![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
119 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Mitral valve area using the pressure half time method |
MVA=220 ÷ PHT |
|
|
MV area using the Deceleration time method |
MVA= 759 ÷ DT |
|
|
Pressure half time from DT equation |
PHT= 0.29 × DT |
|
|
Cross sectional area equation |
CSA= (0.785)(LVOT diameter)2 |
|
|
MV area using continuity equation method |
MVA cm2 = (CSA x VTI lvot) / VTI MV
Or (0.785)(LVOT diameter)2 (VTI LVOT) / VTI MV |
|
|
Stroke volume equation |
SV= CSA x VTI lvot |
|
|
Aortic valve area continuity equation |
AVA (cm)2 = (.785) (LVOT diameter)2 (LVOT VTI)/ VTI AV |
|
|
Aortic valve velocity ratio |
VR= V1/V2 Remeber V1 happens before V2 V1: LVOT velocity V2: Max AV valve velocity VR is the velocity ratio |
|
|
Aortic valve velocity ratio |

Normal ratio is 1. Severe stenosis is 0.25 or less. This means the valve area is 25% of normal |
|
|
early aortic valve opening |
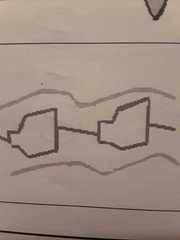
Aortic insufficiency |
|
|
early closure of the MV |
Aortic insufficiency |
|
|
With M-mode you detect diastolic flutter of the anterior mitral valve leaflet and the aortic valve, early closure of the mitral valve, and early opening of the aortic valve. What is the diagnosis? |
Aortic insufficiency |
|
|
T or F? In cases of mild AI, the pressure difference gradually decreases creating a flatter pressure halftime waveform. |
True |
|
|
True or false? Severe AI causes the aorta's pressure to drop quickly creating a more rapid LV pressure increase and a flatter pressure halftime. |
False. Severe AI has a steeper waveform. |
|
|
Which of the following would most likely cause chronic AI? Aortic dissection, aortic stenosis, trauma, or left atrial myxoma? |
Aortic stenosis |
|
|
T or F? AI is the result of an incompetent aortic valve that permits backward systolic flow from the aorta, through the aortic valve, into the left ventricle. |
False AI is backward diastolic flow when the valve is closed |
|
|
A low-pitched, mid-diastolic, rumble at the apex. (Austin Flint murmur) is heard in patients with what? |
Severe AI |
|
|
Patient is experiencing exertional dyspnea, syncope, and chest pain. Echo reveals LV enlargement, decreased LV function and diastolic dysfunction. What is most likely the diagnosis? |
AI |
|
|
High-pitched, blowing, diastolic decresendo murmur at the left sternal border is heard with |
AI |
|
|
What pressure halftime would you expect on a patient with mild AI? A.) > 500 msec B.) 350-500 msec C.) < 200msec D.) 16-30 mmHg |
Greater than 500 msec |
|
Small D shaped left ventricle, flattened IVS, and a dialated, hypertrophied right ventricle. |
MS with Pulmonary hypertension |
|
Possible left atrial thrombus and spontaneous echo contrast, decreased mitral valve area, and hockey stick mitral valve |
Mitral Stenosis |
|
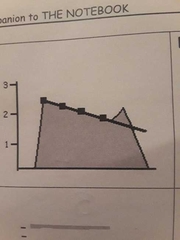
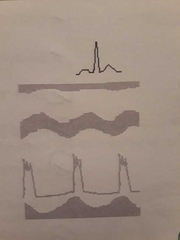
Flattened E-F slope, pressure half time, Deceleration slope. |
Mitral stenosis |
|

Absent a wave and Mid systolic closure of Pulmonic valve creating "flying W" happens with___ |
Ms with associated pulmonary hypertension |
|
|
What is the most common cause of mitral stenosis? |
Rheumatic fever |
|
|
Increased LA pressure, scarring of the MV apparatus, dilatation of the IVC and SVC are all complications of what? |
Mitral stenosis |
|
|
Mitral regurgitation associated with mitral stenosis is most likely due to |
