![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
165 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
|
|
|
What kind of authorization document(s) is required to conduct a criminal or civil investigation?
|
search warrant or subpoena.
|
|
|
What U.S. Constitution amendment protects against unreasonable search and seizure?
|
The Fourth Amendment
|
|
|
What two conditions be must be met for authorized search to satisfy the Fourth Amendment requires seizure?
|
1.Probable cause
2.describing the place to be searched and the persons or things to be seized |
|
|
What must be done in order to obtain a search warrant and affidavit ?
|
An application must be filed.
|
|
|
A _________should be established before drafting the application and warrant .
|
search strategy
|
|
|
What are the following roles search strategies generally consider of the computer in a crime investigation?
|
1.Contraband,
2.repository of evidence of a crime, 3.an instrument of a crime |
|
|
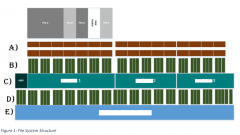
What are the six levels of abstraction from a storage device’s file system?
|
1. DISK 2. VOLUME 3. FILE SYSTEM
4. DATA UNIT 5. META DATA 6. FILE NAME |
|
|
A data unit in Windows is called_____?
|
clusters
|
|
|
A data unit in UNIX/Linux is called_______?
|
Blocks
|
|
|
Clusters and blocks are multiples of ________?
|
512 byte sectors.
|
|
|
What are common artifacts of the file name layer ?
|
Files, folders, and directories
|
|
|
To be protected under the Fourth Amendment, an individual must have_____?
|
the reasonable expectation of privacy, meaning they must demonstrate an expectation of privacy through their behavior society must be prepared to accept that expectation of privacy as reasonable
|
|
|
Give 3 examples of when privacy has been found to be NOT established by the courts.
|
1) Activities conducted in plain view
2) Garbage disposed of outside a person’s property 3) Passwords displayed openly |
|
|
When may No-Knock Warrants be requested?
|
when there is reason to believe a suspect may destroy evidence, and can be requested for searches involving digital evidence. Or be threatening.
|
|
|
What are Three exceptions allow warrantless searches?
|
1. Plain View
2.Searching a individual when being arrested 3.When Voluntary consent is given |
|
|
What factors of voluntary consent does the Supreme Court recognizes?
|
1. Age 2.intelligence 3. physical 4.mental condition
|
|
|
What should be done concerning a voluntary search when possible?
|
Consent should be written to explicitly state the scope of the search.
|
|
|
Do Subpoenas give the authorization to search or seize property?
|
subpoenas order a person to
appear in court surrender evidence |
|
|
What are the three categories Privacy legislation can be grouped into?
|
1.General Privacy
2.Financial Legislation 3.Healthcare And Education Legislation |
|
|
For evidence or testimony to be considered in a court of law, it must be _______.
|
Admissible
|
|
|
What three conditions must be met for evidence to be admissible established as Federal Rules of Evidence as legal requirements of?
|
1.relevance
2.authenticity or credibility 3.competence. |
|
|
What two conditions must be evaluated so that the evidence is relevant?
|
evidence must be material, relating directly to the case
evidence must be probative, meaning it proves something significant in determining the case |
|
|
What two conditions must be met for evidence to be authentic?
|
1.factual
2.credible |
|
|
__________must demonstrate the source and integrity of evidence to demonstrate it is credible .
|
Investigators
|
|
|
What are the most critical steps digital investigators can take to ensure evidence is not ruled inadmissible due to statutory or constitutional violations?
|
Understanding and complying with the authority to search and seize evidence
|
|
|
In order for evidence to be competent it must _________?
|
Not be prejudicial, have any statutory constraints , and not be in violation of the suspects Constitutional rights
|
|
|
What rules are particularly important to digital investigations?
|
Hearsay rules
|
|
|
The 3 categories Digital evidence falls into are?
