![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
17 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
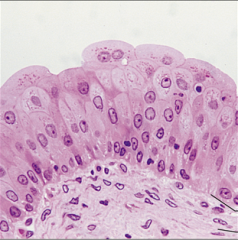
Transitional Epithelium - Stretches - Change from round to flat - Lines uterus, bladder, and part of urethra |
|
|
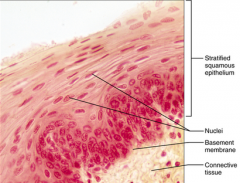
Stratified Squamous Epithelium - Used to protect underlying tissues subject to abrasions - Esophagus, mouth, vagina, epidermis of the skin |
|
|
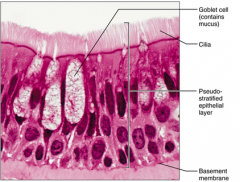
Pseudostratified Columnar - Secrete substances (mucus), propulsion of mucus by ciliary action - sperm-carrying ducts, ducts of large glands, trachea and upper respiratory |
|
|
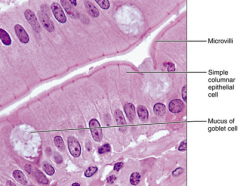
Simple Columnar - absorption, secrete mucus, enzymes and more - lines digestive tract (stomach and rectum), gallbladder, excretory ducts of some glands, small bronchi, uterine tubes, parts of the uterus |
|
|
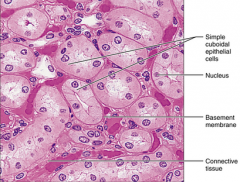
Simple Cubodial - secretion and absorption - kidney tubules, ducts and secretory parts of small glands, ovary surface |
|
|
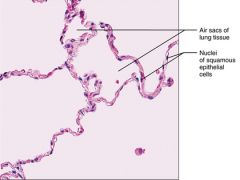
Simple Squamous - Allows materials to pass by diffusion and filtration where protection is not important, secretes lubricating substances in serosae - kidney gomeruli, air sacs of lungs, lining of hearts, blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, lining of ventral body cavity (serosae) |
|
|
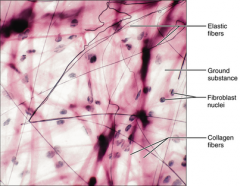
Loose Connective Tissue (areolar) - wraps and cushions organs, plays role in inflammation, holds and conveys tissue fluid - mostly under eipthelia, forms lamina propia of mucus membranes, envelopes organs, surrounds capillaries |
|
|
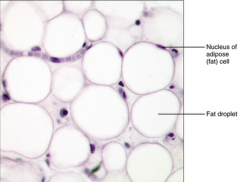
Loose Connective Tissue (adipose) - provides reserve food fuel - insulates against heat loss - supports/protects organs - under skin in subcutaneous tissue, around kidney and eyeball, in abdomen and breasts |
|
|
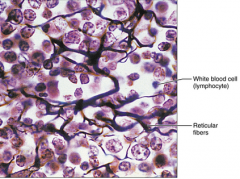
Loose Connective Tissue (reticular) - fibers form a soft internal skeleton that supports other cell types, including white blood cells, mast cells,and macrophages - found in lymph nodes, bone marrow, and spleen |
|
|
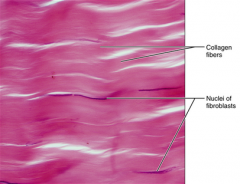
Dense Connective Tissue (Dense Regular) - attaches muscles to to bones or muscles, or bones to bones, withstand tension - tendons, most ligaments, aponeuroses |
|
|
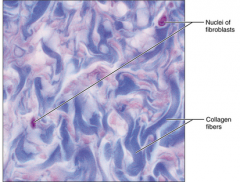
Dense Connective Tissue (dense irregular) - withstands tensions from all directions, provides structural strengths - fibrous capsules of organs and of joints, dermis of the skin, submuccosa of digestive tract |
|
|
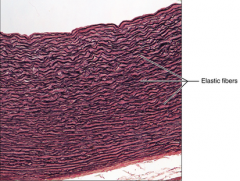
Dense Connective Tissue (elastic) - allows tissue to recoil after stretching, maintains pulsatile flow of blood through arteries, aids passive recoil of lungs - found in walls of large arteries, in certain ligaments in vertebral column, walls of bronchial tubes |
|
|
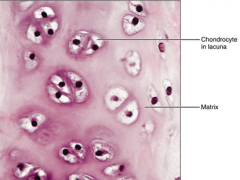
Cartilage - hyaline - supports/reinforces, resilient cushion, resists compressive stress - embyronic skeleton, covers ends of long bones in joint cavities, forms costal cartilage of ribs, cartilage of the nose, trachea and larynx |
|
|
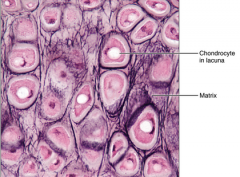
Cartilage - elastic - maintains the shape of a structure while allowing flexibility - supports external ear, epiglottis |
|
|
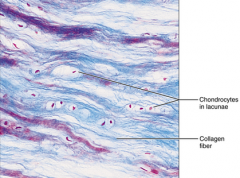
Cartilage - fibrocartilage - tensile strength allows it to absorb compressive shock - intervertebral discs, pubic symphysis, discs of knee joint |
|
|
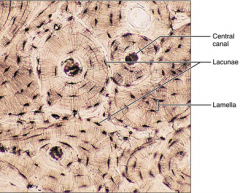
Bone - osseous tissue - supports and protects, provides levers for the muscles to act on, stores calcium/minerals and fat, marrow inside bones is the site for blood cell formation |
|
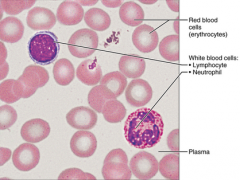
|
Connective - blood - transport respiratory gases, nutrients, wastes, and other substances - within blood vessels |

