![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
55 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Properties of life |
Order: all have complex order Regulation: external change, no internal change Growth & development: information carried by DNA Energy processing: take in and use energy Response to the environment: respond to environmental stimuli Reproduction: reproduce their own kind Evolve: change over time through reproduction |
7 of them |
|
|
Domains of life |
Bacteria (prokaryote) Archaea (prokaryote) Eukarya |
|
|
|
Types of eukarya |
Kindom plantae (multicellular) Kingdom fungi (multicellular) Kingdom animalia (multicellular) Protists (unicellular) |
|
|
|
Different ways of getting energy |
Photosynthesis (plant) Decomposer (fungi) Eating (animal) |
|
|
|
6 steps of the Scientific method |
1. Observation 2. Question 3. Hypothesis (answer) 4. Make a prediction (rephrase 3 as if/then) 5. Experiment 6. Analyze data/make conclusion |
|
|
|
Scientific thoery vs hypothesis |
Scientific theory: Broader hypothesis Need many supported variables Hypothesis: Needs less supported variables |
|
|
|
Element |
Substance that can't be broken down without chemical reaction |
|
|
|
4 main elements |
Oxygen Nitrogen Hydrogen Carbon |
|
|
|
Subatomic particles and their charges |
Proton + Neutron 0 Electron - |
|
|
|
Atom |
Smallest unit of matter that that retains property of an element |
|
|
|
Isotope |
Alternate mass forms of an element due to different amount of neutrons |
|
|
|
Radioisotope |
Nucleus decay spontaneously giving off particles and energy |
|
|
|
Ionic bond |
Attraction between opposite charge |
|
|
|
Covalent bond |
Share electrons |
|
|
|
Hydrogen bonds |
Weak attraction between polar molecules |
|
|
|
Cohesion |
Tendency of the same kind to stick together |
|
|
|
Solution |
Homogeneous mixture |
|
|
|
Solvent |
Dissolving agent liquid Temperature dependant |
|
|
|
Solute |
Dissolved substance Powder |
|
|
|
Aqueous solution |
When water is a solvent |
|
|
|
Acid |
Releases H+ into a solution Low on ph scale |
|
|
|
Base |
Accepts H+ from a solution High on ph scale |
|
|
|
Buffer |
Substance that resists ph change |
|
|
|
Organic compound |
Carbon based molecule Properties depend on: Carbon skeleton Atoms attatched to the skeleton |
|
|
|
Why is carbon a versatile atom |
Backbone structure to life In dna |
|
|
|
Polymer |
String of monomers |
|
|
|
Monomer |
A molecule that can be bounded to other identical molecules |
|
|
|
4 basic types of biological molecules |
Carbohydrates (macromolecule) Lipids (not macromolecule/hydrophobic) Proteins (macromolecule) Nucleic acid (macromolecule) |
And which are macromolecules |
|
|
Monosaccaride |
Simple sugars Cant be broken down by hydrolysis Galactose, glucose, fructose |
|
|
|
Polysaccharides |
Complex carbohydrate Long chain of sugar units Starch, glycogen, cellulose |
Give 1 example |
|
|
Macromolecules and their sub units |
Lipids: fatty acids and glycerol Proteins: amino acids Nucleic acids: nucleotide |
|
|
|
Isomer |
Molecules with the same chemical formula but different structure |
|
|
|
Disaccharide |
Double sugars Lactose, sucrose |
|
|
|
Disaccharide |
Double sugars Lactose, sucrose |
|
|
|
Difference between saturated and unsaturated fat |
Unsaturated has less than max amount of hydrogen Saturated has max amout of hydrogen |
|
|
|
4 levels of protein |
Primary: amino acids (chain) Secondary: hydrogen bonding (folded) Terriary: folding due to side chain (3d) Quaternary: more than 1 amino acid chain (complex 3d) |
What do they look like |
|
|
Dna |
Deoxyrobonucleic acid Base uses thymine 2 strands |
|
|
|
RNA |
Ribonucleic acid Base uses uracil Usually songle strand |
|
|
|
Cell theory |
1800s All living things are composed of cells All cells come from earlier cells |
What and when? |
|
|
Magnification power vs resolving power |
Magnification: increase in size Resolving: ability to show 2 objects as separate |
|
|
|
Different types of microscopes |
Light: dissecting and compound, colorless Electron: color, uses beams of electrons Scanning electron: 3d looks at surface Transmission electron: insides |
|
|
|
Prokaryotes |
Single cell organism that lacks a membrane bound nucleus, mitochondria, or any other membrane bound organelle |
|
|
|
Eukaryotes |
Organisms cell that contains a nucleus and other organelles enclosed with membranes |
|
|
|
Characteristics shared by all cells |
Cell membrane Cytoplasm Ribosomes DNA |
|
|
|
Plant specific cells |
Cell wall Vacuole Chloroplast |
|
|
|
Animal specific cells |
Lysosomes Centrial Cilia Flagella |
|
|
|
Structure of eukaryotic cell |
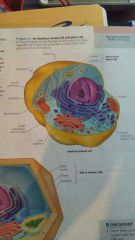
|
|
|
|
Progression from DNA to protein |
DNA to RNA to MRNA to TRNA to protein |
|
|
|
Chloroplast |
Photosynthesis Creates its own DNA Found in plant |
|
|
|
Mitochondria |
Found in plants and animals Where cellular respiratory takes place and where energy is made |
|
|
|
Energy |
The capasity to cause change |
|
|
|
Cellular respiration |
Takes place in the cells Releases energy by breaking down fuel molecules |
|
|
|
Metabolism |
Total of all chemical reactions in an organism Requires enzyme assistance and energy |
What does it require |
|
|
Enzymes |
Reduce amount of activation energy meeded to break bonds of reactand molecules |
|
|
|
ATP |
Adenosine phosphate Transfer energy in cells |
|