|
1.hearsay
2.Non-hearsay 3.Mix of hearsay and non-hearsay |
|
|
Any statement made outside of the court by an individual who is not under oath at the time the statement is made is called?
|
Hearsay
|
|
|
How many exceptions are there to the Hearsay Rule________, and how many of them of those rules are applicable to digital investigations____?
|
24 and 6
|
|
|
What are the exceptions that are applicable to digital investigations?
|
Business records
Certain public records and reports Evidence of the absence of a business record or entry Learned treatises used to question an expert witness Statements of the absence of a public record or entry A catch all rule |
|
|
How is the reliability of digital evidence often established?
|
hash values
|
|
|
What is the two step process pertaining to Rule 901(b)(4) allowing digital evidence from storage media to be introduced.
|
1. Introduce the storage media, with unique identifiers. Ex. Serial numbers.
2. Media introduced with hash values or other accepted forensic identifiers |
|
|
The courts have established that investigators need not have a detailed understanding about the hashing algorithms or the software used to implement those algorithms, but must have knowledge on the operation of the tools they use TRUE or FALSE?
|
TRUE
|
|
|
Hashing is a _________function that computes a ________that uniquely identifies any arbitrary length input
|
lossy compression, fixed-length value
|
|
|
Hash values are generally presented as a____?
|
hexadecimal string
|
|
|
A hexadecimal string is a______ not a_____, which is a more readable representation of a_____.
|
value (number), text string binary value
|
|
|
MD5 hashing algorithm produces a _____hash value.
|
128-bit
|
|
|
_____are required to represent a single hexadecimal digit.
|
Four binary bits
|
|
|
A 128-bit MD5 hash value is represented with a ____hexadecimal value.
|
32-digit
|
|
|
Hash functions are____, meaning the original content _____be recovered from the hash value.
|
Lossy cannot
|
|
|
Any change of the_______, even a_______, must result in a change to _____the bits in the hash value (digest). This quality is known as the_______.
|
input message, single, bit at least half, avalanche effect
|
|
|
It must be computationally infeasible to find ______input messages which produce the same digest.
|
two different
|
|
|
A ________is when two different messages produce the same digest.
|
collision
|
|
|
It must be ____________to determine the input from a given hash value. This quality is referred to as________.
|
computationally infeasible, preimage resistance
|
|
|
It must be computationally infeasible to determine _____message from a given digest. This is
referred to as |
any input, secondary preimage resistance.
|
|
|
Commonly used hash functions for forensics include?
|
MD5 and SHA-1
|
|
|
Fuzzy hashing techniques can be used to search_____, but not _____.
|
Similar, identical files
|
|
|
MD5 produces a _____hash value, while SHA-1 produces a ____hash value.
|
128-bit, 160-bit
|
|
|
Stronger hash functions are available, including RIPEMD and SHA-2. Both of these hash functions produce hash values from _______in length.
|
160 to 512 bits
|
|
|
Digital forensics uses hashing for multiple purposes, to include _____and _____large bodies of data to find evidence of interest, ______integrity, and ensuring ____.
|
Sorting, filtering, verifying, confidentiality
|
|
|
Name a Tool that uses fuzzy hashing to compare multiple, smaller portions of content within files to match similar files.
|
ssdeep
|
|
|
What are the three principles for digital evidence that the DOJ holds as standards?
|
The process of collecting, securing, and transporting digital evidence should not change the evidence.
Digital evidence should be examined only by those trained specifically for that purpose. Everything done during the seizure, transportation, and storage of digital evidence should be fully documented, preserved, and available for review |
|
|
What does Locard’s Exchange Principle state?
|
Everything that enters a crime scene leaves part of itself at the crime scene and takes part of the crime scene with it
|
|
|
Locard’s Exchange Principle is not limited to interactions between_____ and the, but rather ____and the______.
|
Suspects, crime scene, all subjects crime scene
|
|
|
The cardinal rule for first responders is ____.
|
safety first
|
|
|
What is a first responders second priority?
