![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
55 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
This is a principle hormone that releases milk into the mammary ducts.
A. Prolactin B. PRH C. PIH D. GnRH E. Oxytocin |
E. Oxytocin |
|
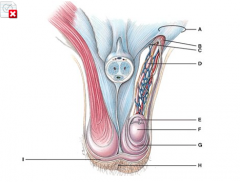
Which structure has a portion removed in a vasectomy?
|
D |
|
|
This ligament arises from the pubic symphysis in males. A. Ejaculatory ligament B. Broad ligament C. Suspensory ligament D. Fundiform ligament E. Perineum ligament |
C. Suspensory ligament |
|
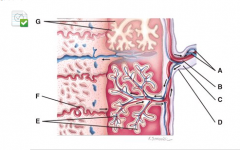
What is line “G” pointing to? |
chorionic villi |
|
|
This exam is performed between 14-16 weeks gestation and is used to detect genetic abnormalities. A. Amniocentesis B. Sonogram C. AFP test D. CBC E. CVS |
A. Amniocentesis |
|
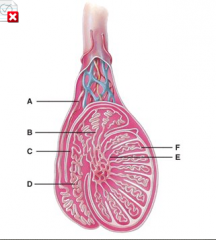
What is line “F” pointing to? |
Seminiferous tubules |
|
What does line “G” point to? |
Tunica vaginalis |
|
|
This structure is the site of sperm production. A. Epididymis B. Vas deferens C. Albuginea D. Raphe E. Seminiferous tubules |
E. Seminiferous tubules |
|
|
This is the portion of the endometrium that lies between the embryo and the stratum basalis. A. Decidua capsularis B. Decidua parietalis C. Lamina propria D. Adventitia E. Decidua basalis |
E. Decidua basalis |
|
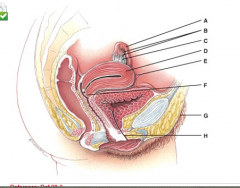
This is the site for implantation of a fertilized ovum. |
D |
|
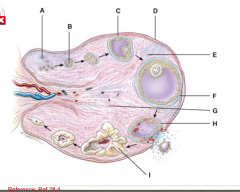
Where is the mature (graafian) follicle? |
F |
|
|
This is a series of functional changes that sperm go through when they are in the female reproductive tract. A. Maturation B. Capacitation C. Polyspermy D. Acrosomal reaction E. Fertilization |
B. Capacitation |
|
|
This is the portion of the uterus that opens into the vagina. A. Uterine tubes B. Inguinal canal C. Ovaries D. Cervix E. Urethra |
D. Cervix |
|
|
This is the site of fertilization. A. Ovaries B. Ureters C. Urethra D. Uterine tubes E. Vagina |
D. Uterine tubes |
|
|
This hormone triggers ovulation. A. Progesterone B. Estrogen C. LH D. FSH E. GnRH |
C. LH |
|
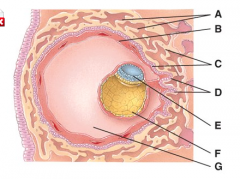
Where is the amniotic cavity? |
E |
|
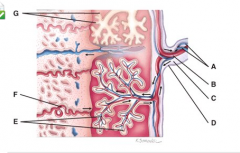
Where are the fetal blood vessels? |
E |
|
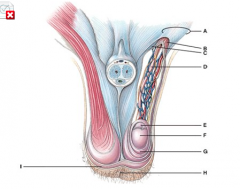
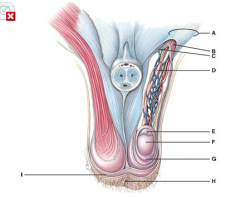
What does line “A” point to? |
Spermatic cord |
|
|
In infants this connects the umbilical vein to the inferior vena cava. A. Anteriosum B. Patent ductus arteriosus C. Ductus venosus D. Ductus arteriosus E. Superior vena cava |
C. Ductus venosus |
|
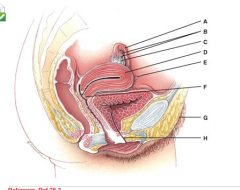
What is line “C” pointing to? |
Ovary |
|
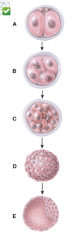
What does diagram “A” represent? |
Cleavage of zygote |
|
|
Involution is... A. When the placenta is expelled B. When the umbilical cord is cut C. When the uterus decreases in size D. When the cervix dilates E. None of the above |
|
|
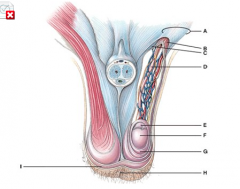
The septum of the tissue is made up of superficial fascia and which muscle tissue? |
I |
|
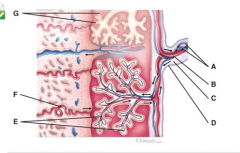
What is line “F” pointing to? |
maternal endometrial arteriole |
|
|
This lies posterior to the bladder and anterior to the rectum and secretes an alkaline, fructose filled fluid. A. Prostate B. Prostatic urethra C. Cowper's glands D. Seminal vesicles E. Spongy urethra |
D. Seminal vesicles |
|
|
Skene's glands secrete A. Androgens B. Testosterone C. Mucus D. Progesterone E. Estrogen |
C. Mucus
|
|
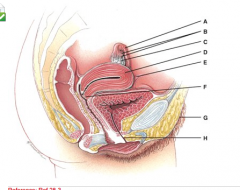
This opens from the uterus to the vagina. |
F |
|
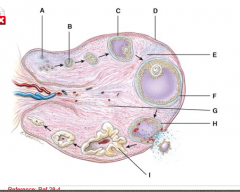
What is line “D” pointing to? |
Germinal epithelium |
|
|
These cells may eventually become spermatozoa A. Spermatogenic cells B. Sustentacular cells C. Speciation cells D. Sertoli cells E. Chief cells |
A. Spermatogenic cells |
|
|
This is composed of three cylindrical masses of erectile tissue each surrounded by a fibrous tissue. A. Penis B. Testes C. Prostate D. Urethra E. Bladder |
