![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
30 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Ernest Haeckel (1879) |
Wrote Evolution of Man |
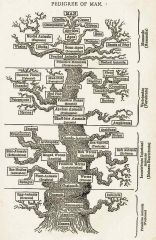
|
|
|
Fundamental assumption of science |
Assumes that there are natural explanations for natural phenomena |
Assumes that there are ______ explanations for _______ phenomena |
|
|
Science: 1. A branch of knowledge dealing with the body of facts __________ arranged & showing the __________ of general _____. (Ex. Mathmatical sciences)
2. ________ knowledge of the _________ or _____ world, gained through ________ and _____________ |
Science: Science: 1. A branch of knowledge dealing with the body of facts systematically arranged & showing the operation of general laws. (Ex. Mathmatical sciences)
2. Systematic knowledge of the physical or natural world, gained through observation and experimentation |
|
|
|
4 components of scientific inquiry: 1.______- observations accepted as true, repeatedly confirmed 2._____-testable statement of relationships. Can be confirmed or falsified 3.______- Generalizations that describe phenomena 4.______- Explanation of some aspect of the natural world. Well sustained. Incorporates the other 3 |
1.FACTS- observations accepted as true, repeatedly confirmed
2.HYPOTHESES- testable statement of relationships. Can be confirmed or falsified
3. LAWS- Generalizations that describe phenomena
4. THEORIES- Explanation of some aspect of the natural world. Well sustained. Incorporates the other 3 |
|
|
|
Criteria for theories
1) Must be ______ by _______ & Observation
2) Must be__________
3) Must be subject to _________ & __________
4) Cannot be ________; only ________ or _________ |
1) Must be tested by experiments & Observation
2) Must be falsifiable
3) Must be subject to revision & change
4) Cannot be Proven; only confirmed or falsified. |
|
|
|
Definitions:
Biology: ____ ______ __ ____
Evolution: ______ ____ ____
Biological Evolution: _______ __ ______ __________ _____ _____
Evolutionary Biology: |

Back (Definition)
|
|
|
|
Evolutionary Biology: _______ change in _____ ______ over ____; The study of __________ as a historical science |
Evolutionary Biology: Investigates change in living systems over time ; The study of populations as a historical science |
|
|
|
Microevolution: changes in ____ ________ within __________ and _______.
Macroevolution: larger evolutionary change, warranting placement of _________ into different _______, families, and higher level ______ |
Microevolution: changes in gene frequencies within populations and species.
Macroevolution: larger evolutionary change, warranting placement of populations into different genera, families, and higher level taxa |
Evolutionary processes give diversity at every level of biological organization. From DNA/Proteins to Individuals, species, orders, phyla, and domains! |
|
|
Evolution as FACT (PATTERNS) Life has changed/ is changing over time
1) ___________ and their allele frequencies change over time
2) Different kinds of related organisms are stratified in ____ _________ ________
3. _______ _______ are heritable; _______ ________ are traceable backwards in time |
1) populations and their allele frequencies change over time
2) Different kinds of related organisms are stratified in the fossil record (faunal succession)
3. Genetic traits are heritable; genetic lineages are traceable backwards in time |
|
|
|
Evo as a THEORY (PROCESSES)
1) Embodies the __. _______. _________ of evolutionary change
2.) Integrates those __________, along with the _____, into an ___________ whole.
3) Empowers us to ______ ________ regarding details we don't know yet |
THEORY (PROCESSES) 1) Embodies the four primary mechanisms of evolutionary change
2) Integrates those mechanisms, along with the facts, into an interconnected whole
3) Empowers us to make predictions regarding details we dont know yet |
Evolution is a theory because mechanisms have been described, tested, and affirmed to explain how it has occurred & is occuring |
|
|
Anaximander (Greek) (510-546 BC) |
"First Scientist" -physical forces created universe - 1st animals sprang from sea -simple life gave rise to more complex forms
-humans sheltered in mouths of fish (jonah and whale)
|
|
|
|
Empedocles (490-430 BC) |
- world made of 4 elements
-wrote on nature---Animals were created through a combination of free roaming body parts
-reincarnation or "transmigration of the soul"
-plants and fungi had souls because of movement towards the sun |
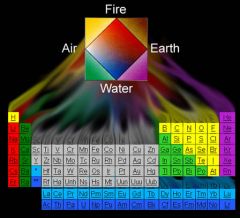
|
|
|
Plato (428-348 BC) |
-student of Socrates
-"Theory of forms" immaterial forms /ideas represent fundamental reality.
