![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
72 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Define antigen. (Ag) |
A substance that causes the body to produce specific immune response. Typically foreign to the body. |
|
|
|
What are the four important features of immunity? |
aquired (A) - Requires exposure to antigen specific (S) - Immune system recognizes and reacts with individual antigens memory (M) - Faster and stronger immune response upon a subsequent exposure because initial exposure creates increase in antigens responding cells tolerance (T) - Ability to Distinguish self from non self |
S.M.A.T. |
|
|
True or false) Antigens are usually protein or polysaccharide in nature |
True, over 1000 molecular weight (mw) |
|
|
|
True ot false) lipids and nucleic acids make poor antigens |
True |
|
|
|
What are antigenic determinants or epitopes? |
Are the specific sites on antigen that immune system recognizes and responds to. |
|
|
|
Haptens are: |
Small molecules that attach to larger ones and act as antigenic determinant |
|
|
|
Describe humoral immunity: |
Antibody production from B Lymphocytes that protects against extracellular bacteria, toxins, viruses |
|
|
|
What type of immunity contain cytotoxic T cells (T lymphocyte) and secreted cytokines (chemical messengers)? |
Cell-mediated immunity |
|
|
|
What does cell-mediated immunity protect against? |
Virus infected cells, intracellular pathogens, fungi and protozoa |
|
|
|
Adaptive immunity is aquired ____________ & _____________. |
Naturally & artificially |
|
|
|
Artificially and Naturally aquired immunity can be _________ or __________. |
Active or passive |
|
|
|
"Antigens enter the body naturally; body induces antibodies and specialized lymphocytes" is an example of what type of adaptive immunity? |
Active - naturally acquired immunity |
|
|
|
"Performed antibodies in immune serum are introduced by injection" is an example of what kind of adaptive immunity? |
Passive - artificially aquired immunity |
|
|
|
"Antigens are introduced in vaccines; body produces antibodies and specialized lymphocytes" is an example of what kind of adaptive immunity? |
Active - artificially aquired, immunity |
|
|
|
" Antibodies passed from mother to fetus via placenta or to infant via mother's milk" is an example of what kind of adaptive immunity? |
Passive - Naturally acquired immunity |
|
|
|
What is another name for antibody? |
Immunoglobulins |
|
|
|
Name some antibodies? |
IgG, IgA, IgM, IgD, IgE |
|
|
|
Describe antigen binding sites. |
- Variable and constant regions - Complementary to and to antigenic determinants (epitopes) |
|
|
|
True or false) antibodies are polyspecific and bivalent |
False, monospecific and bivalent |
|
|
|
What are heavy chains in antibodies? |
The longer, inner chain, contains Fc regions |
|
|
|
What does it mean to be bivalent? |
Can attach to 2 different copies of the same epitope of the antigen. |
|
|
|
What helps to define the class of the antibody? |
The tail region of the antibody, the FC region |
|
|
|
What protection can occur during Ab - Ag binding? |
- Blocks from reaching/binding to its target cell -induce opsonization -death of pathogen |
antibody(Ab) antigen(Ag) |
|
|
When antibodies cause clumping of bacteria. |
Agglutination |
|
|
|
What does Agglutination prevent? |
-prevents bacteria from successfully reproducing - bacteria mobility impaired to reach target cells -reduces # of infectious units |
3 key points |
|
|
Some antibodies have _______ in their Fc region that have receptors on ________cells. This increase the ability of which cell to do what? |
Tails Phagocytic WBC to attach and engulf antigen |
|
|
|
What is neutralization? |
The antibodies' ability to block adhesion of bacteria and viruses to mucosa. Blocks attachment of toxins. |
|
|
|
True or false) ADCC is a process that can kill large groups of organisms. Explain.