Left atrial enlargement |
|
|
True of false? Diastolic doming of the anterior mitral valve leaflet creates a hockey stick appearance when MR is present. |
False. This happens with MS |
|
|
Dyspnea hemoptysis and fatigue are all symptoms of what? |
Mitral stenosis |
|
|
___ of the valve leaflets is caused by pressure pushing on the under surface of the leaflets along with comissural fusion. |
Doming |
|
|
Increased E-F slope, increased A wave, and decreased leaflet excursion (D-E) may present on M-mode when mitral stenosis is present. |
False. A decreased E-F slope and decreased or absent A wave with a decreased excursion is seen with MS |
|
|
Mitral stenosis creates a volume and pressure overload pattern, which may result in |
RV hypertrophy, RV enlargement, and a small D shaped LV |
|
|
T or F? RV hypertrophy, RV dialtion, flattening of the IVS, paradoxical wall motion, and a small D shaped LV are the result of pulmonary hypertension. |
True |
|
|
Absent A wave combined with mid systolic closure of the pulmonic valve creates a flying W in the presence of what? |
Pulmonary hypertension |
|
|
If the MV pressure half time is 230 msec, what is present? |
Severe mitral stenosis |
|
|
Mitral Comissurotomoy, catheter balloon Valvuloplasty, and mitral repair or replacement are all treatments for what? |
Mitral stenosis |
|
|
T or F? In the presence of MS, we see increased LA pressure, enlargement of the LA and echo contrast or a thrombus |
True |
|
|
What is the most common method of calculating the mitral valve area? |
Pressure halftime method MVA = 220÷PHT |
|
|
Which one represents the MV area? PHT/220 220/PHT Peak gradient/ 220 4(v)2 where V= peak velocity |
220 ÷ pressure half time |
|
|
Normal mitral valve area equals |
4-6 cm squared |
|
|
Low pitched, diastolic rumble with an opening snap is the murmur associated with |
Mitral stenosis |
|
|
T or F? Regurgitation increases preload. Stenosis increases afterload. |
True |
|
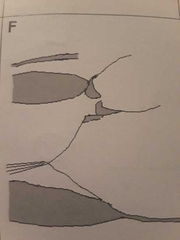
Left ventricular hypertrophy and post stenotic dilatation of the aorta |
Degenerative aortic stenosis |
|

Football shaped opening and raphe |
Bicuspid aortic stenosis |
|
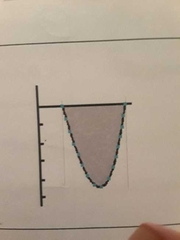
Peak velocity of 4.5 m/sec, max and mean pressure gradient |
AS waveform |
|
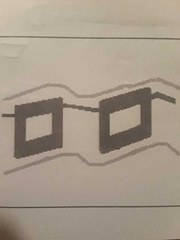
Eccentric closure line (25% have a normal closure by m-mode) |
Bicuspid Aortic valve |
|
|
Systolic crescendo decresendo murmur is associated with what? |
Aortic stenosis |
|
|
During echo on a 74 year old patient, we detect LV hypertrophy, LV enlargement, decreased LV systolic function, and post stenotic dilatation of the aortic root. What is most likely present? |
Degenerative aortic stenosis |
|
|
T or F? According to ICAEL the AS systolic velocity must be evaluated from multiple transducer positions with a dedicated non-imaging CW transducer. |
True |
|
|
What type of AS originates at the sinuses of valsalva and extends medially to the cusps? |
Degenerative |
|
|
According to the continuity equation the AVA = (.785)(LVOT diameter)2 (V1)÷ (V2) |
True |
|
|
T or F In the presence of AS, aortic valve replacement is performed if the patient develops symptoms and or progressive LV hypertrophy |
True, AOV area is also important in determining replacement. |
|
|
What type of stenosis originates at the AV cusps and moves toward the commissures? |
Rheumatic |
|
|
When is a raphe typically seen? |
