![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
20 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Arterial supply of breast |
Internal thoracic artery Lateral thoracic artery Superior Thoracic artery |
|
|
Venous drainage of breast |
Axillary vein Internal thoracic vein , superficial veins Posterior intercostal vein,deeps veins |
|
|
Nerve supply |
2nd to 6th nerves |
|
|
Middle ear Arteries |
Anterior tympanic branch of maxillary artery Posterior tympanic branch of posterior auricular artery Ascending pharyngeal arteries |
|
|
Veins of middle ear |
Pterygoid venous plexus Superior petrosal sinus |
|
|
Lymph of middle ear |
Rwtropharyngeal lymph node Parotid lymph node |
|
|
Nerve ,ear |
Tympanic branch of glossopharyngeal nerve Facial nerve Mandibular nerve |
|
Ear
|
Location - petrous part of temporal bone Cube like Connection, nasopharynx-eustachian tube Mastoid Antrum-aditus Parts-tympanic cavity proper,epitynpanic recess Boundaries - Contents 3 bone-malleus,incus, stapes 2muscles-tensor tympani,stapedius 2Nerve-chorda tympani, tympanic plexus Arterial Venous Lymph Nerves Clinical-otitis media Respiratory tract infection,to middle ear thruu pharyngotympanic tube
|
|
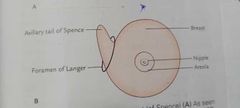
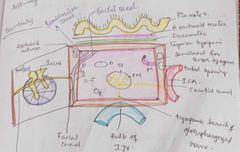
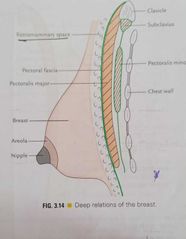
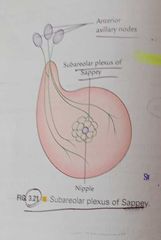
Breast |
Location -superficial fascia of pectoral region, axillary tail of spense ,pierces deep fascia. Foramen of langer-aperture Extent vertically,2 To 6 ribs H- lateral border of sternum ,mid axillary line
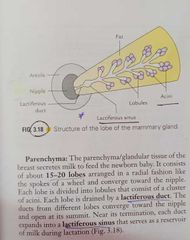
Relations - 3 muscles, pectoralis major ,external oblique,Serratus Anterior Structure - skin -nipple, areola Stroma- suspensory ligaments of Cooper Parenchyma - lactiferous ducts
Arterial- internal thoracic artery Lateral thoracic artery Superior Thoracic artery
Veins Axillary vein Internal thoracic vein, superficial Posterior intercostal veins Deep veins, all three Nerve 2-6 intercostal nerves
*Secretion of milk from breast is not under neural control, prolactin
Lymph
Axillary lymph nodes Internal mammary nodes Cephalic Supraclavicular Posterior intercostal nodes
Applied+
Breast cancer, Hard painless lump Loss of mobility of breast Retraction of nipple Arises from epithelial cells of lactiferous ducts Peau d orange , obstruction of superficial lymphatics
Krukenbergs tumor- inferomedial quadrant ,subperitoneal lymph plexus ,2dry tumor if ovary
Development-
Milkline /Schultz 4th week Axilla to groin extends
Pectoral region Defects Polythelia Polymastia ,more than 1 Gynecomastia,
|
|
M |
G |
|
A |
C |
|
S |
S |
|
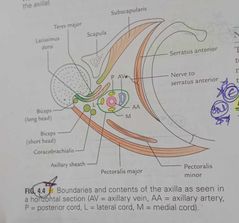
Axilla |
Boundaries Apex-passage bln neck and axilla, infront by clavicle,behind by scapula, medially outer border of 1st rib, axillary artery and brachial plexus enter axilla,through this,cervicoaxillary canal Base,lower end of axilla,directed downward. Anterior axillary fold, pectoralis major Posterior axillary fold,lattismus dorsi-teres major Anterior wall Pectoralis major, minor,subcalvius Posterior wall Subscapularis,latiismus dorsi,teres major Medial wall Upper 4/5ribs Lateral wall Biceps brachii in bicipital groove, corachobrachialis,short head of biceps brachii Contents Axillary artery,branches Axillary vein,tributaries Cords of brachial plexus Axillary lymph nodes Long thoracic and intercostobrachial nerves |
|
|
Supination and pronation |
For performing skilled movements When elbow semiflexed in midprone position,palm is turned Upward in supination Downward in pronation Beggars supinate Kings pronate These are rotatory movements of forearm Occur at Superior and inferior radio ulnar joints around vertical axis This axis is oblique, Passes from Head of radius above Styloid process of ulna below This axis is not stationary Moves, Forward and medially during supination Backward and laterally during pronation Supination, Radius and ulna lie parallel to each other Pronation, Rotation of lower end of radius along with articular disc on head of ulna So,lower end of radius ,crosses infront of lower end of ulna Supination is more powerful than pronation Antigravity movement Performed by powerful muscle,biceps brachii Pronation done by less powerful muscles,pronator quadratus and pronator teres |
