![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
104 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is Ethics? |
Ethics are a set of beliefs about what is right and wrong behavior |
|
|
What is moral code? |
A moral code is the set of rules. Or is a boundary general accepted behavior |
|
|
What is morality? |
social conventions about right or wrong Morality is the differentiation of intentions, decisions, and actions between those that are distinguished as proper and those that are improper. |
|
|
Define Virtue |
habits that incline people to do what is acceptable |
|
|
Define Vices |
habits of unacceptable behavior |
|
|
Value system |
scheme of moral values. A hierarchy of values that all moral agents possess, demonstrated by their choices.Value systems differ. One's value system is molded by one's virtues or vices. |
|
|
Define Integrity. |
Quality of being honest and adhering to strong moral principles |
|
|
Define Risk |
The product of likelihood of event times the impact of occurrence of event |
|
|
Give reasons why bad risks have increased. |
Globalization and complexity of working environment Challenge of organizations to maintain profits and revenue The heightening of the employee, shareholders, and regulatory agencies vigilance. |
|
|
What does the corporate ethics officer do? |
He is a senior level manager and he is charged with creating: an environment that encourages ethical behavior provides vision and leadership in business conduct ensures ethical procedures creates and maintains an ethical culture collects and analyzes data related to ethics develops and integrates ethics policies develops and administers ethics education and training |
|
|
Who sets the ethical standards of an organization? |
The board of directors. |
|
|
What is a code of ethics? |
The highlight of a company's key ethical issues. |
|
|
Things code of ethics should be developed with |
Employees must be involved and there input valued. Should be endorsed by the organization's leadership Continually applied to the company's decision making emphasized as part of the culture |
|
|
What does an employee ethical training entail |
Encourage employees to act ethically Principle-based decision making Demonstration of recent decisions based on principles from the code of ethics |
|
|
Ethical criteria in Employee Appraisals? |
> Treat each other fairly and with respect > Effective operation in multi-cultural enviroment > Accepting personal accountability > Continually developing themselves and others > Operating openly and honestly with partners and or shareholders |
|
|
How to create an ethical work environment? |
Have knowledgeable and potent resources available to discuss perceived unethical practices |
|
|
How can management affect employee's ethical behavior? |
> Stretching accountability for meeting goals, quotas and budgets with no wiggle room. > Failure to provide a company code of ethics and operating principles to guide them in decision making >Poor example >Failure to punish unethical behavior > Thick ethical procedure manuals can be intimidating |
|
|
Name any points that should be on a manager's checklist for ethics? |
> Is a corporate there a code of ethics > Was there any employee input when developing it. > Is the code of ethics easy to understand and concise > Easy access to code of ethics > Have all employees signed a form saying they read and understood the code of ethics. > Annual training > Feedback > Set an example by communication and practice > Do your employees believe your fair and can come to you to seek advice and counsel >Do you have a Report avenue > Are employees aware of sanctions for breaching ethics |
|
|
List the activities involved in decision making. |
1) Develop a problem statement 2) Identify alternatives 3) Evaluate and choose alternatives 4) Implement decision 5) Evaluate the results 6) Success |
|
|
Explain the process of developing a problem statement in decision making. |
> Create, a clear and concise description It should answer: > Cause of the problem > Those directly affected > Other affected > Occurrence frequency > Impact > Scale of seriousness |
|
|
How do we identify and evaluate alternatives to a problem? |
> Brainstorm alternative solutions and involve employees > Evaluate weigh laws and guidelines > Likely consequences of each alternative > Alternatives should be ethical and legal, consistent with policies and ethics, account for impact and solve the problem. |
|
|
List the philosophical theories for ethical decision making. |
1) Virtue ethics Approach 2) Utilitarian Approach 3) Fairness Approach 4) Common good approach |
|
|
Explain the virtue ethics approach to decision making and any problems it has. |
Virtue Ethics (or Virtue Theory) is an approach to Ethics that emphasizes an individual's character as the key element of ethical thinking, rather than rules about the acts themselves (Deontology) or their consequences (Consequentialism). Problems: > Problem being objective or establishing nature of virtue as circumstances matter a lot. >Not action-guiding but rather concentrates on qualities of person rather than the action |
|
|
Explain the utilitarian approach to decision making and any problems it has. |
The Utilitarian Approach assesses an action in terms of its consequences or outcomes. It strives to achieve the greatest good for the greatest number while creating the least amount of harm or preventing the greatest amount of suffering. Problems: >it's often difficult, if not impossible, to measure and compare the values of certain benefits and costs >We can not be sure if we have predicted everything. Prediction is difficult >Does not account for just if put against the greater good |
