![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
17 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
In general, what do epithelial tissues do? |
Line organs. |
|
|
What are all epithelial tissues bound to? |
A basement membrane. membrane. |
|
|
Describe the general structure of squamous epithelial cells, and the advantages of these properties. |
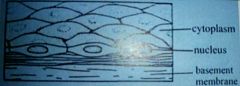
Thin - reduces diffusion distance. Smooth - reduces friction. Flat - increases exposed surface area. |
|
|
Give two examples of where are squamous epithelial cells found. |
Walls of the alveoli and the outer layer of skin. |
|
|
Describe the general structure of cuboidal epithelial cells. |
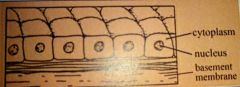
Cube-shaped. |
|
|
Describe the general functions of cuboidal epithelial cells. |
Absorption and secretion. |
|
|
Give two examples of where are cuboidal epithelial cells found. |
In the nephons of kidneys and salivary glands. |
|
|
Describe the general structure of columnar ciliated epithelial cells. |
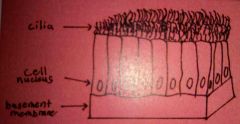
Long and thin, with hair-like structures. |
|
|
Describe the general function of columnar cilliated epithelial cells. |
To shift material. |
|
|
Give two examples of where are columnar ciliated epithelial cells found. |
In the trachea and fallopian tubes. |
|
|
Describe the general structure of columnar microvilli epithelial cells, and the advantages of these properties. |
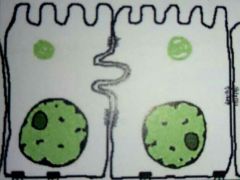
Long and thin, with one side being highly-folded.The highly-folded section has a large surface area, which optimises absorption. |
|
|
Describe the general function of columnar microvilli epithelial cells. |
To absorb material. |
|
|
Give two examples of where are columnar microvilli epithelial cells found. |
In the small intestine and stomach. |
|
|
Describe the general structure of columnar glandular epithelial cells. |

Long and thin, with areas which secrete mucus. |
|
|
Describe the general function of columnar glandular epithelial cells. |
To secrete mucus. |
|
|
What are columnar glandular epithelial cells also known as? |
Goblet cells. |
|
|
Give two examples of where are columnar glandular epithelial cells are found. |
In the small intestine and skin. |

