![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
52 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
define Evolution |
The adding up of adaptions over time. |
|
|
define Adaptions |
Any change that makes an organism more likely to make it survive or reproduce. |
|
|
Examples of Adaptations |
Camouflage mimicry better eye sight etc |
|
|
What is the significance of Charles Darwin |
created the theory of evolution. After his voyage, he concluded the theory but waited a while to release it in fear of criticism from the church. |
|
|
Artificial Selection |
-Humans mate organisms to get a desired phenotype. - selective breeding/mating |
|
|
natural selection |
-main mechanism of evolution - where nature selects for or against phenotypes. - since theres always variation in populations, natural selection will favor one variation over another, The desired variation will increase over time. the undesirable variation will decrease over time. -allows for variations that make an organism more likely to survive and reproduce increase in frequency over time. |
|
|
examples of natural selection |
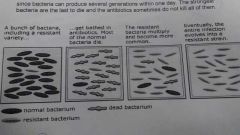
a bunch of bacteria on the table. We wipe the table down with anti bacterial, however the one resistant will remain there while the others are dead. Soon ts'll multiply and become more common.
(or giraffes) |
|
|
What must be there for evolution to occur? |
-variation in population. -w/o variation, natural selection will not be able to favor one allele over another. |
|
|
_________ do not evolve, ______________ do. |
individual populations |
|
|
When natural selection selects for.......... |
the allele is favored by natural selection and will increase in frequency over time within the population. |
|
|
When natural selection selects against...
|
the allele is not favored and will decrease in frequency in a population over time. |
|
|
What 3 things must there be for Natural Selection to occur? |
1. Variation must exist among individuals w/in a population. 2. Variation results in differences in number of offspring in the next generation. 3. Variation must be genetically inherited. |
|
|
Define Mimicry |
an example of adaptation allows one organism to resemble another organism that is dangerous or feared. (scientist believe that its a result of the continual adding up of adaptations.) |
|
|
Define Camouflage |
is an adaptation that allows an organism to blend into its surrounding (scientists believe that its a result of the accumulation of adaptations over time) |
|
|
What is used as Evidence of evolution? (4) |
Fossil Records Comparative Anatomy Embryology Molecular Biology |
|
|
Fossil Records |

-Dating fossils -shows that organisms change over time -the older the fossil, the simpler the organism is (law of superposition) |
|
|
Define Law of Superposition |
older fossils are simple and found low in the rock strata while newer fossils are more complex and found high in the rock strata. |
|
|
What 3 events create fossils? (fossilization) |
1. the organism becomes buried in sediment 2. the calcium in bones or other tissues must mineralize. 3. the surrounding sediment must harden to form rocks. |
|
|
Why is fossilization is rare? |
b/c most organisms will decay or are scavenged before the process can begin. Therefore, only a small fraction of the organisms that lived has become fossilized. but the fossil record does provide evidence for evolution. |
|
|
comparative anatomy |
the study of similarities and differences in the anatomy of different species.
|
|
|
Homologous structures |
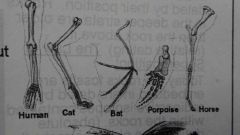
Structures in organisms that may appear different and have a different function, but they come from a shared common ancestor. (the forelimbs of animals) |
|
|
analogous structures |
-structures that may appear similar but do not evolve from each other and is different ancestry(bird vs insect wing) -an example of convergent evolution. |
|
|
vestigial structures |
structures with no apparent function but once did in an ancestor and are remnants of the past. (hipbones in whales and leg fragments in snakes) |
|
|
Bird wing vs Insect Wing |
-Bird is hallow -Insect is made of chitin -means no recent common ancestor |
|
|
Evidence from Embriology |
during development our embryos show our evolutionary history. We have girls and a tail during development because we descend from previous organisms that do have those phenotypes. |
|
|
Evidence from Molecular Biology |
Comparing proteins and DNA sequences to determine evolutionary similarities Best way to determine evolutionary relatedness -compare DNA sequences of a commonly found protein with its amino acid sequences of the protein. -in both cases the more similarities, the closer the evolutionary relatedness. -the more difference, the more ddistantly related the organism is. -use the amino acid sequences and the more similarities, the closer the relative. |
|
|
Evidence from molecular biology |
DNA Sequence chimps share 99% of their DNA nucleotide (Base) sequences w/ humans so they are closely related to humans. Comparing Amino Acid Sequences of Proteins find a common protein like hemoglobin in many organisms |
|
|
Evolutionary Divergence |
Information processed vby comparing amino acid sequences within commonly found proteins. More similarities, the closer the relative. |
|
|
Evidence from Embryology |
In our early stages of development, humans go through a stage where we have gills and a tail and fine hair all over our bodies. |
|
|
Types of Evolution (2) |
Convergent Divergent/Adaptive Radiation |
|
|
Convergent Evolution |
when sometimes distantly related organisms evolve similar phenotypes in different places b/c of similar environmental stressors. Analogous structures arise by convergent evolution. |
|
|
Example of convergent evolution |
North American placental mammals and Australian marsupial mammals are both evolved similar traits b/c of their environment and environmental stressors. The streamline bodies of animals that live in the water. |
|
|
Divergent Evolution |
-when divergent evolution occurs, one large population of organism gets separated into smaller populations that each evolve different traits b/c of the different found sources and environmental stressors. -organisms branch to look very different From one ancestral species many species evolve. Like Darwin's finches! |
|
|
Influence of Darwin's Finches |
Darwin was the first to recognize that animals and plants living on oceanic islands resemble the forms on the closest continent. Like Darwin's finches, all 13 species evolve from 1 early finch. |
|
|
What is this an image of? |