|
|
Explain the Fairness approach to decision making and any problems it has. |
The fairness or justice approach to ethics says What is ethical is what develops moral virtues in ourselves and our communities. Problems > Easy to apply personal bias > Others may consider the decision unfair. not everyone has the same ideal of fairness |
|
|
Explain the Common good approach to decision making and any problems it has. |
This approach to ethics assumes a society comprising individuals whose own good is inextricably linked to the good of the community. Problems > Consensus is difficult > Some members of the society may be required to bear greater costs than others |
|
|
How to implement the decision made? |
> Efficient, effective, timely implementation > Communication > Plan free and easy transition |
|
|
How to evaluate results of a solution? |
> Monitor results > Observe impact > Refinement |
|
|
List down places in IT where ethical issues may occur. |
> Email & Internet access monitoring > Downloads in violation of copyrights > Unsolicited email (spam) > Hackers and identity theft > Students and plagiarism > Cookies and spyware |
|
|
What is the importance of ethics in IT? |
> Educate the impact > Nature recognition > Provide tools approaches and insight |
|
|
Who is a professional? |
A person with specialized knowledge and has passed licensing requirements. Earned the right to practice through long and intensive academic preparations. |
|
|
Why are IT workers not considered professionals? |
> Often not licensed > They are not liable for malpractice |
|
|
People IT professionals may work with. |
Employers Clients Suppliers Other professionals Users Society as awhole |
|
|
What is software piracy? |
Illegally making copies of software or enabling others to access it illegally. |
|
|
What is a trade secret? |
A trade secret is a formula, practice, process, design, instrument, pattern, commercial method, or compilation of information not generally known or reasonably ascertainable by others by which a business can obtain an economic advantage over competitors or customers |
|
|
Who is considered a whistleblower? |
A person who reports unethical or illegal practices of their company. |
|
|
What is Fraud? |
Obtaining goods, services or property through deception or trickery. |
|
|
When is a person or organization considered in breach of a contract? |
When a party fails to meet the terms of a contract. |
|
|
What is misinterpretation? |
–A misrepresentation is a false statement of factor law which induces the representee to enter a contract |
|
|
Define the types of misrepresentation |
Innocent misrepresentation - it is a misrepresentation made by someone who had reasonable grounds for believing that his false statement was true Negligent misrepresentation - when the defendant carelessly makes a representation while having no reasonable basis to believe it to be true. Fraudulent misrepresentation Instance of false statement where (1) the party making the statement is aware that it is false. |
|
|
What is bribery? |
Providing money, property, or favors to someone in business or government to obtain a business advantage. |
|
|
Common ethical IT problems |
Resume inflation Inappropriate sharing of corporate info |
|
|
What is a professional code of ethics? |
A professional code of ethics states the principles and core valuesthat are essential to the work of a particular occupational group |
|
|
What are the main parts of a professional code of ethics? |
–Outlines what the professionalorganization aspires to become –Lists rules and principles by whichmembers of the organization are expected to abide |
|
|
Benefits of having a professional code of ethics |
–Improves ethical decision making –Promotes high standards of practiceand ethical behavior –Enhances trust and respect from thegeneral public –Provides an evaluation benchmark |
|
|
What is Certification? |
its an indicator of skill set, knowledge, or abilities. |
|
|
What is malpractice? |
In a legal term, malpractice is an instance of negligence or incompetence on thepart of a licensed professional, suchas a lawyer, a doctor, a dentist, or an accountant. |
|
|
What is negligence? |
hasbeen defined as not doing something that a reasonable man would do, or doingsomething that a reasonable man would not do |
|
|
What is duty of care |
refers to the obligation to protectpeople against any unreasonable harm or risk |
|
|
IT Policy components to prevent misuse include. |
Policy components include: –Defining and limiting theappropriate use of IT resources –Establishing guidelines for use ofcompany software –Structuring information systems toprotect data and information –Installing and maintaining acorporate firewall |
|
|
What acts are classified as computer crimes? |
Computer crime is an act performed by a knowledgeable computer user, sometimes referred to as a hacker that illegally browses or steals a company's or individual's private information |
|
|
List type of IT attacks |
Viruses Worms Denial of service attacks Spoofing |
|
|
What is DoS attack? |
is a cyber-attack where the perpetrator seeks to make a machine or network resource unavailable to its intended users by temporarily or indefinitely disrupting services of a host connected to the Internet |
|
|
ingress filtering vs egress filtering |