|
|
Rotator cuff, Dynamic stabiliser of shoulder joint |
Blending together of SITS Supraspinatus Infraspinatus Teres minor Subscapularis Around joint capsule Tone of rotator cuff muscles,grasp head of humerus,pull it medially, To hold it against smaller,shallow glenoid cavity Also helps head of humerus ,rotating against glenoid fossa,during joint motion |
|
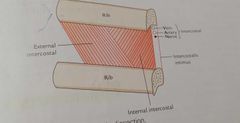
Typical intercostal space |
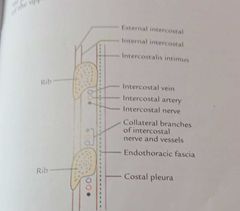
Space bln 2 adjacent ribs 11 total 3-6 are typical , bcz blood n nerve supply of these are confined only to thorax
Content of typical spaces
1.3 intercostal muscles, External intercostal Internal intercostal Innermost intercostal 2. Intercostal nerves 3.intercostal arteries 4.intercostal veins 5.intercostal lymph vessels and nodes
Plane of neurovascular bundle in intercostal space Internal intercostal,innermost intercostal Arranged,above downward Intercostal Vein Artery Nerve |
|
|
Carotid traingle |
A triangle of anterior triangle of neck So called because it contains all carotid arteries, Internal carotid,common carotid n external carotid Boundaries Superiorly, Post. Belly of digastric Anteroinferiorly, Superior belly of omohyoid Posteriorly, Ant. Border of sternocleidomastoid Roof Investing layer of deep cervical fasica, Superficial fascia over roof contains,platysma,facial nerve,transverse cervical nerve Floor, Thyrohyoid, Hyoglossus, Middle constrictor, Inferior constrictor Contents Carotid arteries, Common c. Internal c. External c. Internal jugular vein 3 cranial nerves Vagus, straight Spinal accessory,left Hypoglossal,rt Carotid sheath Ansa cervicalis Ascending pharyngeal arteries Deep cervical lymph nodes Clinical, Carotid tubercle, Common carotid ar. Compressed against transverse process of 6 cervical vertebrae Carotid pulse, Common carotid artery Strongest pulses in body,routinely checked Absense of cardiac pulse,cardiac arrest |
|
|
Lateral wall of nose |
Lateral wall of nose, contains shelf like projections called conchae,increase surface area and for effective air conditioning of inspired air
Skeleton of lateral wall, partly bony,partly Cartilaginous and partly soft tissue
Bones
Nasal, Frontal process of maxilla, Lacrimal, Conchae and labyrinth of ethmoid, Inferior nasal concha, Platine, Sphenoid,
Cartilages
Lateral nasal cartilage Major alar cartilage 3-4 tiny cartilages of ale
Conchae,curved bony projections, directed downward medially
Space below conchae called meatus labyrinth 2. Inferior, independent bone
Meatus, Passage beneath overhanging conchae,
Inferior,largest ,lies beneath inferior concha
Middle, lies below middle concha
Ethmoidal bulla,round elevation Hiatus semilunaris,deep semicircular Sulcus
H.s Ethmoidal sinus,behind F.A.S 1. Superior and middle , projections of medial surface of ethmoidal labyrinth2. Inferior, independent boneMeatus,Passage beneath overhanging conchae,Inferior,largest ,lies beneath inferior conchaMiddle, lies below middle conchaEthmoidal bulla,round elevationHiatus semilunaris,deep semicircular SulcusOpening of frontal air sinus,ant. Part of H.sEthmoidal sinus,behind F.A.SMaxillary,post. Part of H.SSuperior,smallestSphenoethmoidal recess,Traingular fossa,Just above sup. ConchaReceives sphenoidal air sinusArter.Ant. Ethmoidal,FacialSphenopalatineGreater palatine V Ant. Facial veinMiddle. pterygoid plexusPost. Pterygoid plexusN.Anterior ethmoidalPost. Sup. Lat. Nasal branchesAnt. Sup. Alveolar nerveNasal br. Of palatine nerve Maxillary,post. Part of H.S
Superior,smallest
Sphenoethmoidal recess, Traingular fossa, Just above sup. Concha Receives sphenoidal air sinus
Arter. Opening of frontal air sinus,ant. Part of H.s Ethmoidal sinus,behind F.A.S
Maxillary,post. Part of H.S
Superior,smallest
Sphenoethmoidal recess, Traingular fossa,Just above sup. Concha
Receives sphenoidal air sinus
Arter Ant. Ethmoidal, Facial Sphenopalatine Greater palatine
V Ant. Facial vein Middle. pterygoid plexus Post. Pterygoid plexus
N.