Bicuspid aortic valve |
|
|
T or F? The continuity equation assumes that flow through a tube is constant. Flow is equal to velocity multiplied by area. Therefore if the area decreases, the velocity must also decrease. |
False, if the area decreases, the velocity must increase. |
|
|
The LVOT diameter is aquired from LAX in cases of what? |
Aortic stenosis to calculate the AVA |
|
|
T or F? Causes of AS are myxomatous degeneration, hereditary factor, connective tissue disorders, or skeletal abnormalities. |
False |
|
|
During an echo if you detect thickened aortic valve with a peak velocity greater than 2 m/sec the patient has aortic |
Stenosis |
|
|
If the patient has a thickened AOV with a peak velocity less than 2 m/sec they have aortic |
Sclerosis |
|
|
2 year old patient has valvular congenital AS. What most likely caused it? |
Bicuspid aortic valve |
|
|
AS patient usually gets serial echos to track changes in the |
Degree of AS, systolic and diastolic dysfunction, chamber and wall size |
|
|
Patient has decreased cardiac output, chest pain, syncope, and possible cerebral infarct. What is the likely diagnosis? |
Aortic stenosis |
|
|
What would you expect to see on m mode of an 11 year old with bicuspid AS |
Eccentric closure |
|
|
T or F? AS can decrease aortic valve systolic flutter. |
True |
|
|
All of these windows should be used for the aortic valve doppler waveform |
Apical, suprasternal, and parasternal |
|
|
T or F? Doppler echo is the method of choice for diagnosis of aortic stenosis |
True |
|
|
If LVOT diameter is 1.7, V1 is 1, and V2 is 4 what is the AVA? |
.57 cm squared |
|
|
T or F? The aortic valve doppler waveform always appears below the baseline. |
False |
|
|
PHT from DT |
.29 × DT |
|
|
MVA using DT |
759÷DT |
|
|
MVA using PHT |
220÷PHT |
|
|
MS impedes ___ bloodflow traveling from the LA into the LV Systolic or Diastolic? |
Diastolic. when the valve is open |
|
|
Which murmur is a low pitched DIASTOLIC rumble with an opening snap |
Mitral Stenosis |
|
|
What can be caused by severe mitral annular calcification? MAC |
Mitral stenosis |
|
|
MV artesia (absence of normal opening) or parachute MV (only one papillary muscle attached to MV) are both causes of what? |
Congenital MV stenosis |
|
|
Left atrial mass, tumor or vegetation due to infective endocarditis or anything that obstructs MV flow are examples of what? |
Secondary Mitral stenosis |
|
|
With mitral stenosis, LA enlargement and scarring of the MV apparatus that shortens and thickens the leaflets and chords can cause |
Associated mitral regurgitation. |
|
|
LA thrombus (particuarly in the left atrial appendage) and systemic embolization, increased LA size and pressure, spontaneous echo smoke, infective endocarditis, and decreased cardiac output can be seen with ___ |
Mitral stenosis |
|
|
classic finding of MS |
Hockey stick appearance of the Anterior mitral valve leaflet |
|
|
A large RV and a small D shaped LV are seen with |
Mitral stenosis |
|
|
What part of the cycle should you do planimetry of the MV for MVA? |
Early diastole, during maximal opening |
|
|
M-mode of MS |
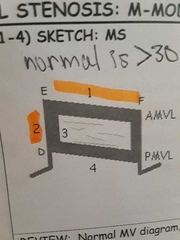
1. Decreased EF slope (0-30mm/sec), reduced amplitude of E wave, and absent A wave 2. Decreased DE excursion (amplitude) 3. Thick MV leaflets 4. Anterior motion of the PMVL |
|
|
Normal MV m-mode |
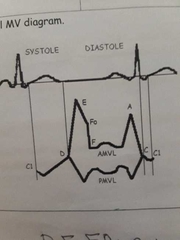
|
|
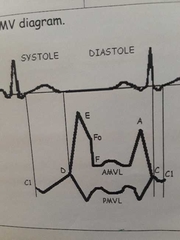
