![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
167 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the 4 regions of the stomach
|
cardiac
fundus body antrum |
|
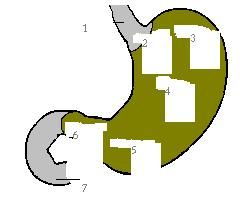
|
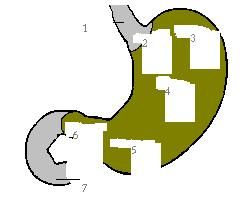
esophagus
cardia fundus body antrum pylorus duodenum |
|
|
G cells of the stomach secrete what?
|
gastrin
|
|
|
These cells release histamine in the stomach
|
enterochroffamin cells
|
|
|
This helps to increase pH
|
somatostatin
|
|
|
The H/K ATPase pump is found in these cells
|
parietal cells
|
|
|
How is the stomach protected from gastric acid?
|
gastric mucosal barrier
(bicarb rich mucosus and local prostaglandins) |
|
|
What actin dose pepsin perform in the stomach?
|
digests protein
|
|
|
Lipase dose what in the stomach?
|
digests fat
|
|
|
How is the alkaline tide produced?
|
H20->H+ (in stomach) and -OH and HCO3 -> with the HCO3 going into the blood
|
|
|
What are the 4 main categories of stomach disease
|
inflammation
ulceration neoplasia obstruction |
|
|
General clinical signs of stomach disease:
|
vomiting
hematemesis melena retching burphing hypersalivation ABD distention ABD pain weight loss |
|
|
This is a common cause of acute onset of vomiting
|
acute gastritis
|
|
|
This is a common cause of vomiting, hematemesis, melena, +/- anemia
|
gastric ulceration/or erosions
|
|
|
This is a common cause of non-productive retching, ABD distention, tachycardia
|
GDV
|
|
|
This is a cause of acute/chronic cause of vomiting 8-10 hours after feeding
|
delayed gastric emptying
|
|
|
This is a cause of chronic vomiting of food or bile
|
chronic gastritis
|
|
|
This is a cause of chronic weight loss, chronic vomiting, +/- anemia
|
gastric neoplasia
|
|
|
What are some common causes of acute vomiting (acute gastritis) (8)
|
mudosal insult/inflammation
dietary indescretion FB RX/toxins systemic disease parasites bacteria viruses |
|
|
With what clinical signs should a work up for acute gastritis be done?
|
FB
RX/toxins systemic disease hematemesis melena vomiting that fails to respond to therapy |
|
|
Most animals with simple gastritis respond to...
|
symptomatic treatment.
|
|
|
TX for acute gastritis:
|
SQ fluids (<5% dehydrated)
dietary restriction pepto 1 ml/5kg TID kaolinpectain 1 ml/kg TID sulcralfate |
|
|
What are some diseases that cause Gi erosion and ulcerations (6):
|
-Metobolic/endocrine: Cushings, uremia, liver disease, DIC, hypergastrinemia
- Inflammation: gastritis - Neoplasia - RX induced: NSIAD/Pred - Hypotension: shock/sepsis - Ideopathic: stress, exercise induced (sled dogs) |
|
|
Clinical signs of gastric erosions/ulceration
|
vomiting
hematemesis melena weakness inappetance |
|
|
Clinical pathology changes with gastric ulcers
|
Anemia - initally regeneraive, but can b/c microcytic (MCV) and hypochromic (MCHC) and thrombocytosis
|
|
|
Diagnosing gastric ulcers
|
Rads- R/O other causes
Endoscopy - best Ultrasound |
|
|
Where in the stomach do NSAID ulcers tend to be found
|
antrum and are not associated with mucosal thickening or irregular ulcerated edges
|
|
|
How do gastric tumor look endoscopically
|
Irregular and ulcerated edges that are frequently thicked edges of mucosa
|
|
|
Where should ulcers be endoscopically biopsied?
|
Periphery to avoid perforation
|
|
|
This combination of signs on endoscopy should be suggestive of a gastric hypersecretory state
|
mucosalulceration
antral mucosal hypertrophy copious gastric juice esophagitis |
|
|
When should gastric pH & serum gastrin be measured?
