![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
88 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What type of muscle is canine esophagus
|
all striated muscle
|
|
|
What type of muscle is the feline esophagus?
|
the distal 1/3 is smooth muscle and rest striated
|
|
|
What are generic C/S of esophageal disease?
|
regurgitation
dysphagia odynophagia repeated swallowing xs. salivation |
|
|
If get acute severe signs in young/old animal, what condition should be suspected
|
esophageal FB
|
|
|
This conditional has slowly worsening esophageal C/S and results in gastroesophageal reflux
|
hiatal defects
|
|
|
What type of muscle is canine esophagus
|
all striated muscle
|
|
|
What type of muscle is the feline esophagus?
|
the distal 1/3 is smooth muscle and rest striated
|
|
|
What are generic C/S of esophageal disease?
|
regurgitation
dysphagia odynophagia repeated swallowing xs. salivation |
|
|
If get acute severe signs in young/old animal, what condition should be suspected
|
esophageal FB
|
|
|
This conditional has slowly worsening esophageal C/S and results in gastroesophageal reflux
|
hiatal defects
|
|
|
These are 2 conditions that MC cause odynophagia
|
FB
esophagitis |
|
|
Besides megaesophagus, what two other C/S are seen with dysautonomia?
|
dilated pupils
dry MM |
|
|
How are diseases of the esophagus diagnosed (in general)
|
radiographs
endoscopy ACTH - Addison's Acetylcholine receptor Ab titier (acq MG) |
|
|
This diseases is a congenital neuromuscular disorder where the UES can't relax? Etiology?
|
cricopharyngeal dysplasia
unknown |
|
|
This disease is noted shortly after being weaning and affected animals have repeated attempts to swollow, gag, retching, and aspiration pneumonia
|
circopharyngeal dysplasia
|
|
|
How is cricopharyngeal dysphagia diagnosed?
TX? |
fluorscopy
cricopharygeal myotomy - high failure rate. medical mangement with tube feedings and caution of aspiration pneumonia |
|
|
This disease is acute or chronic inflammation of the esophagus?
|
esophagitis
|
|
|
What are some common causes of esophagitis?
|
chemical injury
reflux FB tetracycling/clindamcin - cats |
|
|
C/S of mild and moderate/severe esophagitis?
|
mild - none
mod/severe - anorexia dysphagia, extending head to swallow, red ropy blood tinged saliva |
|
|
DX esophagitis?
|
bloodwork and rads WNL
endoscopy - highly erythemic, erosions and changes in mucosal tecture |
|
|
If suspecting esophagitis and on endoscopy, if see reflux plus dillated LES this is suggestive of ?
|
hiatial disorder
|
|
|
TX for mild esophagitis?
|
dietary - small meals, low fat and high protein
|
|
|
TX for moderate/severe esophagitis?
|
sulcralfate - best
metoclopramide H2 blockers Ab if aspiration pneumonia? |
|
|
if mild esophagitis, how long do you TX?
|
1 week
|
|
|
If moderate esophagitis, how long do you TX?
|
1 month
|
|
|
What is the prognosis for esophagitis? When is it guarded?
|
good with medical TX. Guarded for stricture
|
|
|
What do you do if the esophageal FB is too big to remove orally?
|
Push into the stomach
|
|
|
This type of FB dosen't require SX removal
|
moste bone FB, but non-digestable materials will require SX removal
|
|
|
Post esophageal FB removal, what should be evaluated?
|
esophagus for esophageal perforation
|
|
|
Post esophageal FB how long should food be w/held
|
24-48 hours
|
|
|
Post esophageal FB, what oral TX should they be started on?
|
sucralfate - best
metoclopramide H2 blockers AB if aspiration |
|
|
How are small esophageal perforations TX?
|
Broad spectrum AB
|
|
|
How long dose it take for the esophagus to fibrose?
|
1-3 weeks
|
|
|
Most common cause of esophageal strictures?
|
reflux (anesthesia) or trauma
|
|
|
C/S for esophageal stricture
|
regurgitation
dysphagia ptyalism Bettwer with liquid meals, ravenous appetite with weight loss. |
|
|
DX esophageal stricture
|
rads - WNL
barium - stenosis most only have one stricutre |
|
|
TX for esophageal stricutre
|
ballon dilation
|
|
|
What are some causes of congenital megaesophagus?
|
possibly familial
rare in cats |
|
|
What is the etiology of ideopathic ME?
|
Unknown - possible diffuse neuromuscular dsfxn
|
|
|
MG accounts for what % of ME acquired cases?
|
25%
|
|
|
What is dysautonomia?
|
Generalized autonomic neuropathy.
|
|
|
What is autonomic innervation?
|
innervates the blood vessels
heart smooth muscle viscera glands & controls their involuntary fxn |
|
|
What are other causes besides ideopathic and congenital ME
|
FB
stricture vascular ring anomolie esophagitis |
|
|
What are clinical signs of ME?
|
regurgitation
weight loss aspiration pneumonia |
|
|
If patient has ME and signs of pain and stiff gate?
|
polymyositis
|
|
|
If patient has ME and generalized weakness
|
neuromuscular disease
|
|
|
If patient has ME and GI signs?