What does ADCC stand for? |
False, usually happens when targeting larger parasites that are too large to be engulfed by phagocytes
"Antibody-Dependent Cell-Mediated Cytotoxicity" |
|
|
|
Antibodies attach a large target cell, causing destruction by macrophages, eo, and eosinophils |
Antibody-Dependent Cell-Mediated Cytotoxicity (ADCC) |
|
|
|
What's the most common antigen? What percentage? Half-life? |
IgG - Immunoglobulin G Makes up 80% of antibodies 23 days |
|
|
|
What is IgA known for? What percent? |

It is the primary antibody that is found on mucosal surfaces. Makes up 10-15% of antibodies |
|
|
|
What antibodies can fix complement? |
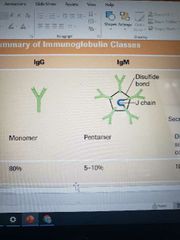
IgG and IgM |
|
|
|
Which antibodies are monomers? |
IgG, IgD, IgE |
|
|
|
Which antigen is a Pentamer? What makes it special? What percentage? |
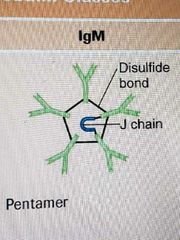
IgM First antibody produced from initial exposure to antigen (1st exposure) Makes up 5-10% of antibodies |
|
|
|
What does it mean when IgM levels are higher than IgG levels? |
There is a new, first time infection |
|
|
|
True or false) IgG and IgM can fix complement which means they can pass through the placenta. |
False, IgM is too large to pass through the placenta. |
|
|
|
Which cells are primarily responsible for the production of antibodies? |
B Lymphocyte |
|
|
|
What happens after a B Lymphocyte is activated? |
- start to reproduce - differentiate into 2 types of cells 1.) Antibody-producing plasma cells 2.) Memory cells |
|
|
|
What is BCR? |
B cell receptor - receptor for B Lymphocytes |
|
|
|
True or false) There are various types BCRs on B cells. |
False, BCRs are a single type of receptor on B cells that are capable of recognizing billions of different antigenic determinants |
B cell receptor |
|
|
Describe clonal selection. |
Activation of a specific B Cell results in increase in the population of that same B cell (clone) to eliminate specific antigen |
|
|
|
What can happen when BCR are crosslinked? |
Activation of B cell, cross linkage happens when multiple copies have attached to the same type of epitope |
T - independent antigens |
|
|
True or false) T-independent antigens are proteins |
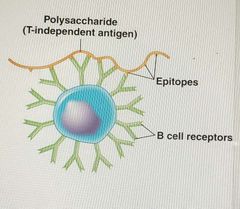
False, they are polysaccharides. |
|
|
|
What is required for T-dependent antigens to activate B cells? |
1.) antigen-presenting cell (APC), in association with MHCII, degrade antigens and present fragments to TH cell by APC. This activates TH cell. 2.) TH cell activates the appropriate B cell
|
Requires 2 signals |
|
|
These cells engulf and degrade antigens into fragments which are then presented to another cell to activate appropriate B cell. |
Antigen-presenting cells |
TH cells activate appropriate B cell |
|
|
True or false) Fragments of an antigen can be considered epitopes |
True |
|
|
|
What is the role of MHC-2? |
Combined with epitope fragments, it notifies T helper cells that foreign material is present |
|
|
|
Where can you find APCs? |
Lining of tracts and portals of entry |
Antigen- Presenting cells |
|
|
True or false) All T lymphocytes have T-cells receptors. Looks like and antibody embedded in the cell membrane. |
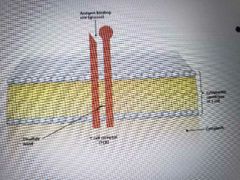
Second statement make it false. |
|
|
|
CD4+ cells are also called ___________. Why "CD4+"? |
TH cells, T helper cells
They have a CD4 proteins that serve as markers on their surface. |
|
|
|
These receptors recognize specific epitope when associated with MHC II protien complex on APC. |
T cell receptors |
|
|
|
Activated TH cells produce specific cytokines called: |
Interleukins |
|
|
|
Interleukins are specific __________. |
cytokines |
|
|
|
T helper cells differentiate into: |
TH 1 - Activate cells related to cellular immunity TH 2 - Activate to humoral immunity TH 17 - proinflamatory response Memory T-helper cells |
|
|
|
These make up the majority of cells produced during B cell proliferation |
Plasma cells |
|
|
|
Each _________ cell secretes only one type of antibody molecule for a specific antigenic determinant. They also die within a few days of activation. |
Plasma cells |
|
|
|
True or false) Memory cells are short-lived cells |
False |
|
|
|
True are false) Memory cells don't secrete antibodies |
True |
|
|
|
____________ are clones of the origin type of B cell. Their receptors are for the same antigenic determinant that triggered initial production. |
Memory cells |
|
|
|
What does cell-mediated immunity (CMI) result in? |
Activate: Cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL) that destroys abnormal host cells Secretion of cytokines by T H1 cell -cytokines activate macrophages
|
|
|
|
In cell mediated immunity (CMI) the activation of macrophages are an important response to: |
Fungi and protozoa |
|
|
|
CTL have __________ that recognize epitope on cell surface when presented with ___________. |
TCR - T cell receptors MHC1 |
cytotoxic T lymphocytes |
|
|
True or false) MHC class 1 and 2 are polysaccharides |
False, they are protiens |
|
|
|
Describe MHC class 1. |
-Protien on all nucleated cells (including APC) -Presents fragments of proteins synthesized in cell (look what I made) |
|
|
|
Describe MHC2. |
-Protien only on APC -presents fragments of proteins ingested and degraded by cell (look what I made) |
APC |
|
|
CD8+ are also knowns as __________. |
Tc cells |
|
|
|
The effector cell for Cell-Mediated immunity. |
CD8+ or Tc cells. |
|
|
|
CD4+ cells are known to be attacked by which virus? |
HIV |
|
|
|
CD8+ or Tc cells activate into ___________. |
Cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) |
|
|
|
In cell mediated immunity, after actived, these cells recognize fragmented epitope presented by ___________ proteins. |
CTLs - cytotoxic T lymphocytes
MHC1 |
|
|
|
Cytotoxic T lymphocytes release ___________ & ____________ that induce ____________ in target cell. |
Perforin & granzymes apoptosis |
|
|
|
What are some examples of antigen presenting cells (APC) listed from the ppt? |
Macrophages and dendritic cells |
|

