![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
60 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
SV |
EDV-ESV |
Normal 70-110ml |
|
|
Ejection Fraction |
EF=SV/EDV x 100 |
Normal is >55% |
|
|
Cardiac output (CO) |
CO=SV x heart rate (HR) Or CO= HR x CSA |
Normal is 4-8L/min. Varies w/BSA |
|
|
Bernoulli Equation |
P1-P2= 4v2 |
Doppler velocity |
|
|
Doppler Stroke Volume |
SV= VTI ( or FVI ) x CSA |
VTI- velocity time integral CSA- cross-sectional area |
|
|
VTI |
Velocity time integral, calculated by tracing the Doppler spectral display "flow velocity integral FVI" - it represents how far the blood travels in centimeters w/ea. ejection. |
Normal is 12cm for mitral - 20cm for aortic ( can give peak and mean but only method of providing a mean pressure gradient) |
|
|
CSA is calculated |
CSA (cm2) = 3.14 x ( D/2) or CSA (cm2) = 0.785 x (D2) -D is the diameter of any orifice |
|
|
|
Peak LV pressure |
Pk LV pressure= SBP + LV/Ao grad |
If BP is 110/84 Velocity is 5m/sec. (100 mmhg)
110 + 100 = 210 |
|
|
Using continuity equation when would severity of AS be underestimated ? |
LVOT measures too large |
|
|
|
Which pressure is obtained during Doppler for AS |
Peak or peak instantaneous - for AS it's the highest gradient anytime during systole |
|
|
|
Nonna Syndrome |
Classified as a cardio facial syndrome w/PS, HCM and ASD 30% (Dysplastic, thickened and malformed PV leaflets) |
|
|

Etiology for PS |

Also know |
|
|
|
M-mode of valvular PS |
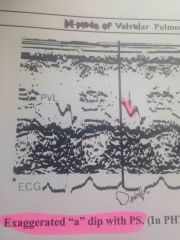
Exaggerated "a" dip |
PHTN you lose the "a" dip |
|
|
Does PS cause pulmonary hypertension |
No |
|
|
|
If unable to obtain PS gradient from the parasternal window where else can you go? |
Subcostal short axis |
|
|
|
Etiology for MS |
-Rheumatic (commissarial fusion)- most common -Congenital (rare)(parachute) -Acquired (mitral annular calcification -MAC |
|
|
|
Parachute MV is |
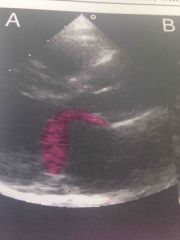
Congenital abnormality |
|
|
|
Longstanding MS leads |
Congestive heart failure Pulmonary hypertension Left atrial dilatation |
|
|
|
M-mode MS shows |
Decreased E-F slope Anterior motion of the posterior leaflet Reduced amplitude of the "E" wave Multiple echoes |
Thickened MV leaflets w/decreased mobility (Hockey stick- goes w/rheumatic MS) |
|
|
Least likely to be affected in rheumatic heart disease |
Pulmonic |
|
|
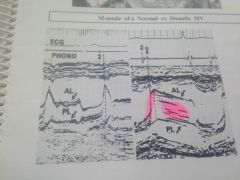
Normal MV vs stenotic MV |
No E A point just a straight line |
|
|
|
MV area for pressure half time |
MVA(cm(2squared))= 220/ Pressure half time |
Mitral pressure half time of 400 what is the area? .5cm2 |
|
|
Normal AV area |
3.0-5.0 cm2 (Less then 1 is sever stenosis) |
|
|
|
Bicuspid AV cause AS becomes symptomatic at age 20-50 |
True |
|
|
|
AI <200msec is severe 600 msec is mild |
True |
|
|
|
LVEDP=diastolic BP-AI gradient 4v2 BP = 160/80 AI peak = 3.5 m/sec(V) |
80-4(3.5)2 (12.25) = 80-49 = 31mmhg |
|
|
|
Pressure 1/2 time |