|
gastric erosions not associated with RX or gastric tumors
|
|
|
Why do dogs with MCT have low gastrin levels
|
Histamine is causing the gastric acid release and not gastrin
|
|
|
If gastric pH <3 and increased gastrin levels suggestive of
|
gastrinoma
|
|
|
TX of gastric ulcers
|
TX underlying cause
ensure hydration and blood Q Watch K due to vomiting H2 blockers proglumide (blocks gastrin) PGE analogues H/K AtPase inhibitors |
|
|
These two medication swill directly decrease gastric acid secretion and have been used to TX gastrinomas
|
octereotide (somatostatin analoge)
omeprazole (K/H ATPase inhibitor) |
|
|
For dogs with stomach ulcers, what medication is generally started and what is added on if first isn't working
|
H2 blockers
omeprazole |
|
|
Where should ulcers be endoscopically biopsied?
|
Periphery to avoid perforation
|
|
|
Misoprostal can cause this side effect
|
diarrhea
|
|
|
When should ABs be added in for gastric ulcerations
|
shock
GI barrier dysfunction |
|
|
This combination of signs on endoscopy should be suggestive of a gastric hypersecretory state
|
mucosalulceration
antral mucosal hypertrophy copious gastric juice esophagitis |
|
|
When should gastric pH & serum gastrin be measured?
|
gastric erosions not associated with RX or gastric tumors
|
|
|
Why do dogs with MCT have low gastrin levels
|
Histamine is causing the gastric acid release and not gastrin
|
|
|
If gastric pH <3 and increased gastrin levels suggestive of
|
gastrinoma
|
|
|
TX of gastric ulcers
|
TX underlying cause
ensure hydration and blood Q Watch K due to vomiting H2 blockers proglumide (blocks gastrin) PGE analogues H/K AtPase inhibitors |
|
|
These two medication swill directly decrease gastric acid secretion and have been used to TX gastrinomas
|
octereotide (somatostatin analoge)
omeprazole (K/H ATPase inhibitor) |
|
|
Where should ulcers be endoscopically biopsied?
|
Periphery to avoid perforation
|
|
|
For dogs with stomach ulcers, what medication is generally started and what is added on if first isn't working
|
H2 blockers
omeprazole |
|
|
This combination of signs on endoscopy should be suggestive of a gastric hypersecretory state
|
mucosalulceration
antral mucosal hypertrophy copious gastric juice esophagitis |
|
|
Misoprostal can cause this side effect
|
diarrhea
|
|
|
When should gastric pH & serum gastrin be measured?
|
gastric erosions not associated with RX or gastric tumors
|
|
|
When should ABs be added in for gastric ulcerations
|
shock
GI barrier dysfunction |
|
|
Why do dogs with MCT have low gastrin levels
|
Histamine is causing the gastric acid release and not gastrin
|
|
|
If gastric pH <3 and increased gastrin levels suggestive of
|
gastrinoma
|
|
|
TX of gastric ulcers
|
TX underlying cause
ensure hydration and blood Q Watch K due to vomiting H2 blockers proglumide (blocks gastrin) PGE analogues H/K AtPase inhibitors |
|
|
These two medication swill directly decrease gastric acid secretion and have been used to TX gastrinomas
|
octereotide (somatostatin analoge)
omeprazole (K/H ATPase inhibitor) |
|
|
For dogs with stomach ulcers, what medication is generally started and what is added on if first isn't working
|
H2 blockers
omeprazole |
|
|
Misoprostal can cause this side effect
|
diarrhea
|
|
|
When should ABs be added in for gastric ulcerations
|
shock
GI barrier dysfunction |
|
|
Misoprostal and H2 blockers can help prevent against formation of ulcers from these medications, but not these
|
NSAID
Corticosteriods |
|
|
What mediations should be used to help prevent ulcers from Prednisone
|
Sucralfate
|
|
|
How dose histamine from MCT cause vomiting and gastric acid secreation?
|
chemoreceptor trigger zone (CRTZ)
histamine causes direct incresase in gastric acid secretion |
|
|
How should histamine from MCT be TX
|
corticosteriods for the tumor
H2 blockers to decrease central and peripheral histamine effects |
|
|
When is SX implemented for gastric ulcers
|
Non-healing
Large ulcers perforated |
|
|
What physiological changes occur with GDV
|
caval obstructin
decreases blood Q to heart results in hypovolemic shock |
|
|
Cause of GDV
|
No singe cause
Lg breed with deep chest Possible Abn electrical activing and gastric emptying Possibly length of hepatosplenic ligament |
|
|
C/S of GDV
|
Non-productive retching
salivation Abd distention wealkness collapse |
|
|
With radiographs difference between gastric dillitation vs volvulus
|
dillation- gas distention with gas in fundus
volvulus - band of soft tissue with pylorus located dorsally |
|
|
Labratory changes with GDV
|
increased Hct
metabolic acidosis hypokalemia coagulation px - DIC |
|
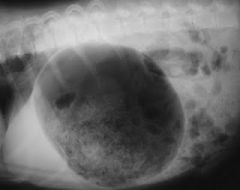
|
gastric dillitation - no volvulus
|
|
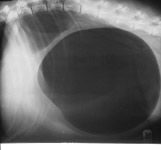
|
GDV
|
|
|
PE findings for possible GDV
|
ABD distention
tympany tachycardic pale mm |
|
|
TX in general for GDV
|
Fluid support
gastric decompression AB Cardiac arrhythmias |
|
|
Fluid support for GDV
|
shock therapy 60-90 mls/kg/hr crystaloids
colloids |
|
|
How is gastric decompression performed for GDV?
