![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
105 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Atomic Structure |
Protons and Neutrons in Nucleus Electrons outside
|
|
|
Nucleus |
dense Positively charged center of Atom containing Protons and neutrons |
|
|
What determines the atomic # of an element? |
# of Protons
|
|
|
What is the element #on the Periodic table called? |
Atomic Number |
|
|
You cannot change _________ in regular chemistry? |
Protons |
|
|
Are atoms of an elements of the periodic table charged? |
No unless you are told, They are neutral because the # of Protons = # of electrons |
|
|
You can change the # of__________ in an atom without changing what element it is. |
Electrons |
|
|
Atomic Theory |
1. All matter is composed of atoms. 2. Atoms of a given element differ than all other elements. 3. Chemical compounds have a defined ratio. 4. Chemical Reactions only change the way atoms are combined in compounds, the elements are unchanged. |
|
|
Atomic masses are expressed in _________? |
Atomic Mass Unit (amu) |
|
|
Subatomic Particle |
very small particle that is a building block for an atom |
|
|
What are the 3 types of subatomic particles? |
Protons Neutrons Electrons
|
|
|
Electron |
smallest subatomic particle and has negative charge |
|
|
Proton |
Subatomic particle with + charge
|
|
|
The charge of ______ and __________ are equal but opposing. |
Protons and Electrons |
|
|
Charge of Proton |
+1` |
|
|
Charge of Electron |
-1 |
|
|
Neutron |
subatomic particle with no charge |
|
|
Nucleon |
Any subatomic particle in nucleus; thus protons and neutrons |
|
|
A mass # = |
Number of protons and Neutrons |
|
|
Element |
Pure substance in which all atoms have same atomic # |
|
|
Isotope |
atoms of an element that have same number of protons and electrons but different neutrons |
|
|
19 A F F 9 Z |
Mass # (A) Symbol Atomic # (z) |
|
|
Atomic Mass |
Calculated average mass of isotopes of a given element and takes in to account abundant of each isotopes |
|
|
Why do some elements have similar characteristics? |
Similar number of electrons and their arrangement |
|
|
Shells Characteristics |
Principle energy Levels 1st shell is n=1 Each shell has subshells The further away the higher the energy
|
|
|
S shell has how many subshells? |
1orbital
|
|
|
P shell has how many subshells? |
3 orbital |
|
|
d shell has how many subshells? |
5 Orbital |
|
|
How many electrons can be in each orbital? |
2 |
|
|
Electron Shell |
a region of space about a nucleus that contains electrons that have approx. the same energy and that spend most of their time approx. the same distance form the nucleus |
|
|
Electron Subshell |
region of space within a shell that contains electrons with about same energy
|
|
|
# of Subshells = # of ___________ |
Shells |
|
|
Electron orbital |
region of space within a subshell in which the electrons are most likely to be |
|
|
Describe two electrons in an orbital |
they always spin in opposite directions |
|
|
Rules for electrons
|
1. Subshells are filled in order of increasing energy
2. Each orbital gets one before a second adds to any orbital 3. only 2 and they have opposing spin |
|
|
Electron Configuration |
statement of how many electrons are in each subshell |
|
|
Example of Electron Configuration |
# Lower case letter (s,p,d,f) followed by superscripts of the # of electrons in that subshell |
|
|
Orbital Diagram |
Uses same 1s Followed by arrows noting electrons in orbital and direction of spin; 1st is always upward followed by downward |
|
|
Why does the d row of the periodic table drop? |
Some overlap of energy levels occur beginning in shell 3 and 4 |
|
|
if you add all superscript or arrows the # should = |
# of electrons
|
|
|
Distinguishing electron |
last electron added to electron configuration |
|
|
Noble Gas |
element located in the far right column; colorless gas and not very reactive |
|
|
Representative Element |
element located the S area of or the first 5 columns of the P |
|
|
4 most abundant elements in human body |
C, H, O, N |
|
|
Alkali metals |
most left column; excluding H, react rapidly with water to form flammable H2 gas and alkaline or base solutions, low melting points, ; soft shiny metals |
|
|
Alkaline earth Metals |
second column to the left; |
|
|
Transition Metal |
element located in d area; metals; |
|
|
Inner Transition metal |
Man made elements in f subshell |
|
|
How can we find atomic weight without table? |
% isotope/ 100 X mass of isotope +
%/100 X mass of isotope
|
|
|
Z represents |
# of protons
|
|
|
A represents |
# of Neutrons |
|
|
Types of electron Configurations |
1. Long hand complete 2. Orbital 3. Short hand
|
|
|
How do you short hand electron configurations? |
You bracket the last noble gas and add form there
|
|
|
Valence Shell |
outermost shell with highest energy |
|
|
Valence electrons |
electrons in outermost valence shell that have a lot of energy and are loosely held |
|
|
What is important in determining an electron's properties? |
valence electrons |
|
|
Halogens and Halides |
F, Cl, Br, I and Ar; Colorful corrosive nonmetals, found in nature with other in combination with other elements ie: NaCl |
|
|
Octet Rule |
1. Atoms want 8 valence electrons 2. They will react to gain or lose until they have 8 3. Atoms that gain or lose electrons by reacting with another atoms is an ion |
|
|
Do Noble gas gain or lose electrons easy? |
No |
|
|
Can Transition Metals form more than one oxidation state? |
Yes |
|
|
Al oxidation state |
+3 |
|
|
Zn oxidation state |
+2 |
|
|
Ag oxidation state
|
+1 |
|
|
Chemical compound |
attractive force that holds two atoms together |
|
|
Ionic Compound |
compound that contains ions |
|
|
Covalent Bond (molecular Bond) |
chemical bond formed by sharing of one or more electrons
|
|
|
ion |
atom that has added or lost an electron
|
|
|
Cation |
ion with a positive charge |
|
|
Anion |
ion with a negative charge |
|
|
Fixed oxidation state |
only make one oxidation state ie: Alkalis +1, Alkalines +2 |
|
|
variable oxidation state |
atom may make a + or negative oxidative state C and N columns and transition metals vary
|
|
|
Group |
Vertical column on periodic table
|
|
|
Period |
horizontal row on periodic table
|
|
|
Metals Always make what type of ions? |
Cations |
|
|
Nonmetals usually make what type of ions? |
Anions |
|
|
Compounds have what charge? |
Always neutral, no charge
|
|
|
ionic bond |
electrical attractions between ions of opposing charges |
|
|
Oxidation State |
charge on an ion |
|
|
FeCl2 |
Cl is 1- iron must be 2+ |
|
|
ions
|
Write Cation 1st
|
|
|
Polyatomic ion |
composed of more than 1 atom |
|
|
Naming Ionic Compounds |
1. Write cation name 1st 2. Write anion+ide 3. If cation has more than one oxidation state write it |
|
|
Roman Numerals |
Type 1 only make one ion NO Roman! Type 2 makes more than 1 cation ROMAN NUmeral! |
|

