![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
48 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
What's another name for DNA?
|
Deoxyribonucleic acid.
|
|
|
|
What are chromosomes made out of?
|
DNA!
|
|
|
|
How many strands do DNA have?
|
Two. Double stranded!
|
|
|
|
What are the strands of DNA made up of?
|
Each strand is made up of units called nucleotides.
|
|
|
|
What is Binary Fission?
|
It's asexual reproduction. The mother cell splits, and 2 same cells are produced. Each has the potential to grow to the size of the original. Some examples are protists, archaea, bacteria.
|
|
|
|
What is Spore Formation?
|
It's asexual reproduction. In the spore is DNA, and can be dispersed in water or air. They grow into the exact copies of the parent. An example is fungi.
|
|
|
|
What is Fragmentation?
|
It's asexual reproduction. The parent organism breaks into fragments, and each piece is capable of growing independently into a new organism. (The whole thing isn't completely fragmented). Some examples are lichen and sea stars.
|
|
|
|
What is Vegetative Reproduction?
|
It's asexual reproduction. It's most common in plants. Runners under the soil make new plants that are genetically identical.
|
|
|
|
What are some points on Asexual Reproduction?
|
There is only one parent. Large #'s of genetically identical offspring are created. No specialized structures are required. Also, the offspring take advantage of favourable environmental conditions.
|
|
|
|
What are some points on Sexual Reproduction?
|
There are 2 parents (most of the time). They have genetically varied offspring. The process requires genetically specialized structures, and the structures are only used in reproduction.
|
|
|
|
What are genes?
|
They are large segments of nucleotides on a chromosome.
|
|
|
|
What do genes do (or give)?
|
They give the cell the ability to make certain proteins and dictate traits. Some examples are enzymes, bloodcells, Kerstin (hair), and muscles.
|
|
|
|
What are homologous chromosomes?
|
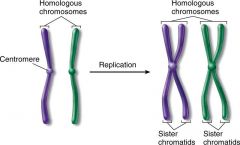
They are a pair of chromosomes, one from each parent. They occur in sexually reproducing cells (the pair together). They contain the same types of genes in corresponding positions.
|
|
|
|
What are diploid cells?
|
They are cells containing pairs of homologous chromosomes, one from each parent (2 sets of chromosomes).
Body cells are diploid. Represented by 2N. (2N=46) (Humans have 46 chromosomes, 23 pairs) |
|
|
|
What does ploidy mean?
|
Refers to the # of sets of chromosomes within a cell or organism.
|
|
|
|
What are haploid cells?
|
They are cells that contains only one of each of the homologous pair (only a single set of chromosomes). An example of a haploid cell would be a gamete, or a sex cell.
(Sex cell = 23 chromosomes) (N = 23) |
|
|
|
What would triploid be?
|
3N!
|
|
|
|
What is a mutation?
|
Changes to DNA, or an error in a genetic sequencing (nucleotides) of a cell. Can be caused during cell reproduction (as/s).
|
|
|
|
What can a mutation result in?
|
The inability to make some proteins or change a trait.
|
|
|
|
What is Mitosis?
|
It's the process of asexual reproduction, when chromosomes are replicated.
|
|
|
|
What is Meiosis?
|
It's the process of sexual reproduction, where the # of chromosomes are reduced by half, cells turning from diploid to haploid. There are 2 parts, I and II.
|
|
|
|
What is a genome?
|
It's the information in an organism that contains all the information required to reproduce itself (genetic make-up).
|
Genetic makeup
|
|
|
What is an allele?
|
It's a variation of a particular gene found in a homologous pair.
|
|
|
|
What is an example of an allele?
|
T = tall allele. t = short allele.
(A plant! Every plant has 2 genes for height but comes in 2 variations or alleles.) |
|
|
|
What is Allele Frequency?
|
It's the number of times an allele occurs in a gene pool compared w/ the number of times other alleles for the same gene occur in the population.
|
|
|
|
Where are alleles found on homologous pairs?
|
One allele will be found on one of the homologous pairs and the second allele will be found in the corresponding position of the second chromosome of the homologous pair.
|
|
|
|
What is a genotype?
|
It refers to the complement of genes within an organism, or what alleles it has.
Eg. TT, Tt, or tt. |
|
|
|
What is a Phenotype?
|
It refers to how the alleles are expressed (physical features you can see).
Eg. TT and Tt are tall plants, tt are short (tall is dominant, short is recessive) |
|
|
|
What is a gene pool?
|
It's the ratio of all the alleles of all the genes of a species in a population. [The ratio of these genes in the gene pool is the genetic makeup of the species]
|
|
|
|
When does evolution occur?
|
When the ratio of the genes in the gene pool changes.
|
|
|
|
Evolutionary change is more likely to happen when there are ________ members than _________ members.
|
Less members than more members!
|
|
|
|
What happens in Meiosis 1?
|
Homologous chromosomes (which have been replicated) separate (one to each new cell) creating 2 haploid (N) daughter cells.
|
|
|
|
What happens in Meiosis 2?
|
The sister chromatids line up in the centre of both cells and then separate @ the centromere. One sister goes to one cell and the other to the second cell, resulting in 4 haploid (N) daughter cells (GAMETES).
|
|
|
|
What is the Theory of Natural Selection based on?
|
1) there is variation within the population, resulting in some individuals being better suited for survival than others
2) if the characteristics which allow an individual to survive (and reproduce) and genetic, then these characteristics are being selected for 3) Less fit organisms die, causing some gene combinations to be removed 4) Members of a species that are not suited or adapted do not survive {their phenotype is removed) |
|
|
|
What's an example of this quote "Members of a species that are not suited or adapted do not survive (their phenotype is removed)"
|
Predator eats the more easily seen beetles lacking the brown gene, resulting in an increase in the brown gene frequency.
|
|
|
|
What is Genetic Drift?
|
The genetic composition of a species changes randomly with no identifiable causes. In some generations, some individuals may leave behind a few more defendants than others. It's more pronounced in smaller populations.
|
|
|
|
What is an example of Genetic Drift?
|
If there were few breeding females of a species, so the alleles of each female would have greater representation in subsequent generations.
|
|
|
|
What can Gene Flow be used to explain?
|
The changes in gene frequencies of isolated populations of a species. If an individual from one population joins a different population, it may introduce new alleles into the population. Over time the two populations may become more genetically similar.
|
|
|
|
What is an example of a phenotypic characteristic?
|
Height.
|
|
|
|
Where would you find the alleles for a particular genetic trait, such as eye colour?
|
Corresponding positions on the homologous pairs.
|
|
|
|
Where do the alleles for each of your genetic traits come from?
|
My parents!
|
|
|
|
What are the daughter cells of Meiosis called?
|
Gametes.
|
|
|
|
On what factor does Natural Selection act upon?
|
Phenotype.
|
Physical!
|
|
|
If you have 40 chromosomes in your skin cells, what would the ploidy of your gametes be?
|
20!
|
|
|
|
What is the haploid # of an organism with 20 chromosomes in their eye cells?
|
10.
|
|
|
|
Why is Meiosis necessary during sexual reproduction?
|
A gamete needs to have 23 chromosomes so when it joins with another gamete, they will have 46 chromosomes.
|
|
|
|
What are the 2 types of sexual reproduction?
|
1) Conjugation (very primitive form in bacteria)
2) Gamete production (sperm and eggs) |
|
|
|
What is Budding?
|
It's the formation of a new outgrowth from an organism, and the outgrowth is capable of developing into an individual. Some examples are hydra and yeast.
|
|