Anterior ethmoidal Post. Sup. Lat. Nasal branches Ant. Sup. Alveolar nerve Nasal br. Of palatine nerve
Littles area Anteroinferior part of nasal septum Highly vascular Ant. Ethmoidal,sphenopalatine, greater palatine,sup. Labial - anast. Kisselbechs plexus Epistaxis,bleeding of nose Trauma, hypertension
|
|
|
Parotid gland 6.diagrams 1.Masster , digastric, sternocleidomastoid,ext. Acoustic meatus 2. Horizontal section 3.relations 4,5,6 structures within parotid |
Int.
Largest salivary gland
Loc. Below,external acoustic meatus Bln ramus of mandible n sternocleidomastoid Ant. Overlap masseter
Capsule,
Investing layer of deep cervical facia ,forms capsule Auricular nerve Fascia splits and encloses parotid gland
Superior lamina,thick and adherant to gland, Deep lamina, thin and attached to zygomatic arch
Portion of deep lamina , extend bln styloid process and mandible - thickened forms stylomandibular ligament
Ext. Features
3 sided pyramid Apex,downward 4 surfaces , superior, superficial,anteromedial,posteromedial 3 borders,ant.post.medial
Relations,
Apex, post.belly of digastric Cervical brach of facial nerve 2 div.of retromandibular nerve
Sup. Surface,
Sup. Temporal vessels Auriculo temporal nerve Ext. Acoustic meatus Post. Surface of TMJ
Superf.
Skin Supf. Fascia Deep parotid lymph nodes
Ant.medial
Ramus of mandible Masster Med. Pterygoid Lat. Surface of TMJ
Post.medial
Mastoid process Styloid process
Borders
Ant.
Terminal branches of f. Nerve Parotid duct Transverse facial vessels
Post. Border Sep. Supf. Surface to post.medial surface
Med.border
Sep. Ant.medial to post.medial
Structures within parotid,
Facial nerve Retromandibular vein ECA
Art. ECA EJV,IJV
Auriculotemporal - Sensory Retromandibular vein ECAArt.ECAEJV,IJVN.Auriculotemporal - SensorySymp. - vasomotor ,middle meningeal arteryPar.Secretomotor Retromandibular vein ECAArt.ECAEJV,IJVN.Auriculotemporal - SensorySymp. - vasomotor ,middle meningeal arteryPar.Secretomotor Retromandibular vein ECAArt.ECAEJV,IJVN.Auriculotemporal - SensorySymp. - vasomotor ,middle meningeal arteryPar.Secretomotor Retromandibular vein ECAArt.ECAEJV,IJVN.Auriculotemporal - SensorySymp. - vasomotor ,middle meningeal arteryPar.Secretomotor Retromandibular vein ECAArt.ECAEJV,IJVN.Auriculotemporal - SensorySymp. - vasomotor ,middle meningeal arteryPar.Secretomotor Retromandibular vein ECAArt.ECAEJV,IJVN.Auriculotemporal - SensorySymp. - vasomotor ,middle meningeal arteryPar.Secretomotor Retromandibular vein ECAArt.ECAEJV,IJVN.Auriculotemporal - SensorySymp. - vasomotor ,middle meningeal arteryPar.Secretomotor Retromandibular vein ECAArt.ECAEJV,IJVN.Auriculotemporal - SensorySymp. - vasomotor ,middle meningeal arteryPar.Secretomotor
N.Auriculotemporal - SensorySymp. - vasomotor ,middle meningeal arteryPar.Secretomotor Symp. - vasomotor ,middle meningeal artery
Par. Secretomotor |
|
|
Median nerve |
Root value, C5- T1 Lateral root,medial root Medial root crosses in front of 3 rd part of axillary artery to unite with lateral root In axilla, Median nerve lies lateral to 3 rd part of axillary artery Enters arm at lower border of teres major In arm Intially, Median nerve lies lateral to brachial art. Crosses infront of art. At midhumerus After crossing,run downward to enter cubital fossa In cubital fossa Median nerve lies medial to brachial artery n tendon of biceps brachi Here,it is covered by bicipital aponeurosis,which seperate it