D to E to FO represents ___. This accounts for 70 to 75% of filling FO to first upward of A is what? ___ |
Early and rapid filling. Diastolic filling. |
|
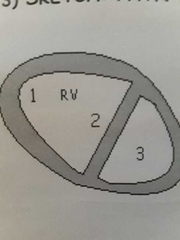
MS associated with PHTN. Flattened IVS is from the increased___ in the RV With ___ overload the IVS will round some in systole |
Pressure. Volume. |
|
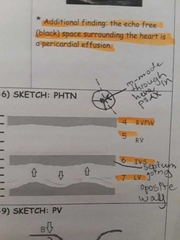
M-mode |
MS w/ PHTN |
|
|
Most common method to access MS is |
Pressure half time |
|
|
With MS, the ___ waveform and the __ the pressure half-time, the more severe the stenosis. |
Flatter, longer (higher number) |
|
|
With AI, the ___ the waveform, and the ___ pressure half-time = more severe |
Steeper, Shorter (lower number) |
|
|
Normal MV area? |
4-6 cm2 |
|
|
MVA w/ mild MS? |
>1.5 cm2 |
|
|
1 to 1.5 cm2 MVA is what degree of stenosis? |
Moderate |
|
|
MVA w/ severe MS |
< 1 cm2 |
|
|
MVA with MS |
Normal: 4-6 Mild: 1.5-4 Moderate: 1-1.5 Severe: <1 |
|
|
A thickened AOV that does open well with a peak velocity <2 m/s is |
Aortic sclerosis |
|
|
A thickened AOV that doesn't open well with a peak velocity >2 is |
Aortic stenosis |
|
|
___ to the stenotic aortic valve flow is laminar |
Proximal |
|
|
___ to stenotic AOV flow is turbulent |
Distal |
|
|
Doppler echo measures ___ pg, while the cath lab provides the peak to peak PG |
Instantaneous ( measures velocity and converts it to PG using Bernoulli equation) |
|
|
Subvalvular congenital AS may be due to a ___ |
Membrane across the LVOT |
|
|
Valvular congenital AS is due to |
Bicuspid or unicuspid AOV |
|
|
Supravalvular congenital AS is due to an aortic ___ |
Coarctation |
|
|
If someone has a bicuspid AOV, the sonographer should always look for___ |
Coarctation ( color flow and spectral doppler in suprasternal) |
|
|
When should you look for bicuspid aortic valve *what part of the cycle |
Systole with the valve open |
|
|
With rheumatic MS, 30% of patients will have ___ as well. |
AS |
|
|
Mini thoracotomy (robotically assisted w/ small incision between ribs) and TAVR (balloon catheter w/ a stent-mounted valve crimped on its tip) are both methods of ____ replacement |
AOV |
|
|
Any turbulent flow (MS, AS, AI) can cause ___ |
Infective endocarditis |
|
|
With quad AOV (4 cusps), the cusps usually open well (no AS) but most cases have associated __ |
AI |
|
|
AS increases___. Therefore,the LV must work harder to pump blood, causing LV hypertrophy. |
Afterload (resistance the heart must pump against) |
|
|
Post stenotic dilatation of AO root and ascending aorta due to high velocity jet striking the aortic root wall can be seen in patients with ___ |
AS |
|
|
Planimetry from SAX of the AOV should be done at what part of the cycle? |
Early systole |
|
|
As vs normal AOV m-mode |
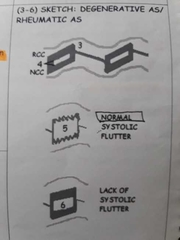
|
|
|
AS waveform from suprasternal or right parasternal, flow traveling toward the transducer |
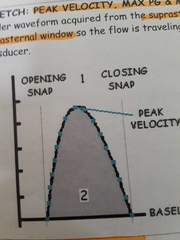
|
|
|
AS doppler waveform from the apex with flow traveling away from transducer |
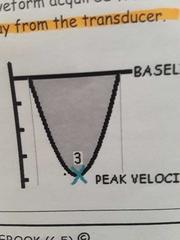
|
|
|
What measurements are needed to get the aortic valve area? |
LVOT diameter, peak LVOT velocity, peak AOV Velocity. (VTI of both if there is AS) |
|
|
AS severity scale |

|
|
|
Flow reversal above the baseline in the descending aorta (SSN) is an indication of ___ |
Severe AI |
|
|
AI PHT of 350-500 is |
Moderate |
|
|
Greater than AI 500 PHT is |
Mild |