|
may need sedation - butorphanol:
OG tube 16G catheter - trocharize (followed by OG tube) |
|
|
PE findings for possible GDV
|
ABD distention
tympany tachycardic pale mm |
|
|
What about AB and steriods for GDV?
|
Cephalsporin and fluoroquinolone
Prednisone sodium succinate Dex SP 10 mg/kg IV |
|
|
TX in general for GDV
|
Fluid support
gastric decompression AB Cardiac arrhythmias |
|
|
What has lipid peroxidation and chelate iron medications helped with for GDV
|
decrease mortality(experimentally)
best given before untwisting torsion |
|
|
Fluid support for GDV
|
shock therapy 60-90 mls/kg/hr crystaloids
colloids |
|
|
What arrythmias are common for GDV
Occur in 40% of patients |
VPCs and ventricular tachycardia
|
|
|
How is gastric decompression performed for GDV?
|
may need sedation - butorphanol:
OG tube 16G catheter - trocharize (followed by OG tube) |
|
|
When should arrhythmias be treated?
|
associated with weakness or syncope
HR>150 bpm |
|
|
What about AB and steriods for GDV?
|
Cephalsporin and fluoroquinolone
Prednisone sodium succinate Dex SP 10 mg/kg IV |
|
|
TX of cardiac arrythmias
|
TX underlying acid/base, lyte, and hemostatic dz
Lidocaine 1-2 ml/kg IV bolus or as CRI |
|
|
What has lipid peroxidation and chelate iron medications helped with for GDV
|
decrease mortality(experimentally)
best given before untwisting torsion |
|
|
Mortality rate of GDV
|
15%
>30 if resection or spleenectomy |
|
|
What arrythmias are common for GDV
Occur in 40% of patients |
VPCs and ventricular tachycardia
|
|
|
When should arrhythmias be treated?
|
associated with weakness or syncope
HR>150 bpm |
|
|
TX of cardiac arrythmias
|
TX underlying acid/base, lyte, and hemostatic dz
Lidocaine 1-2 ml/kg IV bolus or as CRI |
|
|
Mortality rate of GDV
|
15%
>30 if resection or spleenectomy |
|
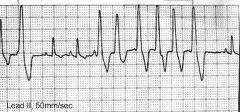
|
ventricular tachycardia
|
|
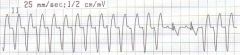
|
ventricular tachycardia
|
|
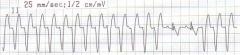
|
ventricular tachycardia
|
|
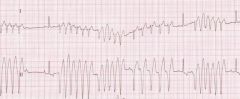
|
ventricular tachycardia
|
|
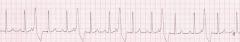
|
ventricular premature contractions (VPCs)
|
|
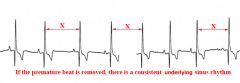
|
VPC
|
|
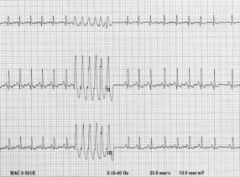
|
VPCs
|
|
|
This disease is classified according to the cellular infiltrat &, architecture abnormalities.
Very common in dogs |
chronic gastritis
|
|
|
This is the most common mild form of chronic gastritis (K9 and Fel)
Etiology? |
superficial lymphoplasmacytic gastritic with lymphoid hyperplasia.
Etiology rarely found |
|
|
What are diseases that should be R/O that can cause chronic gastritis
|
systemic disease
RX induced FB parasties (Physalloptera) Fungal - rare |
|
|
Once systemic, fungal, RX etc are R/O for chronic gastritis - what are you generally left with for DDx
|
dietary intollerance
dietary allergy occult parasitism |
|
|
This disease is classified according to the cellular infiltrat &, architecture abnormalities.
