![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
83 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Geologic Time Scale |
•Representation of the history of Earth •Organizes Earth’s history by major changes or events that have occurred, using evidence fro |
|
|
•Three Basic units of time are used: |
Eras Periods Epochs |
|
|
•Time scale is divided into units based on |
the order in which different groups of rocks and fossils were formed |
|
|
eras |
last ten to hundreds of millions of years-consists of 2 or more periods |
|
|
Evolution: |
Genetic change in a line of descent through successive generations. CHANGE OVER TIME!!! |
|
|
5 types of evidence for evolution |
●Fossils (Paleontology) ●Comparative Biochemistry (Molecular Biology) ●Comparative Morphology/Adaptations – (body structure) *adaptations (structural/physiological/behavioral) *common ancestry *vestigial organs ●Patterns of Development (Embryology) ●Biogeography – study of distribution of plants and animals in the environment. |
|
|
natural casts |
form when flowing water removes all of the |
|
|
adaptation |
feature that allows an organism to better survive it's environment |
|
|
artificial selection |
the process by which humans change a species by breeding it for certain traits |
|
|
heritability |
the ability for a trait to be able to be passed down from one gen to the next |
|
|
natural selection |
A mechanism by which individuals that have inherited beneficial adaptations produce more offspring on average than do other individuals |
|
|
what are the four main pro piles to the theory of natural selection |
variation overproduction adaptation descent w modification |
|
|
what is overproduction |
the process of organisms having several babies to ensure at least some will survive-also increases competition between offspring for resources |
|
|
descent w modification |
over time, natural selection will result in "the survival of the fittest" and a population that are well suited for survival. that certain trait will be passed down until environmental changes occur |
|
|
name 4 places Darwin found support for evolution |
fossils geography embryology anatomy |
|
|
biogeography |
the study of the distribution of organisms around the world |
|
|
homologous structures |
features that are similar in structure but appear in different organisms and have different functions |
|
|
evolution |
process of biological change by which descendants come to differ from their ancestors |
|
|
what to homologous structures tell us |
that organisms containing them could be from common descent |
|
|
analogous structures |
structures that perform a similar function but are not similar in origin ex: a bats' wing and a fly's wing |
|
|
vestigial structures |
structures in organisms today that have no use, but are remnants of organs or structures that had a function in easterly ancestors |
|
|
fossils |
traces of organisms that existed in the past |
|
|
name 3 principles of geological change |
catastrophism gradualism uniformitarianism |
|
|
catastrophism |
huge things responsible for mass extinction and the formation of all land forms |
|
|
gradualism |
the idea that changes on earth occurred by small steps over long periods of time |
|
|
uniformitarianism |
geological processes which are still occurring today add up over long periods of time to cause change |
|
|
variation |
difference in the physical traits of an individual from those of other individuals in the group to which it belongs |
|
|
interspecific variation |
variation among individuals of different species |
|
|
Intraspecific variation |
among members of the same species |
|
|
gene pool |
the combined alleles of all of the individuals in a population |
|
|
imprint fossil |
a remain of a film of carbon-not 3D- a rubbing |
|
|
mold |
impression of the shape of the organism-3D |
|
|
cast |
when the sediment fills the cavity in the mold-3D |
|
|
allele frequency |
measure of how common a certain allele is in the population |
|
|
name two things genetic variation can come from |
mutation recombination |
|
|
a type of distribution in which frequency is highest near the mean value and decrease towards each end of the range is (higher in the middle) |
normal distribution |
|
|
microevolution |
observable change in allele frequencies of a population over time- occurs small scale in a single population |
|
|
divergence |
organisms that had common origin but look different now because of evolution and changed |
|
|
convergence |