|
consider lead or Addisons
|
|
|
How is ME diagnosed?
|
Radiographs - barium if needed
|
|
|
Clinical signs of dysautonomia (10)
|
depression
anorexia constipation regurgitation dry mm dillated pupils elevated third eyelid decreased PLR bradycardia areflexia arus |
|
|
What is TX of megaesophagus?
|
underlying cause
supportive small frequent meals in elevated position (gruel vs. meatballs) TX pneumonia |
|
|
What medications do not work for ME due to not working on striated muscle
|
metoclopramide/cisapride
do not work |
|
|
What is the prognosis for ME?
|
With MG, progosis is 50% with TX
Otherwise poor |
|
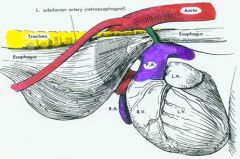
|
Persistant right aortic arch
|
|
|
What is vascular ring anomaly?
|
Congential malformations of the major arteries of the heart that entrap the intrathoracic esophagus and causes obstruction
|
|
|
What breeds are predisposed for persistent right aortic arch
|
GSD
Irish Setters |
|
|
What are C/S occur with persistent right aortic arch
|
puppies and kittens present for regurgitation
weight loss despite good appetite |
|
|
How is persistent right aortic arch diagnosed?
|
survey rads - esophageal body dilation cranial to the base of the heart
barium esophagram |
|
|
TX for persistent right aortic arch
|
surgical ligation and transection of the ligation arteriosum
|
|
|
What is the prognosis for persistent right aortic arch
|
90% improve post-op however, regurtitation may persist
|
|
|
What is an esophageal diverticula?
|
Rare
Pouchlike sacculations congenital or acquired |
|
|
What occurs to create the esophageal diverticula?
|
herniation of the mucosa through the muscularis
|
|
|
C/S of esophageal diverticula
|
regurgitation
doynophagia retching |
|
|
How are esophagus diverticula DX?
|
survey radiographs
barium esophagram |
|
|
TX for esophageal diverticula?
|
diverticulectomy - guraded progenosis b/c of complications.
small ones can be TX medically for esophagitis |
|
|
This is a communication obetween the esophagus and the respiratory tract
|
esophageal fistula
rare |
|
|
C/S of esophageal fistula
|
coughing
dyspnea |
|
|
DX of esophageal fistula
|
survey radiographs - pneumonia
barium esophagram for definitive diagnosis |
|
|
TX for esophageal fistula
|
SX correction
guarded prognosis if SX complications |
|
|
What are the common neoplasias of K9 esophagus?
|
fibrosarcoma
osteosarcoma |
|
|
C/S of esophageal neoplasia
|
esophageal obstruction
|
|
|
DX of esophageal neoplasia
|
barium esophagram
scope wih biopsy for definitive diagnosis |
|
|
TX for esophageal neoplasia
Prognosis: - malignant - benign |
Doramectin for spiracera lupi granulomas - K9
Chemo/radioation/SX are pallative for malignant Benign tumors have good prognosis with SX resection |
|
|
What are the two forms of hiatial hernia?
|
sliding - cranial displacement of distal esophagus and stomach into the mediastinum through the esophageal hiatus
periesophageal hiatal hernia - cranial displacement of a portion of he stomachinto the midiastinum through a defect next to the esophagus hiatus. |
|
|
What is thought to be the most common cause of hiatal hernias? Other causes?
|
MC probably congenital
trauma |
|
|
C/S of hiatal hernia?
|
occurs soon after weaning
|
|
|
DX of hiatal hernia
|
survey radiographs
barium esophagram |
|
|
TX for hiatal hernia
|
SX for large defects
medical TX fsimial for esophagitis for smaller defects (sucralfate, H2 blockers, metoclopramide) |
|
|
C/S of esophageal neoplasia
|
esophageal obstruction
|
|
|
DX of esophageal neoplasia
|
barium esophagram
scope wih biopsy for definitive diagnosis |
|
|
TX for esophageal neoplasia
Prognosis: - malignant - benign |
Doramectin for spiracera lupi granulomas - K9
Chemo/radioation/SX are pallative for malignant Benign tumors have good prognosis with SX resection |
|
|
What are the two forms of hiatial hernia?
|
sliding - cranial displacement of distal esophagus and stomach into the mediastinum through the esophageal hiatus
periesophageal hiatal hernia - cranial displacement of a portion of he stomachinto the midiastinum through a defect next to the esophagus hiatus. |
|
|
What is thought to be the most common cause of hiatal hernias? Other causes?
|
MC probably congenital
trauma |
|
|
C/S of hiatal hernia?
|
occurs soon after weaning
|
|
|
DX of hiatal hernia
|
survey radiographs
barium esophagram |
|
|
TX for hiatal hernia
|
SX for large defects
medical TX fsimial for esophagitis for smaller defects (sucralfate, H2 blockers, metoclopramide) |
|

|
hiatal hernia
|
|
|
What three things found radiographically would make esophageal tears a differential?
|
pneumomediastinum
pneumothorax pleural effusion |
|
|
TX for esophageal tears
|
SX for large performations
Small tears - AB, fluids, and gastrotomy feeding |