Very common in dogs |
chronic gastritis
|
|
|
Clinical signs of chronic gastritis
|
chronic vomiting of food or bile
+/- weight loss, anorexia, melena hematemesis |
|
|
This is the most common mild form of chronic gastritis (K9 and Fel)
Etiology? |
superficial lymphoplasmacytic gastritic with lymphoid hyperplasia.
Etiology rarely found |
|
|
Diagnosing Chronic gastritis
|
MDB- normal
- increased Eos for parasites/dietary issues or MCT ABD rads - normal Endoscopy **** |
|
|
What are diseases that should be R/O that can cause chronic gastritis
|
systemic disease
RX induced FB parasties (Physalloptera) Fungal - rare |
|
|
On endoscopy for chronic gastritis, if seeing large amts of bile stained fluid is suggestive of
|
duodenalgastric reflex
|
|
|
Once systemic, fungal, RX etc are R/O for chronic gastritis - what are you generally left with for DDx
|
dietary intollerance
dietary allergy occult parasitism |
|
|
On endoscopy for chronic gastritis, if seeing large amounts of clear fluid is suggestive of
|
xs. secreation of gastric acid
|
|
|
Clinical signs of chronic gastritis
|
chronic vomiting of food or bile
+/- weight loss, anorexia, melena hematemesis |
|
|
On endoscopy for chronic gastritis, if seeing irregular masses in pyloric outflow tract is suggestive of
|
Pythiosis (southern states)
|
|
|
Diagnosing Chronic gastritis
|
MDB- normal
- increased Eos for parasites/dietary issues or MCT ABD rads - normal Endoscopy **** |
|
|
With endoscopy, how many biopsies are taken and from where?
|
3 from each region:
pylorus fundus cardia |
|
|
On endoscopy for chronic gastritis, if seeing large amts of bile stained fluid is suggestive of
|
duodenalgastric reflex
|
|
|
On endoscopy for chronic gastritis, if seeing large amounts of clear fluid is suggestive of
|
xs. secreation of gastric acid
|
|
|
On endoscopy for chronic gastritis, if seeing irregular masses in pyloric outflow tract is suggestive of
|
Pythiosis (southern states)
|
|
|
With endoscopy, how many biopsies are taken and from where?
|
3 from each region:
pylorus fundus cardia |
|
|
Parasitic chronic gastritis:
Ollulanus tricuspis is a.. |
microscopic worm (<1 mm)
Feline stomach cat to cat transmission via vomit |
|
|
How is Ollulanus tricuspis DX?
|
evaulation of gastric juice, vomitus, or histology
|
|
|
TX of Ollulanus tricuspis?
|
fenbendazole 2 d maybe effective
|
|
|
How do animals acquire Physalloptera?
|
ingestionof beetles, cockroaches, lizards
|
|
|
TX of Physalloptera
|
pyrantel pamoate (Nemex)
dogs - single dose Cats - two doses |
|
|
This parasitic disease causes transmural thickening of gastric outflow tract
|
Pythium insidiosum
|
|
|
DX for Phythium insidiosum
|
special staining
culture serology PCR |
|
|
TX for Pythium insidiosum
|
Aggressive SX resection
itraconazole terbinafine TX for 2-3 months post op medically |
|
|
Prognosis for Pythium insidiosum?
|
Poor
|
|
|
When is Helicobacter associated gastritis TX?
|
The author (A. Jergens) recommends to TX only symptomatic animals with biopsy with confirmed Helicobacter and gastritis
|
|
|
Uncontrolled study showed 90% of dogs/cats responded to TX for Helicobacter associated gastritis with
|
Metronidazole
amoxicillin famotidine 70% of animals re-scoped had no evidence of Helicobactor |
|
|
With medical TX of Helicobacter - instead of cure, what might be a better way to describe what ABs do?
|
Causes a transietn suppression rather than eradication due to when TX stops, it returns.
|
|
|
What drugs maybe better long term solution to eradicate Helicobacter associated gastritis?
|
>21 day of antibiotics:
clarithromycin |
|
|
How common is lymphcytic plasamacytic gastritis of unknown cause?
|
common in K9/Fe
|
|
|
For unknown causes of lymphocytic/plasmacytic gastritis - how is he mild form TX?
|
TX with diet
hydrolized diet novel proteins |
|
|
How is food intollerance suggested for lympoplasmacitic gastritis?
