![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
51 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Ergonomics
|
study of characteristics for the appropriate design of the living and work environment
|
|
|
Anthroometery.
Design workplace for ? |
90% of the population.
5th percentile - 95th percentile. |
|
|
Musculoskeletal disorders are of the ?
|
disorders of muscles, nerves, tendons, ligaments, joints, cartilage, or spinal discs.
|
|
|
Risk factors for MSDs? (5)
|
repetition/duration
joint deviation force cold vibration |
|
|
Non-occupational factors for developing a MSDs?
|
rheumatoid arthritis
endocrinological disorders acute trauma obesity pregnancy recreational activies diabetes |
|
|
higher risk body parts for MSDs?
|
soft tissues:
muscles, tendons, ligaments. bursa (small, flat, synovial filled sac prevents rubbing of muscle or tendon against bone). nerves blood vessels lower back |
|
|
connects muscle to bone
|
tendon
|
|
|
connects bone to bone
|
liagment
|
|
|
hand deviations
radial |
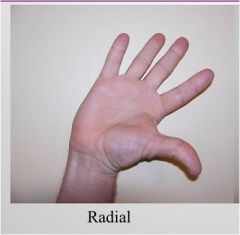
thumb reach to arm
|
|
|
flexion
|
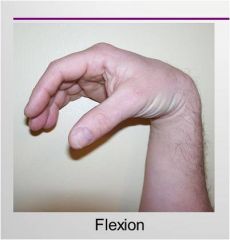
|
|
|
Carpal tunnel syndome (CTS) is often caused by?
swelling of tendones pinches what nerve? |
light, repetitive motion of wrists and fingers.
carpal tunnel on the palmar side of wrist contains nerves, blood vessels, tendons. Swelling on tendons pinches the median nerve. AKA: writer's cramp, neuritis, median neruritis. |
|
|
DeQuervain's Syndrome
special case of? |
tendosynovitis
caused by gripping and hand twisting e.g. wringing clothes. |
|
|
Phalen's Test
|
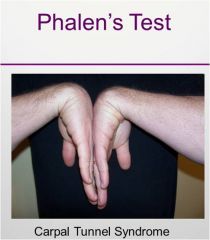
carpal tunnel syndrome
|
|
|
Finklestein's Test
|

DeQuervain's Syndrome.
|
|
|
Extension
|
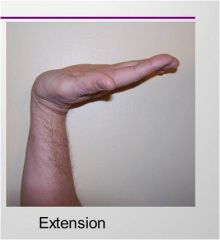
back of hand to arm
|
|
|
ulnar
|
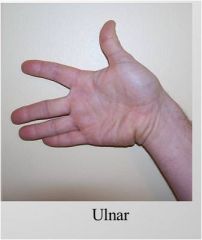
Ulnar - pinky reach arm
|
|
|
Epicondylitis. AKA?
mechanims of injury? caused by? |
tennis elbow
strained tendons on outside of elbow caused by impacting or jerky throwing motions, repeated forceful wrist extensions. |
|
|
Medial epicondylitis . AKA?
|
golfer's elbow.
strained tendons on inside of elbow |
|
|
Tendinitis
|
Inflammation of tendons
Associated with repeated tension, motion, bending, contact with hard surface vibration. |
|
|
Tendosynovitis
|
swelling of the synovial sheath.
tendon becomes irritated, rough, bumpy causing path. |
|
|
Trigger finger
special case of? characterized by? |
special case of tendosynovitis.
finger movement not smooth (snaps or jerks). |
|
|
white finger
caused by? arteries closed due to ? |
insufficent blood supply causes blanching.
arteries closed due to vasopasms triggered by vibrations. |
|
|
Hand-arm segmental vibration.
TLV based on ? Range? |
TLV based on epi data for white finger.
Based on acceleration of tool. Range from 4m/s2 to 12m/s2 |
|
|
Whole body vibration.
TLV based on? |
TLV for minimal risk to lower back pain, adverse health effects and ability to drive vehicle.
Ranges from 0.1m/s2 to 80.0m/s2. seperate table for longitudinal and horizontal vibrations |
|
|
Risk factors for low-back injuries.
|
posture: avoid extremes when lifting.
frequency static work handles, coupling. asymmetrical handling space confinement. |
|
|
Ergo Program includes?
|
All personnel represented.