|
safety and integrity of the evidence
|
|
|
When Documenting the scene – Documentation should include?
|
a) photographic
b) video c) descriptive documentation including documentation of all personnel present at the scene |
|
|
what should evidence details include?
|
Make, model, and serial number of every device present
Note whether devices are on, off, or in sleep mode Determine if devices are connected to a network, whether wireless or wired Record status of lights and indicators Listen to devices for indications of processing or disk activity Identify and document installed peripherals Look for documentation to other devices that are not present. This may indicate those devices exist elsewhere. Photograph front and back of all devices. |
|
|
What two questions must be asked when identifying data sources?
|
What are the obvious data sources?
Ask what data sources may exist that are not obvious? |
|
|
What are examples of other data sources that may not be obvious?
|
remote storage, which might be indicated by software or links to cloud- or network-based storage
|
|
|
What are potential consequences from compromises in the chain of custody?
|
1. Misidentification of evidence
2. Contamination or loss of evidence 3. Tampering with evidence |
|
|
Evidence should be stored in a designated storage facility that?
|
1. limits access to only the evidence custodian,
2. documents all access to evidence, 3. maintains a thorough chain of custody, 4. provides independent auditing |
|
|
The chain of custody ends with the_____.
|
disposal of evidence
|
|
|
_____is destroyed under court order.
|
Contraband
|
|
|
What tools should Investigators be familiar for destroying digital content?
|
1. data dump (dd)
2. shred 3. Disk Scrub 4. WIPE.EXE utilities. |
|
|
What is beginning of computer forensic investigation.
|
Acquisition
|
|
|
What are three categories: Data acquisition tools generally fall into
|
1. live acquisition,
2. static acquisition 3. mobile device acquisition |
|
|
What are the five data analysis and recovery functions all digital forensic tools serve.
|
Acquisition
1. Validation and discrimination 2. Extraction 3. Reconstruction 4. Reporting |
|
|
Name a tool that can create images from both static and live sources.
|
FTK Imager
|
|
|
________tools can also be contrasted by their capability to copy either physical drives or logical partitions.
|
Acquisition
|
|
|
When are Logical acquisitions are useful ?
|
1. the evidence drive is encrypted
2. when only a portion of a physical drive is required |
|
|
When are Logical acquisitions are more suitable?
|
When it is not be practical or permissible to complete a physical acquisition of large or critical storage systems such as network storage, server storage, or RAID
|
|
|
Simple bit-by-bit copies are known as a______, and are usually created with the ____command .
|
raw data formats, Linux dd
|
|
|
Raw formatted copies do not use _______and do not include______, so they can be viewed in _____and are compatible with most forensic tools.
|
Compression, image metadata,
hexadecimal editors |
|
|
__________provide compression and store metadata with the image file, and the metadata includes______, ________, and other results from data discrimination
|
Proprietary formats, file hashes, data carving results
|
|
|
The Linux dd command does not perform verification concurrently when creating a raw image file True or False.
|
True
|
|
|
What are two Linux commands are digital forensic specific versions of the dd command, and perform verification concurrently during copying.
|
dcfldd and dc3dd
|
|
|
________ensures integrity while a forensic copy is being made, where _______ensures the integrity of complete image copies and individual files.
|
Verification, validation
|
|
|
_________ is the process of sorting and searching investigation data to locate items of interest.
|
Discrimination
|
|
|
In________, hashes are calculated not only for the entire image file, but also for individual files within the image, these hashes can be used during discrimination
|
Validation
|
|
|
The goal of ______is to quickly filter data that is of no investigative interest from the full body of data.
|
Discrimination
|
|
|
The ___________maintains a comprehensive list of file profiles in the _______.
|
National Software Reference Library (NSRL), Reference Data Set (RDS)
|
|
|
An _____can be filtered using a pre-compiled list of hashes for OS files, thereby efficiently tagging those files as known good files.