A. Penis |
|
|
This is any agent or influence that causes developmental defects in an embryo. A. Carcinogen B. Toxin C. Nicotine D. Radiation E. Teratogens |
E. Teratogens |
|
|
This hormone stimulates Leydig cells to secrete testosterone. A. GnRH B. LH C. FSH D. DHT E. None of the above |
B. LH |
|
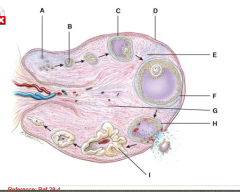
This consists of primary oocyte that is surrounded by several layers of cuboidal granulosa cells. |
B |
|
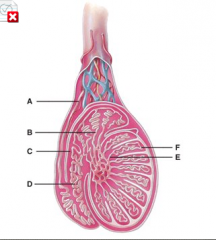
Where are the straight tubules? |
E |
|
|
The straight tubules in the testis lead into the: A. Afferent ducts B. Ductus epididymis C. Epididymis D. Efferent ducts E. Rete testis |
E. Rete testis |
|
|
This is formed by the union of the duct from the seminal vesicle and the ampulla of the vas deferens. A. Spermatic cord B. Ejaculatory duct C. Urtethra D. Inguinal canal E. Prostate |
B. Ejaculatory duct |
|
|
Anterior to the vagina and urethral openings is the... A. Labial frenulum B. Mons pubis C. Labia majora D. Labia minor E. Cervical sphincter |
B. Mons pubis |
|
|
Fertilization normally occurs within which structure? A. Vagina B. Body of uterus C. Ovary D. Ovarian ligament E. Fallopian tube |
E. Fallopian tube |
|
|
What is produced by the ovaries? A. Primary oocytes, insulin and estrogen B. Tertiary oocytes, insulin and estrogen C. Primary oocytes, estrogen and testosterone D. Secondary oocytes, progesterone and cortisol E. Secondary oocytes, estrogen and progesterone |
E. Secondary oocytes, estrogen and progesterone |
|
|
This develops from the epiblast and carries a protective fluid. A. Yolk sac B. Amnion C. Cytotrophoblast D. Exocoelomic membrane E. Lacunae |
B. Amnion |
|
|
This will become the primary structure for exchange of material between the mother and the fetus A. Embryonic disc B. Endoderm C. Amnionic fluid D. Chorionic villi of the placenta E. Amnion |
D. Chorionic villi of the placenta |
|
|
This is the time from the onset of labor to the complete dilation of the cervix. A. Effacement B. Gestation C. Placental stage D. Stage of dilation E. Stage of expulsion |
D. Stage of dilation |
|
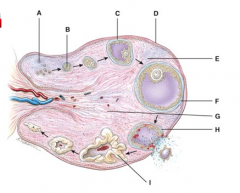
This will produce progesterone, estrogens, relaxin and inhibin. |
I |
|
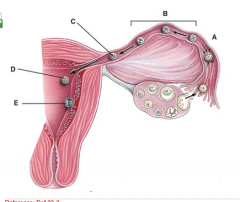
What stage happens 3-4 days after fertilization? |
C |
|
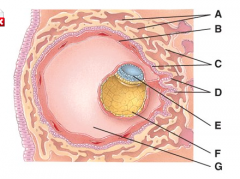
This is composed of the syncytiotrophoblast and the cytotrophoblast. |
C |
|
|
The uterine phase when the thickness of the endometrium doubles. A. Proliferative phase B. Menstrual phase C. Preovulatory phase D. Postovulatory phase E. Follicular phase |
A. Proliferative phase |
|
|
The function of the epididymis is.... A. Sperm maturation B. Absorption of calcium C. Speratid storage D. Produce sperm E. Provide nutrition to sperm |
A. Sperm maturation |
|
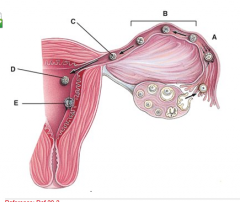
What stage happens 6 days after fertilization? |
E |
|
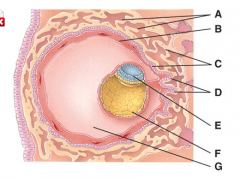
What is line “G” pointing to?
|
None of the above |
|
|
The fusion of the male pronucleus and the female pronucleus results in which developmental stage? A. Blastomeres B. Corona radiata C. Blastopore D. Zygote E. Morula |
D. Zygote |
|
|
The is the ovarian phase between the end of menstruation and beginning of ovulation. A. Postovulatory phase B. Proliferative phase C. Menstrual phase D. Preovulatory phase E. Follicular phase |
D. Preovulatory phase |
|
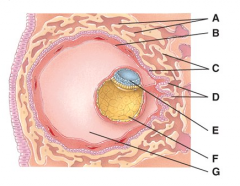
These cells are derived from the yolk sac and form a connective tissue layer. |
B |
|
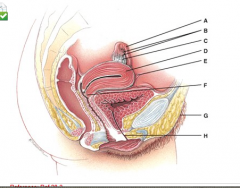
Which structure is part of the connection of the uterus to the pelvic cavity? |
E |
|
|
The structure protects and hold the testes A. Cremaster muscle B. Tunica vaginalis C. Tunica albuginea D. Dartos muscle E. Scrotum |
E. Scrotum |
|
|
This is secreted by the corpus luteum after ovulation A. LH B. Progesterone C. Relaxin D. HGH E. FSH |
B. Progesterone |

