![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
39 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
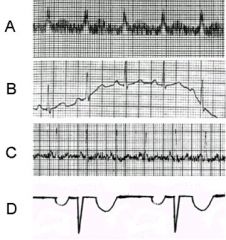
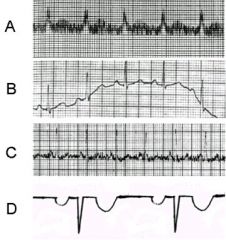
Which of the following ECGs can only be corrected by disconnecting then reconnecting lead wires
|
D
|
|
|
The QRS of an ECG falls on a darker vertical line of the ECG paper. Subsequent QRS complexes fall on every other dark line. What is the ventricular rate?
A. 300 / min B. 200 / min C. 150 / min D. 100 / min |
C. 150 / min
|
|
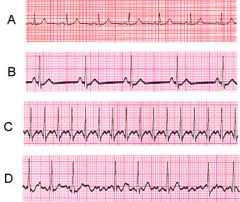
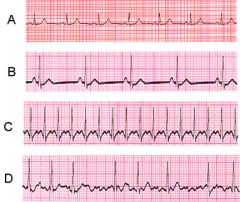
Which of the following ECGs has the closest rate to 50 BPM?
|
B
|
|
|
One benefit of a flow trigger besides decreasing inspiratory work is:
A. a relatively slow rise time B. a lower PIP C. a constant delivered volume D. potential for leak compensation |
D.
potential for leak compensation |
|
|
A. decrease expiratory time
B. decrease inspiratory time C. decrease the flowrate D. a and c |
B. decrease inspiratory time
|
|
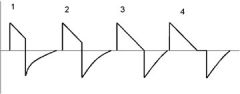
The graphic below represents a pressure targeted breath. Which wave represents the optimal inspiratory time to deliver the maximum tidal volume without causing desynchrony?
|
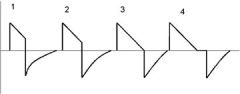
3
|
|
|
Which of the following lists the steps required for an extubation in the correct order?
i. deflate cuff ii untape tube iii suction down the tube iv suction the pharynx v remove the tube A. iii, iv, i, ii, v B. ii, i, iv, iii, v C. iii, iv, ii, i, v D. iii, i, ii, v, iv E. iv, ii, i, iii, v |
C. iii, iv, ii, i, v
|
|
|
During pressure targeted ventilation which of the following factors effect the Vt 840 ventilator.
i delta P ii I time iii expiratory sensitivity iv lung compliance and airway resistance A. i B. i, ii C. i, ii, iv D. iii, iv E. all of the above |
C. i, ii, iv
|
|
|
Which mode will not be appropriate for an apneic patient?
A. A/C at a set rate of 10 bpm B. SIMV at a set rate of 10 bpm C. CPAP with a pressure support of 20 cmH2O D. CPAP with no pressure support E. c and d |
E. c and d
|
|
|
The ventilator (PB840, PB7200, Bird 8400, Servo 900, Servo 300) is set for pressure targeted ventilation in A/C. The set Inspiratory Pressure is 20 cmH2O, and the PEEP is set at 10 cmH2O. What will the PIP equal?
A. 10 cmH2O B. 20 cmH2O C. 30 cmH2O D. the PIP will vary depending on patient effort, RAW, and lung compliance E. 800cc |
C. 30 cmH2O
|
|
|
A patient on a mechanical ventilator should be considered for extubation when they have successfully completed a spontaneous breathing trial…
|
A. over night or at least 8 hours
B. 5 to 10 minutes C. 30 minutes to 2 hours D. 3 to 5 hours |
|
|
Which of the following are characteristics of patients who can be successfully
extubated? i. able to protect airways ii. able to breathe spontaneously iii. hemodynamically stability iv. no lung infiltrates v. decreased lung compliance A. i, ii, v B. i, ii, iii C. i, ii, iv D. all of the above |
B. i, ii, iii
|
|
|
Which of the following chest disorders is most likely to result in the appearance of air bronchograms on the chest radiograph?
