![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
42 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the definition of a polyp?
|
Protrusions of mucosal elements from the surface of the polyp
|
|
|
What are the different kinds of polyps?
|
Pedunculated: attached by a stalk
Sessile: growing into the wall. |
|
|
What are the different kinds of colon polyps?
|
Developmental
Inflammatory (pseudo-polyp) Hyperplatic Neoplastic Normal mucosa Mixed |
|
|
What are the different kinds of neoplastic colon polyps?
|
Adenomas
Carcinomas |
|
|
What are the kinds of developmental polyps?
|
Juvenile
Hamartomas (Peutz-Jeghers) |
|
|
What kind of a polyp is a juvenile polyp? What's inside it?
|
Hamartomas
Excess lamina propria; hardly any muscularis |
|
|
What structures occur inside juvenile polyps?
|
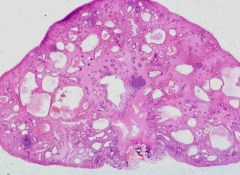
Budding
CYstic tubules (crypts or pits) |
|
|
Where are juveinle polyps found?
|
COLON > small intestine >> stomach
|
|
|
What condition do you find lots of juvenile polyps?
|
Juveinle polyposis syndrome
|
|
|
What mutations are found in juveinle polyposis?
|
Mutations in SMAD4
Mutations in BMPR1A Deletion of PTEN |
|
|
What cancers are people with a SMAD4 at higher risk for?
|
GI
Pancreatic Biliary 80% RISK!!! |
|
|
What is the composition of a peutz-jeghers polyp?
|
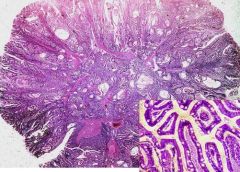
Branched muscularis mucosae
Hamartomas |
|
|
What mutations are found in Peutz-Jeghers polyps?
|
STK11 on 19p
|
|
|
What cancers are people with Peutz-Jeghers polyps at risk for?
|
All cancers; not just GI
|
|
|
Where are peutz-jeghers polyps found?
|
SI >> colon and stomach
|
|
|
What is a classic finding in Peutz-Jeghers syndrome?
|
Oral-perioral pigmented spots
|
|
|
What is the distribution of the colorectal mucosal polyps?
|
Adenomas: 66%
Hyperplatic: 33% Juvenile: 1% |
|
|
What is the definition of a GI adenoma?
|
Localized collection of in-situ dysplastic epithelium that isn't post-inflammatory
Can be low or high grade |
|
|
What are the cellular characteristics of adenomas?
|
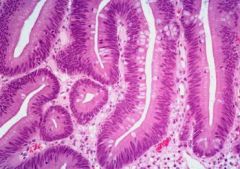
Cell, nuclear crowding
Enlarged, elongated nuclei Increased N:C Less cytoplasmic maturation |
|
|
How do you differentiate between high and low grade adenomas?
|
Degree of crowding
Architecture! |
|
|
How do you differentiate between an adenoma and a polyp?
|
Adenomas BECOME polyps when enough epithelium accumulates to produce a protrusion
|
|
|
What are the different kinds of archistecture for tumors?
|
Villous
Tubular Tubulovillus |
|
|
What are the characteristics of adenomas that are at risk for a carcinomatous epithelium?
|
LARGE
VILLOUS Multiple Carcinoma-associated Flat |
|
|
When does colon cancer metastasis occur?
|
When the tumor reaches the lymphatics, which are in the superficial submucosa.
|
|
|
What is the function of APC? P53? K-RAS?
|
APC:Tumor suppressor
p53: Tumor suppressor K-RAS: oncogene |
|
|
What happens in a colonic hyperplastic polyp?
|
Overgrowth of regular mucosa due to delayed turnover
|
|
|
What is the appearance of hyperplastic polyps?
|
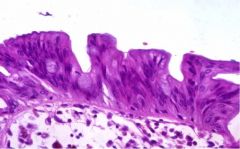
Serrated architecture
Hypermature |
|
|
Where are colonic serrated polyps found? Who gets them?
|
More distal; left colon
Older people get them. |
|
|
Are hyperplastic polyps typically associated with cancers?
|
No, not usually
|
|
|
What are the characteristics of cancerous serrated polyps?
|
Large
Right-sided Architecturally complex You see dysmaturation all throughout the polyp rather than just at the top. |
|
|
Who's more at risk for cancer; crohns or UC?
|
Ulcerative colitis
|
|
|
Where in the world do you typically find squamous cell CA of the esophagus?
|
Asia
Iran |
|
|
What are risk factors for squamous cell CA of the esophagus?
|
Smoking, drinking
HPV |
|
|
What kind of dysplasia do we see in the esophagus in the US?
|
Barrett's
Replacement of the squamous epithelium with columnar; precuros to cancer |
|
|
What population gets adenocarcinama in barrett's?
|
Chronic GERD
Whit emen |
|
|
What are the types of cancers of the stomach?
|
Tubular
Signet ring cell |
|
|
What is the most common cause of gastric cancer?
|
H. pylori
|
|
|
What are some of the types of liver cncer?
|
Hepatocellular carcinoma
|
|
|
What are the risk factors for liver cancer?
|
Viral hepatitis
Cirrhosis |
|
|
Where does pancreatic cancer typically occur?
|
Head of the pancreas
It's a ductal cancer |
|
|
What stage is pancreatic cancer typically found at? Why?
|
High grades
It almost invariably spreads to the lymph nodes. |
|
|
Where do we screen for cancers?
|
Colon cancers
People with GERD |