dissimilar lineages evolve and similar directions (become more and more alike) ex: analogous structure |
|
|
where are the Galapagos islands |
off the coast of South America |
|
|
what does the fossil record provide? |
evidence of extinction of species and origins of new groups and changes w/in groups over time |
|
|
trace fossils |
not actual body part 3 types: imprint, mold, cast |
|
|
relative dating |
looking at the position of fossils in the sedimentary rock & comparing them to index fossils |
|
|
index fossils |
fossils that scientist already know the age of |
|
|
absolute age |
determined by dating fossils w radioactive isotopes |
|
|
how can you use biochemistry as evidence for evolution |
comparative biochemistry- compare the DNA codes or hemoglobin or whatever |
|
|
what is comparative morphology |
looking at anatomical comparisons of major lineages ex:similar body structures |
|
|
endemic species |
organisms that are found nowhere else in the world but could be similar to organisms in nearby islands of continents |
|
|
relative dating |
looking at the position of fossils in the sedimentary rock & comparing them to index fossils |
|
|
index fossils |
fossils that scientist already know the age of |
|
|
absolute age |
determined by dating fossils w radioactive isotopes |
|
|
how can you use biochemistry as evidence for evolution |
comparative biochemistry- compare the DNA codes or hemoglobin or whatever |
|
|
what is comparative morphology |
looking at anatomical comparisons of major lineages ex:similar body structures |
|
|
endemic species |
organisms that are found nowhere else in the world but could be similar to organisms in nearby islands of continents |
|
|
relative dating |
looking at the position of fossils in the sedimentary rock & comparing them to index fossils |
|
|
punctuated equilibrium |
long stable periods of no change followed by brief periods of rapid change |
|
|
gradualism |
slow minute changes that build up over time |
|
|
index fossils |
fossils that scientist already know the age of |
|
|
absolute age |
determined by dating fossils w radioactive isotopes |
|
|
how can you use biochemistry as evidence for evolution |
comparative biochemistry- compare the DNA codes or hemoglobin or whatever |
|
|
what is comparative morphology |
looking at anatomical comparisons of major lineages ex:similar body structures |
|
|
endemic species |
organisms that are found nowhere else in the world but could be similar to organisms in nearby islands of continents |
|
|
speciation |
when members of similar populations no longer interbreed to produce fertile offspring sighing their natural environment |
|
|
when does speciation occur |
when there are significant changes in allele frequencies |
|
|
true or false speciation is not the same thing as natural selection |
true- it could be a consequence of natural selection or any thing else working with NS |
|
|
coevolution |
process by which two species evolve in response to each other over time ex: flowers and insects that pollinate |
|
|
macroevolution |
refers to the evolutionary change about species level involves all of the organisms in a certain area at a certain time |
|
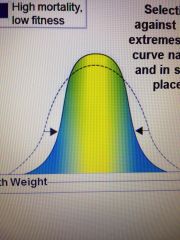
which selection is this |
stabilizing |
|

which is this |
directional selection |
|
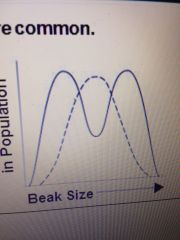
Front (Term) |
disruptive |
|
|
what is the hardy Weinberg equation |
p2+2pq+q2=1 |
|
|
what is p2 |
frequency of homo dom |
|
|
what is 2pq |
frequency of Hetero |
|
|
what is q2 |
frequency of homo recess |
|
|
perimineralization |
occurs when minerals carried by water or deposited a run a hard structure they may also replaced heart structure itself |
|
|
natural casts |
form when flowing water removes all the original donor tissue leaving Justin oppression cinnamon minerals fill in the mold re-creating or original shape |
|
|
Amber preserved fossils |
organisms that become trapped in tree resin that hardens and Amber |
|
|
preserved remains |
form an entire organism becomes encased in material such as ice or volcanic ash |
|
|
Paleozoic |
multicellular organisms organism's first appeared Cambrian explosion occurred |
|
|
Mesozoic |
called the age of reptiles because the dinosaurs roamed the earth during this era |
|
|
Cenozoic era |
now |
|
|
primates have.. |
opposable thumbs large brain volume vision flexible are movement flexible joints and feet and hands capable of grasping |
|
|
what are hominids |
bipedal -walk on 2 legs leaves arms and hands free |