Adaptive Radiation (Divergent Evolution) |
|
|
What is the evolution of the Modern Day Horse? |

Size Toe Reduction the feet of modern horses have a single toe, enclosed in a tough, bony hoof. By contrast, it started with 4 toes on the front and 3 on the back feet. Over time the central toe increases while the other two reduced to nothing. Tooth Size and Shape teeth have gotten larger and ridges wee added to the molars and premolars. Therefore, the teeth are better suited to eat grass. as grasslands become more prevalent adaption was in order. |
|
|
Symbiosis |
close living relationship between different species. Different types of symbiotic relationships. |
|
|
Types of Symbiosis (3) |
Commensalism Mutualism Parasitism |
|
|
Mutualism |
Both species are benefited by living together |
|
|
commensalism |
When one organism benefits and the other is neither benefited or harmed. |
|
|
Paratasitism |
One species is benefited, the other is harmed. |
|
|
What does symbiosis cause? |
Co evolution |
|
|
Co-evolution |

-is a change in the genetic composition of one species(or group) in response to a genetic change in another. -Pollinators and flowering plants. |
|
|
Allele frequencies |
-how common alleles are in populations -all the alleles in a population are called the gene pool. |
|
|
What are the 5 agents of Evolutionary Change? |
Natural Selection Gene Flow Genetic Drift Mutation Non Random Mating |
|
|
What types of genetic drift are there? |
Bottleneck Effect Founder Effect (emigration) |
|
|
What effect does N.S. have on evolutionary change? |
can change allele frequency by "selecting for" an allele it increases the frequency of alleles that benefits the organism over time. |
|
|
What effect does Gene flow have on evolutionary change?
|
when organisms of the same species enter a population (immigration) this changes allele frequencies |
|
|
What effect does genetic drift have on evolutionary change?
|
random event that can change allele frequencies Bottleneck Effect a catastrophe occurs and changes allele frequencies (ex: tornado, earthquake etc) Founder Effect (emigration) some in the population leave and start their own population There will now be less and changes allele frequency. |
|
|
What effect does mutation have on evolutionary change?
|
-any change in the nucleotide of sequence of DNA -mutations result in most variations |
|
|
What effect does Non Random Mating have on evolutionary change?
|
-when selective mating takes place -the desired trait will increase and change the frequencies |
|
|
what is a species?
|
group of organisms whose members successfully mate & have fertile offspring
|