- Aether; The fifth element (quintessence- heavenly) |
|
|
|
Aristotle (384-322 BC) |
-student of Plato, more interested in nature -advocated knowledge based on observation, first to use the scientific method -wrote "history of animals". He described classified and discuss animals -believed in fixity of species, like Plato
- wrote scala naturae aka Great chain of being (ordering least perfect to most perfect) |
Hebrews 2:7-8 (63 AD) "Thou madest him a little lower than the angels… thou hast put all things in subjection under his feet…"
This chain of being concept was carried forward into Western philosophy and still persists today |
|
|
Galen (130-201 AD) Father of ________ First studies of ______ _______, the _____, ______, ______
William Harvey (1578-1657) 1st person to describe _______ _________ in detail
Marcello Malpighi (1628-1694) "Father of _________ " first person to describe ________ __________ |
Galen Father of anatomy First studies of blood vessels, the heart, brain, nerves
William Harvey 1st person to describe blood circulation in detail. British anatomist
Marcello Malpighi "Father of histology" italian physician-used microscope to study animal tissues -first person to describe blood capillaries |
|
|
|
Natural Theology |
Movement of post reformation catholic church. "God could be attained w/out revelation, but by reason and examples from natural world. |
|
|
|
3 main components of Natural Theology:
1. ___ of the Earth 2. Great ____ __ ____ 3. ____ directed by ____ |
1) Age of the Earth (age stated in bible (6000 yrs old)
2) Great Chain of Being Created for purpose. "Higher, lower"
3) variation directed by God All according to a plan |
|
|
|
Archbishop James Ussher: Calculated the ___ ___ __ _____ based on ________ ________
Determined the earth's _____ _____ to be _:_ _am, _ _ _ 23, _ _ _ _ BC |
Archbishop James Ussher: Calculated the age of the earth based on biblical lineages.
Determined the earth's creation time to be 9:00 am, Oct 23, 4004 BC |
|
|
|
"Fixity of species" traced to ____ (ancient _____).
Species organized from _____ to ______.
Aristotle developed this in _____ ______. |
"Fixity of species" traced to plato (ancient greeks).
Species organized from simple to complex.
Aristotle developed this in scala naturae. |
|
|
|
George Buffon (1707-1788)
estimated earth to be _____ years old. Was retracted.
Described _ _____ in the history of the earth |
George Buffon (1707-1788)
estimated earth to be 75,000 years old. Was retracted.
Described 7 epochs in the history of the earth |
|
|
|
Georges Curvier (1769-1833) After start of industrial evolution. *Father of __________
*Described the ______ concept of ________ *_____ occur in _____ The deeper the ____ the _____ |
Georges Curvier (1769-1833)
*Father of Paleontology
*Described the geologic concept of stratigraphy *rocks occur in strata *The deeper the rocks the older. |
|
|
|
Georges Cuvier Composed an evolutionary hypothesis based on three assumptions: 1) Species are _______
2)Species may ______ ________
3)Different assemblages of species (_____) occurred in _____ ____ based upon the _____ where they are found |
Georges Cuvier Composed an evolutionary hypothesis based on three assumptions: 1) Species are fixed
2)Species may become extinct
3)Different assemblages of species (fossils) occurred in diff. times based upon the layers where they are found |
|
|
|
Georges Cuvier: Composed an evolutionary hypothesis based on three assumptions: 1) Species are _______ 2) Species may ______ ________ 3) Different assemblages of species (_____) occurred in _____ ____ based upon the _____ where they are found |
Georges Cuvier: Composed an evolutionary hypothesis based on three assumptions: 1) Species are fixed 2) Species may become extinct 3) Different assemblages of species (fossils) occurred in diff. times based upon the layers where they are found |
|
|
|
Georges Cuvier: Composed an evolutionary hypothesis based on three assumptions: 1) Species are _______ 2) Species may ______ ________ 3) Different assemblages of species (_____) occurred in _____ ____ based upon the _____ where they are found |
Georges Cuvier: three assumptions: 1) Species are fixed 2) Species may become extinct 3) Different assemblages of species (fossils) occurred in diff. times based upon the layers where they are found |
|
|
|
Jean Baptiste Lamarck (1744-1829) *wrote ________ ________ *Species ________. No _______ *individuals make a "______ _______" to _____ within its lifetime. |
Jean Baptiste Lamarck *wrote philosophie zoologique
*Species transformation. No extinction
*individuals make a "conscious effort" to adapt within its lifetime. |
|
|
|
Lamarck's theory: ________ of _______ characteristics.
Many good ideas. Theory eventually discredited. |
Lamarck's theory: inheritance of acquired characteristics.
Many good ideas. Theory eventually discredited for lack of proof. |
|
|
|
Carl Linnaeus (1707-1778) *Swedish _______ & _______. * father of ___________
* developed _______ ________ & hierarchal method of _________
*was a natural _____ but included humans as part of the ___ |
Carl Linnaeus (1707-1778) *Swedish botanist & taxonomist. * Father of Taxonomy * Developed binomial nomenclature & hierarchal method of classification *was a natural theologian but included humans as part of the apes |
|
|
|
Thomas Malthus (1766-1834) British Economist *described the "_______ ___ ______". Modeled ____ ____ under several circumstances.
*became foundation of ___ _____. Helped spark theory of _____ ____ |
Thomas Malthus (1766-1834) British Economist *described the "principle of population". Modeled Pop. Growth under several circumstances. ------------------------------------------------ *became foundation of population biology. Helped spark theory of natural selection. |
|
|
|
Thomas Malthus (1766–1834) British economist * described the "principle of population." * became the foundation of population biology. Helped spark the theory of natural selection |
Thomas Malthus (1766-1834) British Economist *described the "_______ ___ ______". Modeled ____ ____ under several circumstances.
*became foundation of ___ _____. Helped spark theory of _____ ____ |
|
|
|
Sir Charles Lyell (1797-1875) British geologist *Published "____ ___ ____" (1830).
* Advanced the concept of _________
|
Sir Charles Lyell (1797-1875) British geologist *Published "principles of geology" (1830). Describing how geological forces shape the earth
* Advanced the concept of uniformitarianism |
|