MVA and Mean Mitral pressure MVA/P 1/2 time = 215msec Mean MV velocity = 1.9 m/sec So, MVA= 220/p1/2time = 220/215 = 1.0 cm2 Mean PG = 4(v)2 = 4 (1.9)2 = 4(3.61) =14.44 round 14mmhg MVA =1.0cm2 Mean PG= 14mmhg |
|
|
|
An E/E prime measurement is taken from the component of tissue Doppler image (TDI) is used to diagnose? |
Diastolic dysfunction |
|
|
|
1)Normal LV measurements in diastole is? 2)Normal septal and posterior wall thickness is? |
1) 35-55mm or 3.5-5.5cm 2) <11mm or 1.1 cm= .6 -1.1mm |
|
|
|
MV velocity during inspiration _ ? TV velocity __ with inspiration? |
- (MV) decreases - (TV) increases |
|
|
|
4 types of ASD ? |
- Secundum defects 70% - Primum defects 20% - Sinus Venous defect 8% - Coronary sinus defect 2% |
|
|
|
Endocardial Cushion defects are? |
(AVSD- Atrioventricular septal defects) -Primum ASD - VSD - Cleft MV (Patients w/down syndrome are high risk for AVSD) |
|
|
|
What is the function of the spleen? |
-Filters plasma and dead blood cells and stored blood |
|
|
|
What is the function of the spleen? |
-Filters plasma and dead blood cells and stored blood |
|
|
|
Stetho means? |
Chest |
|
|
|
What is the function of the Hepatic veins ? |
- drains directly to the IVC to drain deoxygenated blood from the liver (after 120days) |
|
|
|
Performing treatment without patients informed consent,the physician runs the risk of suit for? |
Assault & Battery |
|
|
|
What is under the skin referred to? |
Sub cutaneous Hypodermic |
|
|
|
Normal left and right Oxygen Saturation levels ? |
-right = 76% -left = 98% |
|
|
|
Coronary artery perfusion occurs from ? |
- epicardium to endocardium (outer to inner) |
|
|
|
ASD surgery is mainly considered when the Qp/Qs exceeds? |
1:5 Normal is 1:1 |
|
|
|
Normal RVOT/PV peak velocity? |
.06-.09 m/s |
|
|
|
Normal RVOT/PV peak velocity? |
.06-.09 m/s |
|
|
|
Normal AV peak velocity? |
-1.0-.7 m/s |
|
|
|
Normal RVOT/PV peak velocity? |
.06-.09 m/s |
|
|
|
Normal AV peak velocity? |
-1.0-.7 m/s |
|
|
|
Normal LVOT peak velocity ? |
-.07-1.1 m/s |
|
|
|
Normal RVOT/PV peak velocity? |
.06-.09 m/s |
|
|
|
Normal AV peak velocity? |
-1.0-.7 m/s |
|
|
|
Normal LVOT peak velocity ? |
-.07-1.1 m/s |
|
|
|
Normal TV peak velocity ? |
-.03-.07 m/s |
|
|
|
Normal RVOT/PV peak velocity? |
- 0.6-0.9 m/s |
|
|
|
Normal AV peak velocity? |
-1.0-1.7 m/s |
|
|
|
Normal LVOT peak velocity ? |
-0.7-1.1 m/s |
|
|
|
Normal TV peak velocity ? |
-0.3-0.7 m/s |
|
|
|
Normal MV peak velocity ? |
-0.6- 1.3 m/s |
|
|
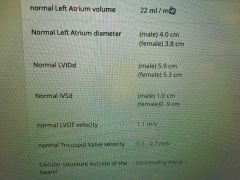
Front (Term) |
Normal LA volume- 22ml/m2 Normal LA diameter - Males- 4.0cm Females- 3.8cm Normal LVIDd- males 5.9 cm - females 5.3 cm Normal IVSd- males 1.0 cm - females 0.9 cm Normal LVOT velocity- 1.1 cm Normal TV velocity- 0.3-0.7 m/s |
|
|
|
Qp/Qs = 2(RVOTd/2)^2 xRVOTvti ---------------------------------- 2(LVOTd/2)^2 xLVOTvti |
*Know on exam* |
|
|
|
AVA= D^2 x .785 x v1/v2 -LVOTd=2.0 -Velocity=1.1 -AVA velocity= 3.9 |
= (2.0)^2 x .785 x (1.1/3.9) = .88 |
|
|
|
Fraction Shortening equation ? |
(LVIDd/LVIDs) x 100 -------------------------- LVIDd |
|

