![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
43 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Phylum Porifera |
Sponge |
Has pores |
|
|
Phylum Nematoda |
Roundworms |
|
|
|
Phylum Platyhelminthes |
Flatworms |
Plat=Flat |
|
|
Phylum Cnidaria/Coelenterata |
Stinging-Celled Animals |
Electric |
|
|
Phylum Annelida |
segmented worms |
|
|
|
Phylum Mollusca |
soft-bodied |
Mollusca = soft animals |
|
|
Phylum Echinodermata |
Spiny-skinned |
|
|
|
Phylum Arthropoda/Class Crustacea |
joined-footed / crustaceans |
|
|
|
Phylum Arthropoda / Clasa Diplopoda |
jointed footed / millipedes |
|
|
|
Phylum Arthropoda / Class Chilopoda |
Jointed footed/ centipedes |
|
|
|
Phylum Arthropoda/ Class Arachnida |
spiders, ticks, mites |
|
|
|
Phylum Arthropoda/ Class Insecta |
jointed footed/ insects |
|
|
|
Phylum Chordata/ Class Agnatha |
jawless fish |
a-ga-nat-ha --> a got no jaws |
|
|
Phylum Chordata/Class Chondrichthyes |
cartilage fish |
|
|
|
Phylum Chordata/Class Osteichthyes |
bony fish |
osteo = bones |
|
|
Phylum Chordata/ Class Amphibia |
salamander, frog, toads |
amphibians |
|
|
Phylum Chordata/ Class Reptilia |
turtles, crocodilians, lizards, and snakes |
|
|
|
Phylum Chordata / Class Aves |
birds who eat prey, seeds, insects, and etc. |
|
|
|
Phylum Chordata / Class Mammalia |
egg-layers, marsupials, placental mammals |
|
|

|
Heron |
|
|

|
Medowlark |
State bird |
|

|
Cardinal |
|
|

|
Sparrow |
|
|

|
Hawk |
|
|

|
Robin |
|
|

|
Owl |
|
|

|
Woodpecker |
|
|
|
Quial |
|
|

|
Hummingbird |
|
|

|
duck |
|
|
|
Kingdom Monera |
Prokaryotic ; Ex: bacteria, cyanbacteria |
|
|
|
Characteristics of Monerans |
- one-celled membrane - cells have no membrane around the nucleus - reproduce by splitting in two - absorbs nutrients from outside their body - some monerans causes diseases, but others are helpful to people |
|
|
|
Characteristics of Protist Kingdom |
- Most are one-celled, but some have many cells - Cells have a membrane around nucleus nucleus - Some get nutrients and energy by eating other organisms - Some get energy from the sun, and nutrients from water around them - Most reproduce by splitting in two - Ex: paramecium, kelp, amoeba |
|
|
|
Characteristics of Kingsom Fungi |
- Most are many-celles and some are one-celled organisms - Cells have a membrane around nucleus - Gets nutrients and energy by absorbing/digesting the surface they live in (decomposer) - Most reproduce by spores - Ex: yeast, mushrooms, bread molds, and lichens |
|
|
|
Characteristics of Kingdom Plantae |
- Many-celled organisms - Cells have a membrane around nucleus, contains chlorophyll and have cell walls - Gets energy from the sun and take in nutrients from their surroundings - Most reproduce from seeds; some reproduce from other special parts - Ex: Ferns, trees, grasses, and bushes |
|
|
|
Characteristics of Kingdom Animalia |
- Many-celled organisms - Cells have a membrane around nucleus - Gets nutrients and energy by eating other organisms - Reproduce with eggs. Some eggs develop inside mother's body, and some develop outside the mother's body - Ex: bears, fish, frogs, birds, starfish, and butterflies |
|
|
|
What is the function of the root |
Absorbs water nutrients and holds the plant in the soil |
|
|
|
What's the function of the seed? |
A new plant grows from these |
|
|
|
What's the function of the leaf? |
Uses the sun and air to make food for the plant |
|
|
|
What's the function of the flower? |
Makes seeds and fruit of the plant |
|
|
|
What's the function of the stem? |
Brings water and food to rest of the plant |
|
|
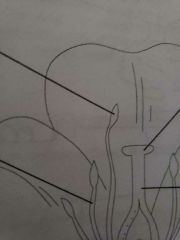
Identify the 4 arrows from left to right |
filament, another, stigma, style |
|
|
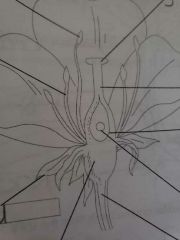
Identify All of the arrows from top to bottom |
anther, stigma, filament, style, ovary, ovule, septal, receptacle, stem |
|