|
Chlorate
|
|
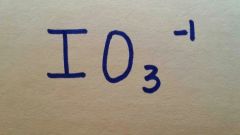
|
Iodate
|
|
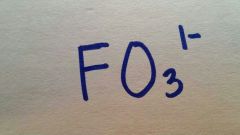
|
Fluorate
|
|

|
Phosphate
|
|
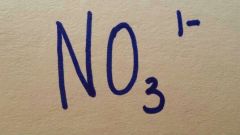
|
Nitrate
|
|
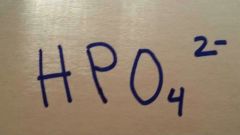
|
Hydrogen Phosphate
|
|
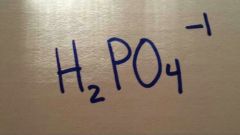
|
dihydrogen hosphate
|
|
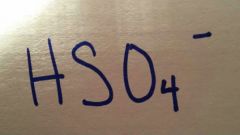
|
Hydrogen sulfate / bisulfate
|
|
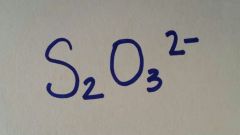
|
Thiosulfate
|
|

|
Oxolate
|
|
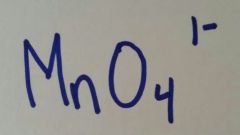
|
Permanganate
|
|

|
Hydroxide
|
|
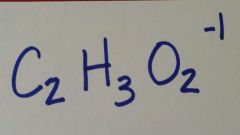
|
Acetate
|
|
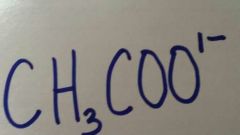
|
Acetate
|
|

|
Ammonium
|
|
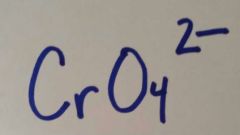
|
Chromate
|
|
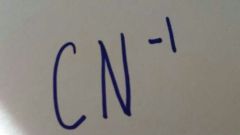
|
Cyanide
|
|

|
Dichromate
|
|
|
How do you go from Bromate to Perbromate?
|
Add an oxygen when you add Per
|
|
|
How do you go from Bromate to Bromite?
|
Going from ate to ite you take away an oxygen
|
|
|
How do you go from Bromite to hypobromite?
|
going from ite to hypo+ite you take away an oxygen
|
|
|
What happens when you have a polyatomic ion ending in ate and you add a H?
|
you take away one electron (charge)
|