from median cubital vein In cubital fossa, muscular branches Supply all flexors , except FCU Leaves cubital fossa,passing bln 2 heads of pronator teres Gives off ant. Interosseous nerve Purely motor, Supply FPL,FDP(later 1/2 ), pronator quadratus Forearm, Passes downward behind,tendinous arch bln 2 heads of FDS In midforearm, Gives muscular branches FDS Before entering carpel tunnel,gives off FCR,PL,FDS,except FCULeaves cubital fossa,passing bln 2 heads of pronator teresGives off ant. Interosseous nerve Purely motor,Supply FPL,FDP(later 1/2 ), pronator quadratusForearm,Passes downward behind,tendinous arch bln 2 heads of FDS In midforearm,Gives muscular branches FDS Before entering carpel tunnel,gives off Palmar cutaneous branch,passes sup. To flexor retinaculum,supply thenar eminence and lateral part of palmEnters pass deep to FR,carpal tunnel, lies Sup. To FDS,FDP,FPLIn palm Flattens at distal border of FR, 2 divisions,Medial and lateralLateral gives recurrent branch ,curls up and supply thenar eminenceExpt. Deep head of FPBMedial div. 2 palmar digital nerves Lateral 3 1/2 1 st and 2 nd lumbricals FDS,except FCULeaves cubital fossa,passing bln 2 heads of pronator teresGives off ant. Interosseous nerve Purely motor,Supply FPL,FDP(later 1/2 ), pronator quadratusForearm,Passes downward behind,tendinous arch bln 2 heads of FDS In midforearm,Gives muscular branches FDS Before entering carpel tunnel,gives off Palmar cutaneous branch,passes sup. To flexor retinaculum,supply thenar eminence and lateral part of palmEnters pass deep to FR,carpal tunnel, lies Sup. To FDS,FDP,FPLIn palm Flattens at distal border of FR, 2 divisions,Medial and lateralLateral gives recurrent branch ,curls up and supply thenar eminenceExpt. Deep head of FPBMedial div. 2 palmar digital nerves Lateral 3 1/2 1 st and 2 nd lumbricals Palmar cutaneous branch,passes sup. To flexor retinaculum,supply thenar eminence and lateral part of palm Leaves cubital fossa,passing bln 2 heads of pronator teresGives off ant. Interosseous nerve Purely motor,Supply FPL,FDP(later 1/2 ), pronator quadratusForearm,Passes downward behind,tendinous arch bln 2 heads of FDS In midforearm,Gives muscular branches FDS Before entering carpel tunnel,gives off Palmar cutaneous branch,passes sup. To flexor retinaculum,supply thenar eminence and lateral part of palmEnters pass deep to FR,carpal tunnel, lies Sup. To FDS,FDP,FPLIn palm Flattens at distal border of FR, 2 divisions,Medial and lateralLateral gives recurrent branch ,curls up and supply thenar eminenceExpt. Deep head of FPBMedial div. 2 palmar digital nerves Lateral 3 1/2 1 st and 2 nd lumbricals Enters pass deep to FR,carpal tunnel, lies Sup. To FDS,FDP,FPL In midforearm,Gives muscular branches FDS Before entering carpel tunnel,gives off Palmar cutaneous branch,passes sup. To flexor retinaculum,supply thenar eminence and lateral part of palmEnters pass deep to FR,carpal tunnel, lies Sup. To FDS,FDP,FPLIn palm Flattens at distal border of FR, 2 divisions,Medial and lateralLateral gives recurrent branch ,curls up and supply thenar eminenceExpt. Deep head of FPBMedial div. 2 palmar digital nerves Lateral 3 1/2 1 st and 2 nd lumbricals In palm Flattens at distal border of FR, 2 divisions, Medial and lateral Lateral gives recurrent branch ,curls up and supply thenar eminence Expt. Deep head of FPB Medial div. 2 palmar digital nerves Lateral 3 1/2 1 st and 2 nd lumbricals |