|
image file
|
|
|
The____ has signatures for both known good (applications, operating systems, and graphic files) and known bad software (i.e., steganography applications and hacking scripts), but does not include signatures for contraband (i.e., graphic files of child pornography).
|
RDS
|
|
|
_____compares hashes from the investigation data to the known hashes from sources such as the NSRL, and quickly filters known good and known bad files.
|
Discrimination
|
|
|
_______provides a server and query tool to look up_____ information, while the _____provides an online search capability to look up individual MD5 hash values.
|
NSRLquery, NSRL RDS, NSRL Hash Search Engine
|
|
|
______can also be performed on header values.
|
Data discrimination
|
|
|
_____ is the process of recovering data in a digital investigation.
|
Extraction
|
|
|
What are the sub functions of Extraction ?
|
1. Data viewing
2. Keyword searching 3. Decompressing 4. Data carving 5. Decrypting 6. Bookmarking |
|
|
_____ allows an investigator to view data in multiple ways. Examples of the ways are hexadecimal or ASCII format, or by sector.
|
Data viewing
|
|
|
______could be deliberately hidden storage space, and could contain evidence. Likewise, _____that contains data flagged as deleted could also contain evidence.
|
Un-partitioned space, unallocated space
|
|
|
______includes RAM and file slack.
|
Slack space
|
|
|
RAM slack is the portion of RAM memory allocated to a file, but not ____.
|
used by that file
|
|
|
______ refers to the space on a physical disk allocated to a file, but not written to by that file.
|
File slack
|
|
|
A ___ may have both RAM slack and file slack.
|
Sector
|
|
|
____,and ____searches is an important sub functions of extraction.
|
Text, hexadecimal string
|
|
|
String searches can help to efficiently locate specific data of interest, but can also generate significant numbers of ____.
|
false positives
|
|
|
_____is another important sub function of extraction.
|
Decompression
|
|
|
______ the process of reconstructing files from file fragments in unallocated space.
|
Data carving, or carving
|
|
|
Carving often attempts to recover file fragments based on ____and _____.
|
Header end-of-file markers
|
|
|
______ is another sub function of extraction.
|
File and file system decryption
|
|
|
________ iteratively attempt words, and common variations of those words, to crack passwords.
|
Dictionary attacks
|
|
|
____attacks attempt every possible combination of potential passwords.
|
Brute force
|
|
|
_____are pre-computed hash values.
|
Rainbow tables
|
|
|
Techniques, such as_____, are used to counter rainbow table attacks.
|
Salting
|
|
|
True or False Most UNIX and Linux distributions do not salt passwords, but Windows operating systems do.
|
FALSE it is the opposite linux does and windows does not.
|
|
|
______features reduce investigator workload.
|
Bookmarking
|
|
|
How can recreating evidence be accomplished?
|
1. Disk-to-disk copy
2. Image-to-disk copy 3. Partition-to-partition copy 4. Image-to-partition copy |
|
|
____ allow investigators to operate applications on the original evidence without altering that evidence.
|
Shadow drives
|
|
|
Because shadow drives expose the original evidence to risk when should they be used.
|
only when necessary for court proceedings.
|
|
|
The____ provides support through the Computer Forensics Tool Testing (CFTT) project, and forensic tool testing products (images and data), procedures, and results.
|
National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST)
|
|
|
Analysis of digital evidence can be very resource intensive, what components should be sufficient to meet immediate and future requirements?
|
1. RAM
2. storage 3. ports 4. networking capacities |
|
|
The major steps in the digital forensics process are
|
Preparation
Survey/Identification Preservation Examination & Analysis Presentation |
|
|
Preparation served two primary objectives:
|
to maximize the collection of evidence and to
minimize the cost of response and investigation. |
|
|
Operational readiness is established by-
|
developing and implementing the policies and procedures to direct and support the digital investigators
|
|
|
infrastructure readiness ensures
|
the systems and tools to process various types of digital evidence are in place.
