![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
38 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Epithelium
|
sheet cells covers body surface or lines body cavity; composed of apical and basal surfaces 1. covering and lining 2. glandular |
|
|
5 special characteristics epithelium |
1. polarity (layers) 2. specialized contact (junctions) 3. supported by connective tissue 4. avascular (no vessels) but innervated (has nerves) 5. regeneration |
|
|
apical surface |
(upper) free surface exposed to exterior/cavity |
|
|
basal surface |
deep to apical surface |
|
|
basal lamina |
adj to basal surface, thin supporting sheet; selective filtering and scaffolding |
|
|
reticular lamina
|
supports epithelium (rests upon)
|
|
|
basement membrane
|
2 laminae (basal and reticular)
|
|
|
simple epihtelium |
single cell layer; absorption, secretion, filtration |
|
|
stratified epithelium |
multiple cell layers; protection |
|
|
classification epithelium (naming) |
1.# cell layers 2. shape (top layer) cells |
|
|
simple squarmous epithelium (appearance) |
flattened, scale like; nucleus flattened disc; sparce cytoplasm |
|
|
simple squarmous epithelium (function) |
diffusion, filtration, secretes lubricating substance serosae |
|
|
simple squarmous epithelium (location) |
lining heart and blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, lining ventral body cavity (serosae), air sacs lungs, kidney glomeruli |
|
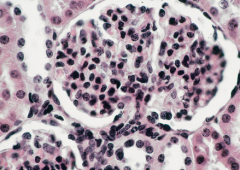
|
simple squarmous epithelium, kidneys, 100x |
|
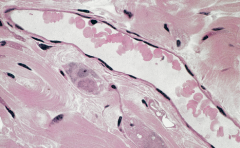
|
simple squarmous epithelium (longitudinal), venule, 1000x |
|
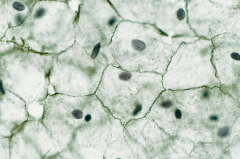
|
simple squarmous epithelium, mesothelium, spread prep 400x |
|
|
simple cubodial epithelium (appearance) |
cube (as tall as wide) like cells; large spherical nucleus |
|
|
simple cubodial epithelium (function) |
secretion and absorption |
|
|
simple cubodial epithelium (location) |
kidney tubules, ducts and secretory portion small glands, ovary surface |
|
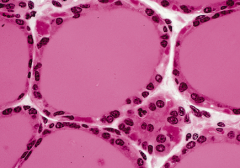
|
simple cubodial epithelium, thyroid gland, cross section 100x |
|
|
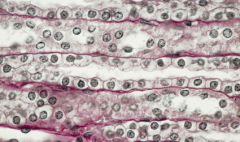
simple cubodial epithelium, kidney, longitudinal 1000x |
|
|
endothelium |
lining lymphatic vessels, blood vessel and heart (simple squaremous) |
|
|
mesothelium |
serosae membranes (simple squaremous) |
|
|
simple columnar epithelium |
tall cells with oval nucleus, some bear cilia or microvilli on apical surface; layer may contain goblet cells |
|
|
simple columnar epithelium (function) |
absorption; secretion; cilia propel |
|
|
simple columnar epithelium (location) |
non-ciliated: lower digestive tract (stomach--> rectum), gallbladder, excretory ducts some glands
ciliated: small bronchi, uterine tube, some region uterus |
|
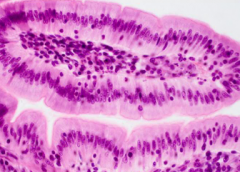
|
simple columnar epithelium |
|
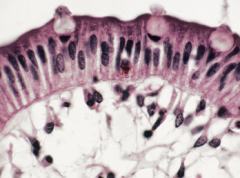
|
simple columnar epithelium |
|
|
pseudostratified epithelium (appearence) |
cells and nucleus vary in heigh giving false impression stratification; all cells rest on basement membrane; may contain goblet cells or cilia |
|
|
pseudostratified epithelium (function) |
secretion (particularly mucin), absorption |
|
|
pseudostratified epithelium (location) |
non-ciliated: sperm ducts, ducts large glands
ciliated: trachea and upper resperatory tract |
|
|
stratified squarmous epithelium (function) |
protection areas abrasion |
|
|
stratified squarmous epithelium (location) |
keratinized- epidermis non-keratin- moist linings |
|
|
stratified cubodial epithelium (location) |
rare; ducts larger glands (mammery and sweat) |
|
|
stratified columnar epithelium (location) |
rare; small amounts pharynx, male urethra, some ducts |
|
|
transitional epithelium (appearance)
|
stratified; apical cells appearance depends on destention
|
|
|
transitional epithelium (function) |
stretches (distention) |
|
|
transitional epithelium (location) |
lines uteres, bladder, part urethra |

