![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
45 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back

|
binary fission |
|

|

|
|

|
chromatin |
|

|

|
|

|
homologous chromosomes |
|

|
sister chromatids |
|

|
20 |
|
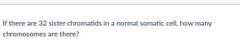
|
16 |
|

|

|
|

|
g1 |
|

|
cytokenesis |
|

|
S |
|

|
interphase |
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|
Metaphase |
|

|
Anaphase |
|

|
telophase |
|

|
prophase |
|

|
the nucleolous disappears |
|

|
prometaphase |
|
|
Animal cells typically achieve cytokenesis by |

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|
p53 |
|
|
Edouard van Beneden proposed that an egg and a sperm, each containing half the complement of chromosomes found in somatic cells, fuse to produce a single cell called a(n) ________. |
zygote |
|
|
The process of nuclear division which reduces the number of chromosomes per cell from 2 sets to 1 set, is called ________. |
Meiosis |
|
|
What type of cells contain only one set of chromosomes? |
haploid |
|
|
Homologous chromosomes pair along their length during prophase I of meiosis. While two homologues are paired, genetic exchange may occur between them in a process called ________. |
crossing over |
|
|
Compared to asexual reproduction, the main advantage of sexual reproduction is that it |
increases the genetic diversity of the offspring. |
|
|
Evidence of crossing over can often be seen under the light microscope as a structure called a ________. |
chiasma |
|
|
Diploid organisms use meiosis to produce haploid cells. Meiosis consists of how many rounds of nuclear division? |
2 |
|
|
The pairing of chromosomes along their lengths, which is essential for crossing over, is referred to as |
synapsis |
|
|
The point of connection between two sister chromatids, before anaphase II of meiosis separates them, is called the |
centromere |
|
|
What process produces new cells that are genetically identical to the original cell? |
mitosis |
|
|
The synaptonemal complex is |
a network of proteins that holds homologues together. |
|
|
Which best describes the process of independent assortment? |
The way one pair of homologues lines up along the metaphase plate does not affect how any other pair lines up. |
|
|
In plants and animals, the zygote develops into an embryo by what process? |
mitosis |
|
|
One of a pair of chromosomes with similar genetic information and from different sources like the sperm and egg. |
homologue |
|
|
You are studying meiosis in an organism where 2n=24. How many chromosomes will each nucleus have after meiosis II is complete? |
12 |
|
|
When do homologous chromosomes separate from each other during meiosis? |
anaphase 1 |
|
|
In 95% of cases of Down's syndrome, there is one extra chromosome (number 21) in every cell. This aneuploid condition is most likely the result of In 95% of cases of Down's syndrome, there is one extra chromosome (number 21) in every cell. This aneuploid condition is most likely the result of |
failure of 1 homologous pair to segregate during meiosis. |
|
|
The most common form of gene therapy involves inserting a normal gene into cells that contain a defective version of the gene. In order to use gene therapy to prevent a man from passing a defective gene on to future generations, you should try to insert normal copies of the gene into |
germ-line cells. |
|
|
Meiosis results in a reassortment of maternal chromosomes (inherited from the mother) and paternal chromosomes (inherited from the father.) If n=4 for a given species, and ignoring the effects of crossing over, what is the probability that a gamete will receive only paternal chromosomes? |
1/16 |
|
|
A cell in G2 before meiosis begins, compared with one of the four cells produced at the end of meiosis II, has |
four times as much DNA and twice as many chromosomes. |