|
If hydrolized diet works and re-challange with original diet
|
|
|
If hydrolized diet isn't enought for lymphocytic plasmacytic gastritis of unknown cause, what can be added
|
prednisone 1-2 mg/kg/day
taper to EOD at lowest dose |
|
|
How is moderate/severe lymphocytic plasmacytic gastritis of unknown cause TX?
|
prednisone & diet
+/- sucralfate/H2 blockers if ulcers or melena present |
|
|
If prednisone and diet are not working for lymphoplasmacytic gastritis of unknown cause, what other disease should be re-evaluated?
|
re-evaluate biopsies for
LSA |
|
|
If need to increase immunosuppression for unknown cause of lymphoplasmacytic gastritis, what medications can be used?
|
K9 - azithroprim
Fe - chlorambucil |
|
|
With eosinophillic gastritis, TX?
|
similar to lymphoplasmicitic gastritis.
diet & prednisone |
|
|
With eosinophillic gastritis, what must be R/O with cats?
|
hyperesoinophillic syndrome
|
|
|
This gastritis is associated with marked cellular infiltrate
|
atrophic gastritis
infrequent in animals, but some simalarities to people |
|
|
Atrophic gastritis results in decrease of _____ and hyperplasia of ____ which has been associated with gastric adenocarcinoma in Lundehunds
|
parietal cells
neuroendocrine cells |
|
|
How do you TX atropic gastritis?
|
TX just like Helicobacter and immunosuppressive therapy
|
|
|
This condition is ideopathic in brachycephalic dogs
|
hypertropic gastritis
|
|
|
Delayed gastric emptying and motility disorder is caused by one of these two things
|
outflow obstruction
defective propulsion |
|
|
What clinical sign should be suspicious of delayed gastric emptying & motility disorder
|
vomiting food less than 8-10 hours after ingestion
|
|
|
If puppies develope vomiting after weaning, what motility disorder should be considered?
|
pyloric stenosis
|
|
|
What are differentials for outflow obstruction (7)
|
congenital stenosis
FB hypertrophic stenosis granuloma polyps neoplasia extragastric masses |
|
|
DDX for defective Propulsion (14)
|
gastric disorder
gastritis ulcers neoplasia gastroenteritis peritonitis pancreatitis metabolic nervous inhibition dysautonomia GDV SX RX ideopathic |
|
|
Diagnosing outflow obstruction/defective propulsion?
|
MDB- fecal/triple to R/O systemic dz
Radiographs U/S Endoscopy (prior to barium) |
|
|
TX for delayed gastric emptying and motility disorder?
|
TX underlying cause
GI ulcers - medical TX pyloric stenosis/polyps/hypertrphic disorders - SX Prokinetic agents - metoclopramide, cisapride, erythomycin, or ranitidine |
|
|
This RX may only facilitate the emptying of liquids and less effective in promoting organized gastroduodenal intestinal motility than this RX.
|
metoclopramide
cisapride |
|
|
This RX is better promotion of solids
|
cisapride
|
|
|
How long should prokinetics be given to see if effective for motility dissorders
|
5-10 days
|
|
|
Which is more common benign or malignant gastric neoplasia?
|
malignant
|
|
|
This gastric neoplasia occurs at the pyloric antrum and/or lesser curvature
|
adenocarcinoma
|
|
|
These two gastric neoplasias are common at the cardia
|
leiomyoma
leiomyosarcoma |
|
|
This gastric neoplasia is diffuse
|
LSA
|
|
|
This gastric neoplasia is common in dogs
|
adenocarcinoma
|
|
|
Where do adenocarcinomas metastasize to?
|
liver and LN
|
|
|
What are the three types of presentations of adenocarcinoma
|
diffuse
rasied central ulcer polyploid |
|
|
What is the most common gastric neoplasia
|
LSA
involvment of liver, LN, SI, BM |
|
|
What is the MST for leiomyosarcoma?
|
10 months
|
|
|
What type of C/S or syndromes are seen with Leiomyosarcoma
|
paraneoplastic hypoglycemia
seizure due to insulin like growth factors |
|
|
DX gastric neoplasia
|
survey rads - WNL
US endoscopy |
|
|
How do you TX for gastric SX
|
surgery for everything but LSA
|
|
|
What gastric neoplasia have excellent prognosis
|
leiomyosarcoma
unless not localized and not able to SX removed. |
|
|
Prognosis for GI LSA
|
poor in dogs
Feline - dependent on Lg cell/Sm cell small cell - substantial remission with pred & chlorambucil Lg cell - TX with chemo & carries much poorer prognosis |