A. Pneumonia B. Pneumothorax C. Pleural effusion D. Empyema |
A. Pneumonia
|
|
|
Which of the following is true about a chest X-ray done with an anterior - posterior view?
A. the 10th rib is visible above the diaphragm B. the intervertebral spaces is barely visible through the heart C. there is a magnification effect on the heart D. a and b E. all of the above |
C. there is a magnification effect on the heart
|
|
|
The width of the heart shadow on the normal chest film should not exceed what portion of the width of the entire chest?
A. 25% B. 33% C. 50% D. 60% |
C. 50%
|
|
|
Which of the following is NOT a reason for mechanical ventilation involving
neurological control. A. drug overdose B. spinal trauma C. stroke D. kyphoscoliosis |
D. kyphoscoliosis
|
|
|
Oxygen is transported in the blood:
I. dissolved as a gas (PaO2) II. combined with Hemoglobin ((HbO2) III. as carbonic acid (H2CO3) IV. as nitrous oxide (N2O) A. I, II, and IV B. I and II C. III and IV D. I, III, and IV E. II and IV |
B. I and II
|
|
|
The P(A-a)O2 may be used to calculate which of the following ?
I. shunt II. dead space III. oxygen content A. I only B. II only C. I and II D. II and III E. I, II, and III |
A. I only
|
|
|
The flow during exhalation does not return to baseline. The best way to fix this
problem would be to: A. decrease expiratory time B. decrease inspiratory time C. decrease the flowrate D. a and c |
B. decrease inspiratory time
|
|
|
A mechanically ventilated asthmatic patient has become more bronchospastic over several hours. Which of the following changes would you expect to see during that time?
i. decreasing PIP ii. increasing PIP iii. increasing plateau iv. decreasing plateau v. no change in plateau |
A. i, iv
B. ii, iii C. i, v D. ii, v |
|
|
Which of the following could represent hypoxemia caused by shunt?
A. atrial septal defect B. drainage of Thebesian veins into the left ventricle and drainage of Bronchial veins into the pulmonary circulation C. hypoventilation D. ARDS E. a and d |
E. a and d
|
|
|
The pressure and volume beyond the upper inflection point represents:
A. deadspace B. tube compensation C. over distention D. alveolar recruitment |
C. over distention
|
|
|
A weaning patient is ordered for a spontaneous breathing trial via an aerosol T tube for 45 minutes. Ten minutes into the SBT the patient’s respiratory rate increases from 20 to 35; heart rate increases from 92 to 116; there is now use of accessory muscles; blood pressure has increased from 110/85 to 130/90. What would be the most appropriate course of action at this point.
A. place the patient back on the vent to prevent further fatigue B. follow the orders, keep the patient on an aerosol T tube for another 35 minute, fatigue is good exercise for respiratory muscles C. increase the aerosol flowrate to decrease the WOB D. increase the pressure support during this T tube trial E. Extubate the patient the tube must be too narrow |
A. place the patient back on the vent to prevent further fatigue
|
|
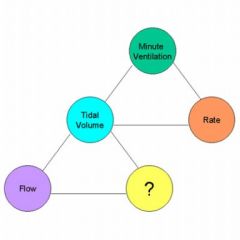
The circle with the question mark represents ________________ in the graphic below.
A. I:E ratio B. inspiratory time C. compliance D. PIP |
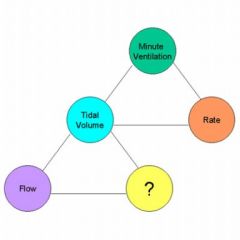
B. inspiratory time
|
|
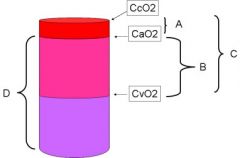
Which letter represents shunt?
|
A
|
|
|
What parameter is measured on the vertical axis of the ECG paper?
A. time B. voltage C. cardiac contraction rate D. blood flow |
B. voltage
|
|
|
The following is true about ECG lead placement.