Training Identify existing or potential problems Evaluate risk factors Design and implement corrective action. Monitor effectiveness of corrections. |
|
|
Material Handling Guidelines
Horizontal movements (push/pull) are _ stressful than vertical movements (lift, lower)? |
Horizontal movements (push/pull) are LESS stressful than vertical movements (lift, lower)?
|
|
|
Material Handling Guidelines
Lifting and lowering best range? |
kuckle height to shoulder height.
|
|
|
what is convection?
|
transfer of heat directly to fluids (usually the air) contacting the body.
C=0.65V^0.6(Ta-95) C=convection transfer (BTU/hr) V=air speed (ft/min) Ta=air temperature |
|
|
Radiation is the transfer of heat through?
|
transfer of heat through infrared radiation. An approximation of the radiant heat transfer is given by:
R=15(Tw-95) R=radiant transfer (BTU/hr) Tw=mean radiant temp of surrounding objects (F degrees) |
|
|
Evaporation is the transfer of heat?
|
to the evironment through evaporative cooling. Maximum evaporative heat loss is approximated by:
Emax=2.4 V^0.6 (42-PWa) Emax=max evaporative heat loss (BTU/hr) V=air speed (ft/min) PWa=vapor pressureof water at air temp (mmHg) |
|
|
Heat Stress Index
|
HSI = (Ereq / Emax ) *100
HSI=heat stress index Ereq=required evaporation to maintain body temp Emax=maximum rate of evaporative cooling |
|
|
Wet Bulb Globe Temperature
Estimates of ? |
environmental contribution to heat stress.
WBGT = 0.7WB+0.3GT (no solar load) WBGT=0.7WB+0.2GT+0.1DB (solar load) WB= wet bulb temp GT=globe temp DB=dry bulb temp |
|
|
Heat stroke
definition? |
body fails to regulate body temp.
|
|
|
Heat stroke sx
|
skin is hot and dry
confused behavior LOC convulsions medical emergency |
|
|
heat hyperpyrexia
|
less severe form of heat stoke
some sweating still occurs other sx are also less severe |
|
|
heat syncope
sx tx |
non-acclimatized persons standing in the heat faint.
blood flow reduced to the brain. Tx: remove victim to cooler location and lie down. |
|
|
heat exhaustion
sx tx |
excess loss of water through sweating.
fatigue nausea cold, clammy skin Tx: get to cooler location, replace body fluids |
|
|
heat cramps
sx tx |
painful muscle cramps during or following work in hot environments.
body salts lost through sweating. Tx: replace fluids with containing appropriate salts. |
|
|
heat illness prevention
|
drink plenty of fluids
frequent breaks PPE (cooling vests) Engineerig controls : air conditioner, mists in air, fans) |
|
|
excessive strain is probable when ?
sustained heat rate = ? |
sustained heart rate = 180bpm - age
|
|
|
excessive strain is probable when ?
recovery heart rate = ? |
recovery heart rate (after 1 minute) > 120bpm
|
|
|
excessive strain is probable when ?
core body temp = ? |
core body temp >101.3F (38.5C)
|
|
|
Trenchfoot
triggered by? mechanism of injury? appearance? |
several days of exposure to cold (not freezing) temp and moist skin.
vasoconstriction in feet/legs. pale appearance and numbness |
|
|
Chillblains
Sx caused by? |
itching, painful reddening of skin.
caused by congestion of capillaries when tissues are exposed to cold. |
|
|
Cold Urticaria
cold can cause? sx? may cause? |
(Hives)
cold can cause histamine releases in the body tissue. sx: itchy red blotches may cause vomitting, rapid heart rate, swlling of breathing passages. |
|
|
Frostbite
mechansim of injury? appearance? damage denpendent on ? |
freezing of body tissue.
white or grayish yellow skin damage dependent on depth of freezing. |
|
|
Hypothermia
|
lowering of core body temp. 26C-30C.
unconsciousness cardiac arrythmia muscular rigidity |
|
|
Cold stress management
maintain core body temp at ? tissue freezing occurs at ? |
>36C (98.6F)
<-1C |
|
|
machine controls when temp <_ should be designed for operation with gloved hands.
|
<-17.5C
|
|
|
additional consideration for working with temp extremes (5)
|
working with evaporative liquids
wet clothing sweating dehydration feelings of euphoria |

