![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
20 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
articulation or joint
|
A place where two bones come together.
|
144
|
|
|
The terms used for degree of motion for a joint include:
|
synarthrosis-nonmovable joint
amphiarthrosis-slighly movable joint diarthosis-freely movable joint |
144
|
|
|
Define and list examples of:
Fibrous joint |
The bones that are united by fibrous tissue and exhibit little or no movement.
Sutures between the skull, between tooth and skull, and the distal end of the ulna and radius. |
144
|
|
|
Define and list examples of:
Cartilaginous Joints |
Two bones united by cartilage. Only slight movement can ocur at these joints.
Ribs and sternum. |
145
|
|
|
Synovial Joint
|
Freely movable joints that contain synovial fluid in a cavity surrounding the end of articulating bones.
Most joints of the appendicular skeleton are large, synovial joints, whereas many of the joints that unite the bones to the axial skeleton are not. |
145
|
|
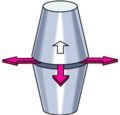
List the type of joint and some examples
|
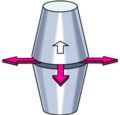
Plane Joint
Between ribs and vertebrae Between carpals, metatarsals, tarsals Between sacrum and sacrum |
|
|
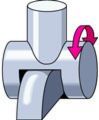
List name of joint and some examples
|
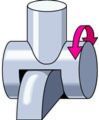
Saddle joint
carpal and metacarpal of thumb between carpals between sternum and clavicle |
|
|
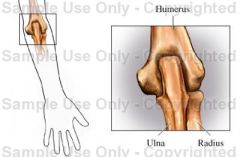
List name of joint and some examples
|
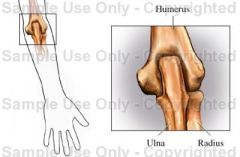
Hinge Joint
Humerus, ulna, and radius femur and tibia between phalanges talus, tibia, and fibula |
|
|

List name of joint and some examples
|
Pivot joint
Atlas and axis Radius and ulna |
|
|

List name of joint and some examples
|
Ball-and-Socket
Coxa and femur Scapula and humerus |
|
|

List name of joint and some examples
|

Ellipsoid Joint
atlas and occipital bone metacarpals/tarsals and phalanges radius and carpals mandible and temporal bone |
|
|
|
abduction
|
Movement away from the median or midsagittal plane
|
|
|
|
adduction
|
The movement toward the median plane.
|
|
|
|
Pronation and supination
|
The elbow flexed at a 90-degree angle. Pronation is rotation of the forearm so that the palm is down, and supination is rotation of the forearm so that the palm faces up.
|
|
|
|
Eversion
|
Turning the foot so that the plantar surface faces laterally
|
|
|
|
inversion
|
Turning the foot so that the plantar surface faces medially.
|
|
|
|
protraction and retraction
|
Protraction is a movement in which a structure, such as a mandible, glides anteriorly. In retraction, the structure glides posteriorly.
|
|
|
|
Excursion
|
The movement of a structure to one side or the other, such as in moving the mandible from side to side.
|
|
|
|
flexion
|
movement anterior to coronal plane.
|
|
|
|
extension
|
movement posterior to the coronal plane.
|
|