ingress filtering is a technique used to ensure that incoming packets are actually from the networks from which they claim to originate. egress filtering is the practice of monitoring and potentially restricting the flow of information outbound from one network to another |
|
|
What is spoofing? |
a spoofing attack is a situation in which one person or program successfully masquerades as another by falsifying data, thereby gaining an illegitimate advantage |
|
|
Classification of IT perpetrators |
Hacker Cracker Insider Industrial spy Cybercriminal Cyber-terrorist |
|
|
Ways to reduce vulnerability of systems |
> Security > Threat assessment on computers and network •Identify actions that address the most serious vulnerabilities •Educate users •Monitor to detect a possible intrusion •Create a clear reaction plan |
|
|
What is risk management? |
review of potential threats probability of happening and impact. |
|
|
What is a security policy? |
Identifies company's security requirements, control and sanctions needed |
|
|
Common security policy measures |
•Trade-off between –Ease of use –Increased security •Areas of concern –E-mail attachments –Wireless devices •VPN uses the Internet to relay communications but maintains privacy through security features •Additional security includes encrypting originating and receiving network addresses •Educate users about the importance of security –Motivate them to understand and follow security policy •Discuss recent security incidents that affected the organization •Help protect information systems by: –Applying strict access controls to protect data –Reporting all unusual activity |
|
|
Prevention of attacks measures |
•Implement a layered security solution –Make computer break-ins harder •Firewall–Limits network access •Antivirus software •Departing employees –Promptlydelete computer accounts, login IDs, and passwords •Carefully define employee roles •Create roles and user accounts |
|
|
Example anti-virus software |
Norton. Kaspersky , Symantec, McAfee |
|
|
Example firewall software |
Norton Personal Firewall Tiny personal firewall BlackICE Defender Personal Firewall ZoneAlarm Pro |
|
|
Roles of an intrusion detection system |
–Monitorssystem and network resources and activities –Notifiesthe proper authority when it identifies Possibleintrusions from outside the organizationMisuse from within the organization –Knowledge-basedapproach –Behavior-basedapproach –Preventattacks by blocking •Viruses•Malformedpackets•Otherthreats –Sitsdirectly behind the firewall - |
|
|
What is a honeypot |
–Provideswould-be hackers with fake information about the network–Decoyserver–Well-isolatedfrom the rest of the network Can extensively log activities ofintruders |
|
|
What is privacy? |
Privacy is the ability of an individual or group to seclude themselves, or information about themselves, and thereby express themselves selectively. |
|
|
What is the right of privacy? |
Right to left alone The right to privacy is an element of various legal traditions to restrain government and private actions that threaten the privacy of individuals |
|
|
Why Right to privacy? |
–Protectionfrom unreasonable intrusion upon one’s isolation –Protectionfrom appropriation of one’s name or likeness –Protection from unreasonablepublicity given to one’s private life –Protection from publicity thatunreasonably places one in a false light before the public |
|
|
Identify key privacy issues |
•Identity theft •Customer profiling •Need to treat customer dataresponsibly•Workplace monitoring •Advanced surveillance techniques |
|
|
Four ways to limit or even stop thedeposit of cookies on hard drives |
–Set the browser to limit or stopcookies –Manually delete them from the harddrive –Download and install acookie-management program –Use anonymous browsing programsthat don’t accept cookies |
|
|
Manager’s Checklist for Treating Consumer Data Responsibly |
> Data privacy policy > Data viewable by user >Choice to opt out or in data policy >Collect only needed info for your service > User can view or edit data > Inform of info usage for research and marketing > There is a responsible part for policy implementation |
|
|
What is freedom of expression? |
Freedom of expression is the right of every individual to hold opinions without interference and to seek, receive and impart information and ideas through any media and regardless of frontiers |
|
|
Free speech includes: |
–Nonverbal, visual, and symbolicforms of expression –Right to speak anonymously |
|
|
Things not protected by free speech |
–Obscene speech –Defamation –Incitement of panic - Sedition |
|
|
What forms of expression are considered obscene |
–Average person finds the workagainst the moral or ethical principles of a society –Work depicts or describes sexualconduct in an offensive way –Lacks serious literary, artistic,political, or scientific value |
|
|
What is defamation |
Publication of a statement ofalleged fact that is–False –Harms another person •Slander–Oral defamatory statement •Libel–Written defamatory statement |
|
|
Key issues of Freedom of expression |
•Controlling access to informationon the Internet •Anonymity •Defamation •Hate speech •Pornography |
|
|
Popular Internet filters |
–ContentProtect–CYBERsitter–NetNanny–CyberPatrol–HateFilter |
|
|
Manager’s Checklist for Handling Freedom of Expression in the Workplace |
> Is there a written data privacy policy > limit access to non business websites > inappropriate of anonymous email remailers > detection of anonymous remailers > Prohibit view or sending or pornography > Monitor > Tell employees what to do if they receive hate mail or pornography |