A. limb leads must be placed on the correct upper arm and lower leg, while chest leads must be in the correct order around to the left but no specific location B. limb leads only have to be on the correct limb, while chest leads must be placed in specific locations C. limb leads can be placed any where, there are no specific locations. The machine will recognize the particular limb. Chest leads must be placed in specific locations D. all limb leads and chest leads may be placed in any position because the modern computerized machines |
B. limb leads only have to be on the correct limb, while chest leads must be placed in specific locations
|
|
|
During a pressure supported breath the pressure waveform rises near the end of inspiration and the flow wave form ends abruptly without tapering down toward baseline. This would indicate that:
A. that inspiration is synchronized with the patient's effort and ends correctly B. the ventilator must be a 7200 C. the breath is not synchronized and ends by increasing pressure rather than decreasing flow D. the system has a leak that cannot be corrected and has been compensated for by increasing the flowby |
C. the breath is not synchronized and ends by increasing pressure rather than decreasing flow
|
|
|
If a patient is allowed to breath spontaneously with variable tidal volumes between the machine set VT and set rate, the ventilator mode must be
A. SIMV B. Pressure Support C. Pressure Control D. AC E. Apnea |
A. SIMV
|
|
|
What abnormality is associated with the pleural meniscus sign?
A. Pneumothorax B. Hemothorax C. Pneumonia D. Congestive heart failure (CHF) |
B. Hemothorax
|
|
|
A mechanically ventilated asthmatic patient has become more bronchospastic over several hours. Which of the following changes would you expect to see during that time?
i. decreasing PIP ii. increasing PIP iii. increasing plateau iv. decreasing plateau v. no change in plateau A. i, iv B. ii, iii C. i, v D. ii, v |
D. ii, v
|
|
|
Mixed venous blood entering the pulmonary capillaries normally as a PO2 of about 40 mmHg. At a PO2 of 40 mmHg the saturation of hemoglobin is approximately:
A. 50% B. 65% C. 75% D. 85% |
C. 75%
|
|
|
The QRS of an ECG falls on a darker vertical line of the ECG paper. Subsequent QRS complexes fall on every other dark line. What is the ventricular rate?
A. 300 / min B. 200 / min C. 150 / min D. 100 / min |
C. 150 / min
|
|
|
The PetCO2 monitored on a ventilator patient with normal V/Q matching has trended downward for several hours after a vent settings change. What is the most likely
explanation for this decrease? |
A. the patient is hyperventilating
B. the patient is hypoventilating C. the ventilator circuit has developed a leak D. respiratory rate has increased |
|
|
the following is true for the machine breaths in pressure targeted SIMV.
i. time triggered ii. volume limited iii. pressure limited iv. volume cycled v. pressure cycled vi. time cycled A. i, ii, iv B. iii, v C. i, iii, iv D. i, iii, vi E. ii, vi |
D. i, iii, vi
|
|
|
Which of the following do not cause hypoxemia.
A. increased barometric pressure B. increased PCO2 C. V/Q mismatch D. shunt E. diffusion defect |
A. increased barometric pressure
|
|
|
A Vt equal to __________and a set respiratory rate equal to ___________are the usual initial settings used for volume targeted adult mechanical ventilation.
|
A. 10-15cmH2O.....25
B. 1.25 seconds...... the patients last spontaneous rate C. 15cc/Kg..... 3 - 5 BPM D. 8 -10cc/Kg.....10-12 BPM |
|
|
What is the first indication of patient fatigue during the ventilator weaning
process? A. tachypnea with decreased Vt B. increased Vt and decreased use of accessory muscles C. cyanosis, hypoxemia, and hypercarbia D. unable to speak above a whisper |
A. tachypnea with decreased Vt
|
|
|
Which of the following is the most common cause of hypoxemia?
A. shunt B. anemia C. diffusion defect D. V/Q mismatches E. hypoventilation |
D. V/Q mismatches
|

