right support at the right place at the right time. |
|
|
6 Functions of Tactical Logistics |
-Supply: is a cyclic process ofacquiring and issuing materiel to supported units. This materiel may be consumable or durable materiel, components, and end items. -Maintenance: involves those actions taken to keep materiel in serviceable condition (preventive maintenance) and actions required to return materiel to serviceable condition (corrective maintenance). -Transportation: Transportation is moving from one location to another usingrailways, highways, waterways, pipelines, oceans, and airways. -General Engineering: Heavy equipment transportation, Construction materials, Utilities support, Water Purification, Fuel distribution, and power generating equipment. -Health Services: Health services support seeks to minimize the effect that wounds, injuries and disease have on unit effectiveness and morale. -Services: Provides for the effective administration, management, and employment of military organizations. Services subfunctions are essentially administrative in nature. |
|
|
MAGTF Elements
|
CommandElement (CE): The core element of a Marine air-ground task force (MAGTF)is the headquarters. The command element is composed of the commander, general or executive and special staff sections, headquarters section, and requisite communicationssupport, intelligence, and reconnaissance forces, necessary to accomplish the MAGTF’smission.
Ground CombatElement (GCE): The core element of a Marine air-ground task force (MAGTF) that is task-organized to conduct ground operations. It is usually constructed around an infantry organization but can vary in size from a small ground unit of any type to one or more Marine divisions that can be independently maneuvered under the direction of the MAGTF commander. Aviation CombatElement (ACE): The core element of a MAGTF that is task-organized to conduct aviation operations. The aviation combat element (ACE) provides all or a portion of the six functions of Marine aviation necessary to accomplish the MAGTF’s mission. These functions are antiair warfare, offensive air support, assault support, electronic warfare, air reconnaissance, and control of aircraft and missiles. Logistics CombatElement (LCE): The core element of a Marine air-ground task force (MAGTF) that is task-organized to provide the combat service support necessary to accomplish the MAGTF’s mission. The logistics combat element varies in size from a small detachmentto one or more Marine logistics groups. It provides supply, maintenance, transportation, general engineering, health services, and a variety of other services to the MAGTF. |
|
|
Marine Expeditionary Force (MEF) |
The largest MAGTF and the principle Marine Corps warfighting organization. Example: I MEF (Command Element (CE)) 1st Mar Dive (Ground Combat Element (GCE)) 3rd Marine Aircraft Wing (Aviation Combat Element (ACE)) 1st Marine Logistics Group (Logistics Command Elelement (GCE)) |
|
|
The Marine Divisions depend on LCE for CSS however they should use their organic capabilities before requesting outside support |
Organic Capabilities include: 2 truck companies -Division G-4 Staff section under HQ BN -BN S-4 sections |
|
|
MLG, CLRS and subordinate Combat Logistics Battalions are distinguished by their support role and formal mission |
They are either in general support mission or a direct support mission. |
|
|
A CSS unit or organization with a direct support mission |
-Responds to CSS requests in priority from: -Supported unit -Higher CSS headquarters -Own units -Provides liaison personnel to the supported unit -Establishes comm with: -The Supported Unit -Higher CSS headquarters -Is positioned by the supporting unit |
|
|
A CSS unit or organization with a General Support Mission |
Responds to CSS requests in priority from: -Higher CSS headquarters -Supported unit -Own units -Establishes liaison with supported units -Establishes comm with: -Supported Units -Higher CSS headquarters -Is positioned by higher CSS headquarters |
|
|
Marine Aircraft Wing CSS Capabilities (MWSS) |
MWSS (Marine Wing Support Squadron) provides the following support to the ACE: -Internal airfield communications -Weather services -Expeditionary airfield services -Aircraft rescue and firefighting -Essential engineering services -Motor transport support -Field mess support -Medical services -Personnel training -Nuclear/biological/chemical defense -Security -Air base commandant functions -Explosive Ordnance Disposal (EOD) support |
|
|
Marine Aircraft Wing CSS Capabilities (MALS) |
MALS (Marine Aviation Logistics Squadron) provides the following CSS capabilities: -Aircraft supply support -Assembling/distributing aviation ammunition -Providing supply support to the MWSS expeditionary airfield and weather sections. |
|
|
Logistics planning Concepts |
1. Logistics planning should be concurrent with operations planning. 2. Combat and combat support units should exploit their organic logistic capabilities before requesting assistance from combat service support sources. 3. The impetus of logistics is from the rear, directly to the using unit. 4. The logistic system must be responsive, effective and efficient |
|
|
Functions of Tactical Logistics Supply Class 1 |
Subsistence |
|
|
Functions of Tactical Logistics
Supply Class 2 |
Clothing, individual equipment, tentage, organizational tool sets/kits, hand tools, administrative and housekeeping, supplies and equipment |
|
|
Functions of Tactical Logistics
Supply Class 3 |
Petroleum, oils and lubricants including petroleum fuels, lubricants, hydraulic and insulating oils, liquid and compressed gases |
|
|
Functions of Tactical Logistics
Supply Class 4 |
Construction material and all fortification and barrier material |
|
|
Functions of Tactical Logistics
Supply Class 5 |
Ammunition of all types including NBC |
|
|
Functions of Tactical Logistics
Supply Class 6 |
Personal demand items and nonmilitary sales items |
|
|
Functions of Tactical Logistics
Supply Class 8 |
Medical material to include repair uniue to medical parts |
|
|
Functions of Tactical Logistics
Supply Class 9 |
Repair parts, components and kits, assemblies, and subassemblies. Items required for maintenace |
|
|
Levels of Maintenance |
Field: A unit may conduct field level maintenance for which it is manned. Any maintenance that does not require depot maintenance capability and is performed by equipment crew and equipment operators and mechanics/technicians within Marine Corps organizations and activities, and or approved commercial/contract sources Depot: Marine Corps organic depots, other service depots, and original equipment manufacturers. Includes MCLB in Albany, and Barstow. Equipment requiring major overhaul or rebuild. |
|
|
Field level maintenance and categories |
Organizational: Is conducted by equipment operators, crews and unit equipment technicians at the using unit level. Intermediate: Typically occurs at units task-organized to provides specialized maintenance support. |
|
|
Depot Level Maintenance Phases |
Acceptance of equipment: Initial phase of the maintenance process. Equipment Induction: They physical commitment of a maintenance service request and associated equipment to a specific maintenance section. Active Maintenance: Maintenance activity performed following induction. Maintenance Closeout: Equipment has been repaired and the serviceable item is returned to the owner, or when a decision has been made to evacuate or dispose of the equipment. |
|
|
Tactical Logistics:
Transportation |
Transportation planning is throughput planning. it involves throughput requirements: What, where, when, and how personnel and material must move to sustain the force. |
|
|
Formula for computing rations (Food) required |
(P * D * M)/Ur = R P = unit strength D = number of days M = number of rations fed per day Ur = number of rations per case R = total number of cases of rations required |
|
|
Formula for computing rations (Water) required |
P * D * R * 1.1 =W P = unit strength D = number of days R = consumption rate (gallons per day/event) 1.1 = 10% waste W = total gallons of water required |