|
|
|
Survey/Identification begins when
|
an incident is detected and verified, and culminates with the seizure of evidence
|
|
|
An information system security incident is an event...
|
that compromises the confidentiality, integrity, or availability of an information system
|
|
|
TRUE OR FALSE: Digital investigations are limited to criminal and cybercrime incidents.
|
FALSE- are not limited to criminal and cybercrime incidents.
|
|
|
Preservation is the...
|
acquisition of the current state of potentially volatile digital and physical items.
|
|
|
Examination and analysis does what?
|
recovers, harvests, organizes, searches, and reduces data collected during preservation.
Collectively, these steps reduce the potentially large volume of data acquired during preservation into the evidence that will be reported during presentation. |
|
|
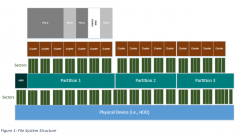
The smallest elements managed by file systems is a _________.
|
Sector
|
|
|
Physical devices are divided into millions of sectors. The beginning of the physical device contains the ___________.
|
master boot record (MBR).
The MBR identifies the primary partitions on the drive and allocates specific sectors to each partition |
|
|
Partitions manage storage by ___________.
|
file allocation units (FAU), more commonly referred to as clusters.
|
|
|
Clusters are a collection of ____________.
|
adjacent sectors.
|
|
|
__________ was deployed in early Windows operating systems, while __________ has been the standard file system since Windows 2000.
|
(1) File Allocation Table (FAT)
(2) New Technology File System (NTFS) |
|
|
Three versions of FAT are?
|
FAT12, FAT16, and FAT32. The versions differ by the file table entry size (12-, 16-, and 32-bit entries).
|
|
|
__________ is also widely used on removable media, such as USB flash and hard disk drives.
|
FAT
|
|
|
Multiple versions of NTFS also exist, but NTFS 3.1 was used in ______________.
|
Windows XP and later versions.
|
|
|
UNIX uses the _______, while Linux uses _____,_____,_____,______. and ____________is
the latest release of the Linux file systems. |
1) UNIX File System
2) Ext2, Ext3, Ext4 or Reiser file systems 3) Ext4 |
|
|
Ext file systems are composed of the __________________.
|
superblock, inode, dentry, and file.
|
|
|
FUN FACT:
The superblock serves as the “master node” and contains data about the file system, to include inodes and dentries. Inodes represent the directories and files that the user recognizes. Metadata about these objects is also maintained in the inode. Dentries index the inodes to specific files. Users view file system content as files. |
-
|
|
|
Deleted files are first marked simply as ________.
|
unallocated space.
|
|
|
Open source tools designed or useful for data carving include:
|
hachoir-subfile
Foremost Scalpel Photorec Autopsy |
|
|
_________involves gather data and metadata about recovered objects and attempts to
build a timeline. |
Harvesting
|
|
|
________________ examine the Modified, Accessed, Creation (MAC) times from a file’s metadata and display them as events. It help investigators relate individual actions as a sequence of events.
|
Timelines
|
|
|
Tools available to automate the creation of timelines:
|
including Log2Timeline, Computer Forensic TimeLab (CFTL), and Tapestry for Timelines
|
|
|
Acquisition of live memory must be done
while the computer is running, but can yield valuable information. This includes: |
a) Passwords in plaintext
b) Encryption keys in plaintext c) Unencrypted data d) Running processes e) Current user information f) Open ports and running services g) Data on attached drives and devices |
|
|
Data volatility spans a continuum. _________are the most volatile data. Next is ________. Next is _______.
|
Data volatility spans a continuum. Registers and cache are the most volatile data. Next is memory, routing tables, process tables, address resolution (ARP) tables, and kernel statistics. Next is temporary files. The first three categories are considered volatile data sources, the last four are considered nonvolatile sources. However, even nonvolatile data sources are subject to some degree of volatility. Of the nonvolatile data sources, hard drives and removable media are the least stable. If available, remote logging and monitoring data for a system is next, followed by physical configuration, and finally archival data.
