![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
40 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back

write and draw this |
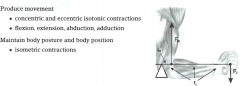
-flexion -extension -abduction -adduction |
|
|
what does isotonic mean? |
same tension |
|
|
what does concentric mean? |
muscle is shortening under tension (curl up)
-concentric isotonic contraction |
|
|
what does eccentric mean? |
muscle is lengthening under tension (lowering curl)
-eccentric isotonic contraction |
|
|
what does isometric mean? |
same length
muscles are contracting but not shortening at all (just holding a barbell)
-isometric contractions |
|

draw and describe this |
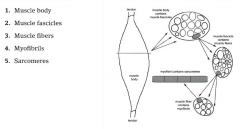
-muscle fasicles --fibers when shredding meat
-sarcomeres are inside myofibrils
|
|

label these parts |
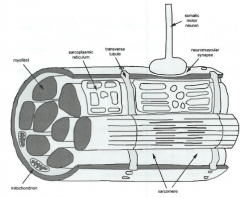
-long in body, narrow diameter cells -somatic motorneuron (nicotinic cholinergic)--every muscle fiber in body has a motor neuron -sarcoplasmic reticulum special type of endoplasmic reticulum -transverse tubule increases surface area of muscle fibers (subway with cell membrane inside) |
|

describe this |

-two main proteins --myosin (thick filam) --actin (thin filament)
-interdigitate (overlapping/sliding) -zline = actin -mline = myosin |
|

describe this |
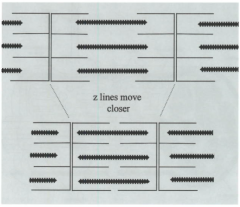
top is relaxed bottom is contracting |
|

describe this |
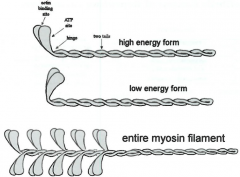
-myosin are like golf clubs -head and shaft can be at different angles -high energy "set like a mousetrap" -low energy "sprung" |
|

describe this |
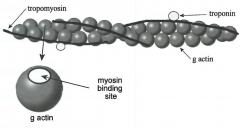
quaternary structure -made of g (globular) actin -two pearl strands twisted together -tropomyosin --filament protein wrapping -troponin (also globular protein)
|
|
|
what is the m line and z line? |
m = backbone of myosin filament z = backbone of actin filament |
|

draw and describe this |
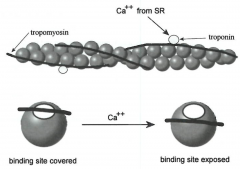
-tropomyosin covers up binding sites of g actins -Ca++ binds to troponin and tropomyosin moves off binding sites |
|
|
where does Ca++ come from in the muscle? |
sarcoplasmic reticulum |
|

write and draw these steps |

7. does not happen until ATP reattaches -rigor mortis caused by Ca++ leakage --myosin attaches and can't detach |
|

|

|
|

|
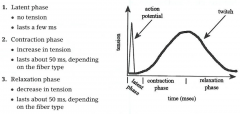
-occurs when muscle fiber is stimulated with single action potential -lasts 50ms to 100ms -latent phase is when action potential arrives |
|

|
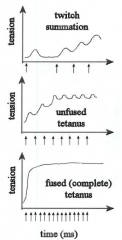
-progression from twitch to useful contraction -arrows are action potentials -summation of twitches
|
|
draw and describe this |
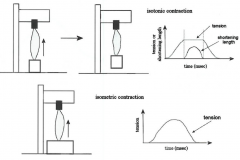
-from start of dotted line to middle, muscle fibers shorten "isotonic concentric contraction", more tension, lifting -center to dotted line "isotonic eccentric contraction", less tension, setting back down --isotonic means same tension -isometric "load never lifted", muscle fibers never shorten |
|
describe this |

-smaller = more dexterity, need more to control -bigger = stronger, clumsier -gastrocnemius = calf muscle -recruitment = motor units brought online as more weight added -rotation = motor units take turns
|
|

|

-recruitment = more and more motor neurons are brought online as needed -rotation = black to white and gray etc -1uN = all muscles contracting, fast fatigue -impossible to make 0.1uN, 0.25, etc |
|

|
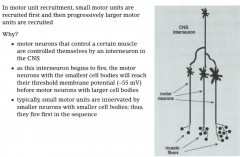
-small first, largest last -size of motor unit (number of muscle fibers) proportional to size of neuron -one book, normal action potential firing freq small turns on; two books, middle and small; three books, all three high fire freq |
|
|
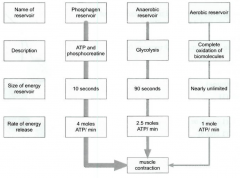
-aerobic reservoir, huge, releases energy at a lower rate -anaerobic, smaller -phosphagen = muscle fiber hydrolyzes ATP to ADP, phosphocreatine turns ADP back to ATP, this reservoir is used mostly in weight lifting |
|
|
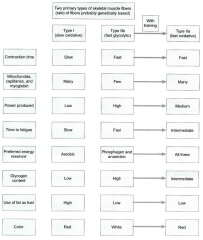
-type 1 = slow twitch, smaller motor units, good at endurance, aerobic reservoir -type 2 = fast twitch, anaerobic reservoir -type 2a = mixed with training -determined by genetics -red due to capillaries, mitochondrion, myoglobin (endurance muscles) |
|
|
what is tetanus? |
sustained contraction as a result of repeated action potentials from a motor neuron
(stepping on a rusty nail can give you tetanus from a bacterial infection) |
|
|
give more info on motor unit recruitment |
-aerobic exercise uses only small muscle fibers -more tension uses more muscle fibers -dexterous motions use small muscle fibers -resistance training uses more muscle fibers, large motor units come online
|
|
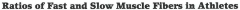
|
oxidative = type 1 glycolytic = type 2 |
|
|
describe classifications of muscle fibers: use of fat as fuel |
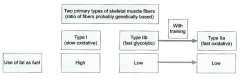
|
|
|
describe classifications of muscle fibers: glycogen content |
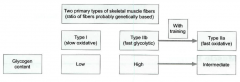
|
|
|
describe classifications of muscle fibers: mitochondria, capillaries, and myoglobin |
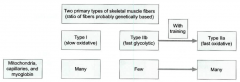
|
|
|
describe classifications of muscle fibers: power produced |
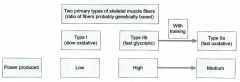
|
|
|
describe classifications of muscle fibers: preferred energy reservoir |

|
|
|
describe classifications of muscle fibers: time to fatigue |

|
|
|
describe classifications of muscle fibers: color |
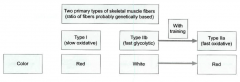
|
|
|
describe classifications of muscle fibers: contraction time |

|
|
|

|
|
|
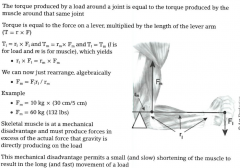
force needed to lift at the elbow is 6x the actual weight being carried |
|
|
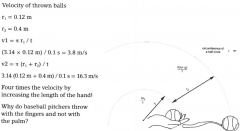
|
|
|
what is abduction? |
moving away from center line |
|
|
what is adduction? |
moving toward center line |