|
|
What is intellectual property? |
Intellectual property refers to creations of the mind: inventions; literary and artistic works; and symbols, names and images used in commerce |
|
|
What is WIPO? |
The World Intellectual Property Organization. WIPO was created in 1967 "to encourage creative activity, to promote the protection of intellectual property throughout the world |
|
|
How is intellectual property protected? |
1) Copyright laws - authored works 2) Patents - inventions 3) Trade secret laws - trade secrets |
|
|
What is the DMCA? |
The Digital Millennium Copyright Act (DMCA) is a United States copyright law that implements two 1996 treaties of the World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO) |
|
|
What is a non-disclosure agreement? |
A non-disclosure agreement (NDA), also known as a confidentiality agreement (CA), confidential disclosure agreement (CDA), proprietary information agreement (PIA) or secrecy agreement (SA), is a legal contract between at least two parties that outlines confidential material, knowledge, or information that the parties wish to share with one another for certain purposes, but wish to restrict access to or by third parties |
|
|
What is a non-compete agreement? |
a non-compete clause (often NCC), or covenant not to compete (CNC), is a clause under which one party (usually an employee) agrees not to enter into or start a similar profession or trade in competition against another party (usually the employer) |
|
|
Key issues in Intellectual property. |
–Plagiarism: Stealing someone’s idea and passing off on someone’s ideas or words as one’s own –Reverse engineering taking something apart in order to –Understand it –Build a copy of it –Improve it –Open source code –Competitive intelligence •Gathering of legally obtainable information –Cybersquatting is the act of registering a popular Internet address--usually a company name--with the intent of selling it to its rightful owner |
|
|
Common Plagiarism detection systems |
iThenticate Turnitin MyDropBox Glatt Plagiarism services EVE plagiarism detection |
|
|
A Manager’s Checklist for Running an Ethical Competitive IntelligenceOperation |
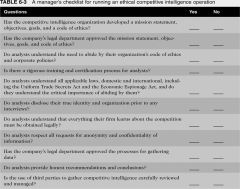
|
|
|
What is a trademark? |
a recognizable sign, design, or expression which identifies products or services of a particular source from those of others, although trademarks used to identify services are usually called service marks •Trademark law –Trademark’sowner has the right to prevent others from using the same mark |
|
|
Ways to prevent cybersquatters? |
–Registerall possible domain names•.org•.com•.info •Internet Corporation for AssignedNames and Numbers (ICANN)–Currenttrademark holders are given time to assert their rights in the new top-leveldomains before registrations are opened to the general public |
|
|
What is software quality? |
Degreeto which software meets the needs of users |
|
|
Software defect |
–Couldcause a system to fail to meet users’ needs–Impactmay be trivial or very serious–Patchesmay contain defects |
|
|
Quality management |
define, measure and refine the quality of the development process and products |
|
|
What is product liability? |
Product liability is the area of law in which manufacturers, distributors, suppliers, retailers, and others who make products available to the public are held responsible for the injuries those products cause |
|
|
What is Strict liability? |
Strict liability is the imposition of liability on a party without a finding of fault (such as negligence or tortious intent). The claimant need only prove that the occurrance and the defendant's product was responsible. |
|
|
Defenses against strict liability |
–Doctrineof supervening event –Governmentcontractor defense –Expiredstatute of limitations |
|
|
Negligence |
Is failure to do what a reasonable person would do, or doing what a reasonable person would not do |
|
|
Defense of negligence may include |
•Legal justification for the allegedmisconduct •Demonstrate that the plaintiffs’own actions contributed to injuries. |
|
|
Warranty |
–Assurancea buyer gets that a product meets certain standards of quality–Expresslystated –Impliedby lawtml> |
|
|
Capability Maturity Model Integration for Software |
CMMI, is a process model that provides a clear definition of what an organization should do to promote behaviors that lead to improved performance. With five “Maturity Levels” The CMMI principal is that “the quality of a system or product is highly influenced by the process used to develop and maintain it”. 1) Initial 2) Managed 3) Defined 4) Quantitatively managed 5) Optimized |
|
|
Redundancy |
–Provisionof multiple interchangeable components to perform a single function –Inorder to cope with failures and errors |
|
|
N-version programming |
–Formof redundancy–Involvesthe execution of a series of program instructions simultaneously by twodifferent systemsUsesdifferent algorithms to execute instructions that accomplish the same result |
|
|
Reliability |
–Probability of a component orsystem performing without failure over its product life |
|
|
ISO 9000 standard |
–Guide to quality products,services, and management–Organization must submit to anexamination by an external assessor –Requirements: •Written procedures for everythingit does •Follow those procedures •Prove to the auditor theorganization fulfilled the first two requirements |