|
|
|
Digital Forensics is:
|
The process of identifying, preserving, [analyzing] and presenting digital evidence in a manner that is legally acceptable
|
|
|
Forensic Soundness
|
acquisition process preserves a complete and accurate representation of the original data, and its authenticity and integrity can be validated
|
|
|
Objectivity
|
Interpreting evidence free from bias whether inculpatory (directs blame) or exculpatory (reflects blame
|
|
|
Repeatability
|
experiments and observations must be repeatable so that they can be independently verified. Documentation is critical to ensure repeatability.
|
|
|
Search Warrant
|
order by a judge authorizing government officials to search and seize specific evidence for a specific crime at a specified location exceptions plain view, during arrest, voluntary consent
|
|
|
Subpoena
|
order to appear before a court or to produce evidence to the court.
|
|
|
Actual Authority
|
derived when the property to be searched belongs to person granting consent or when person granting consent has been authorized to do so.
|
|
|
Apparent Authority
|
a person who has the genuine appearance of authority to give consent.
|
|
|
Relevance material
|
relates to the case being investigated it probative meaning it proves something significant to the case
|
|
|
Authenticity evidence
|
is factual not an opinion(except for expert witness) computer evidence is generally a fact, but interpretation of evidence may be opinion…must demonstrate the source is valid and honest
|
|
|
Competence evidence
|
cannot be prejudicial, not subject to statutory constraints, not in violation of the Constitution
|
|
|
Privacy Act 1974
|
limits government on collecting personal information for approved purposes, notifying individuals about the information collected and the purpose of those records. Only protects US citizens and legal residents
|
|
|
Electronic and Communication Privacy Act (ECPA) 1986
|
restricts government use of wire taps. May not intercept wired or wireless communications without due process
|
|
|
Chain of Custody
|
documentation of the route evidence takes from the time seized until it is disposed of
|
|
|
Hashes
|
mathematical representation of a specific data repository that verifies that data has not been altered verifies integrity…MD5 and SHA-1 are accepted hashing standards…
|
|
|
Preparation – What is it and its two steps?
|
most critical step….serves two objectives 1. Maximizes collection of evidence 2. Minimizes cost of response and investigation
|
|
|
Two types of readiness
|
Operational – policies and procedures that operationalize laws, rules, of evidence, and training. Infrastructure – preparing systems to process various types of evidence(RAID, mobile, ect)
|
|
|
ADVANTAGES TO IMAGE COPIES OVER LIVE MEMORY
|
1. The ability to verify image authenticity through hash functions and hash values. Using multiple acquisition tools and hash functions improves the robustness of an investigator’s claim of authenticity.
2. The ability to recover from processing errors or mistakes with a fresh copy. 3. The ability to use fresh copies when completing analysis processes that may not be compatible. 4. The ability to convert image copies from one format to another, and verify it’s integrity, to process evidence with multiple tools or utilities that use different input formats. 5. The ability to recover from loss, theft, or corruption of an image copy without compromising the investigation. 6. Courts generally insist investigators work from image copies |
|
|
Reporting –
|
recording what was done many tools have features that maintain the logs, metadata, evidences files needed to demonstrate reliability and repeatability
|
|
|
Reconstruction –
|
attempts to explain what happened during a crime or incident in an attempt to explain who did what, when, where, and how….recreating evidence image to disk copy, image to partition copy or disk to disk copy, partition to partition copy
|
|
|
Discrimination –
|
is the process of sorting and searching investigation data to locate items of interest…can also be performed on file types
|
|
|
Verification -
|
ensures integrity by comparing image file to the original drive
|
|
|
Validation –
|
similar to verification validates the integrity of complete image copies and individual files
|
|
|
What kind of authorization document(s) is required to conduct a criminal or civil investigation?
|
search warrant or subpoena.
|

