![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
60 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Photoelectric effect |
Electrons are ejected from charged metal surfaces |
|
|
Quantum theory |
Structure of matter at atomic level |
|
|
Wavelength |
Distance from crest to crest or trough to trough |
|
|
Frequency |
Number of times a wave passes a point per unit of time |
|
|
Amplitude |
The heigh of the crest of depth of the trough |
|
|
Wavelength and frequency related by |
λν = c |
|
|
Atomic absorption spectra |
Characteristic dark lines produced when external source of light passes through free gaseous atoms |
|
|
Atomic emission spectra |
Characteristic patterned of bright lines produced when atoms are vaporized in high temperature flames |
|
|
Black body radiation |
Absorbs light when cold and emit when it's hot |
|
|
Radiant energy is |
Quantized |
|
|
Quantum |
Smallest discrete quantity of energy |
|
|
Photon |
A quantum of electromagnetic radiation |
|
|
Energy of photon |
E=hv or E=hc/ H= 6.626x10^-34 j•s |
|
|
Quantized states |
Discrete energy levels |
|
|
Work function ϕ |
Amount of energy needed to dialogue an electron from the surface of a metal |
|
|
Work function equation |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
Johann balmer |
Formulated empirical equation from experimental results no theoretical explanation. It fits with hydrogen emission spectrum |
|
|
Electromagnetic radiation |
Any forms of radiant energy in the electromagnetic spectrum |
|
|
Electromagnetic spectrum |
A continuous range of radiant energy that includes gamma rays x rays ultraviolet rays visible light infrared radiation and radio waves |
|
|
Photoelectric effect |
The release of electrons from a material as a result of electromagnetic radiation stoking it |
|
|
Threshold frequency (Vo) |
The minimum frequency of light required to produce the photoelectric effect |
|
|
Ground state |
Most stable, lowest energy state of a particle |
|
|
Ground state |
Most stable, lowest energy state of a particle |
|
|
Excited state |
Any energy state above the ground state |
|
|
Ground state |
Most stable, lowest energy state of a particle |
|
|
Excited state |
Any energy state above the ground state |
|
|
Electron transition |
Movement of an electron between energy levels |
|
|
Ground state |
Most stable, lowest energy state of a particle |
|
|
Excited state |
Any energy state above the ground state |
|
|
Electron transition |
Movement of an electron between energy levels |
|
|
Heisenberg uncertainty principle |
The principle that one cannot simultaneously know the exact position and the exact momentum of an electron |
|
|
Ground state |
Most stable, lowest energy state of a particle |
|
|
Excited state |
Any energy state above the ground state |
|
|
Electron transition |
Movement of an electron between energy levels |
|
|
Heisenberg uncertainty principle |
The principle that one cannot simultaneously know the exact position and the exact momentum of an electron |
|
|
Quantum number |
One of the four related numbers that specify the energy, shape and orientation of orbitals in an atom and the spin orientation of electrons in the orbitals |
|
|
Angular momentum quantum number (l) |
An integer having any values from 0 to n (n-1) that defines the shape of an orbital |
|
|
Angular momentum quantum number (l) |
An integer having any values from 0 to n (n-1) that defines the shape of an orbital |
|
|
Magnetic quantum number (Ml) |
Defines the orientation of an orbital in space |
|
|
Quantum number chart |
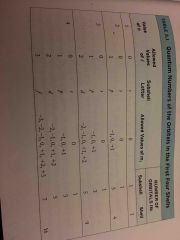
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Spin quantum number |
+ 1/2 or -1/2 |
|
|
Pauli exclusion principle |
No two electrons in an atom can have the same set of four quantum numbers |
|
|
P orbital shape |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
P orbital shape |

|
|
|
D orbital shape |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
Aufbau principle |
The method of building electron configurations of atoms by adding one electron at a time as atomic number increases across the rows of the periodic table |
|
|
Core electrons |
Inner shell in an atom or ion that are not involved in chemical rxn |
|
|
Core electrons |
Inner shell in an atom or ion that are not involved in chemical rxn |
|
|
Valence electrons |
Electrons in the outermost occupied shell of an atom have the most influence on the atoms chemical behavior |
|
|
Core electrons |
Inner shell in an atom or ion that are not involved in chemical rxn |
|
|
Valence electrons |
Electrons in the outermost occupied shell of an atom have the most influence on the atoms chemical behavior |
|
|
Valence shell |
Outer most occupied shell of an atom |
|
|
Core electrons |
Inner shell in an atom or ion that are not involved in chemical rxn |
|
|
Valence electrons |
Electrons in the outermost occupied shell of an atom have the most influence on the atoms chemical behavior |
|
|
Valence shell |
Outer most occupied shell of an atom |
|
|
Hunds rule |
Lowest energy electron configuration of an atom has the maximum number of unpaired electrons |
|
|
Isoelectronic |
Describes atoms or ions that have identical electron configuration |
|
|
Ionization energy |
The amount of energy required to remove 1 mole of electrons from 1 mole of ground state atoms or ions in the gas phase |
|
|
Ionization energy |
The amount of energy required to remove 1 mole of electrons from 1 mole of ground state atoms or ions in the gas phase |
|
|
Electron affinity |
Energy change that occurs when 1 mole of electrons combines with 1 mole of atoms or ions in the gas phase |

