![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
35 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is Epithelium
|
A tissue composed of cells that are strongly adhered together to form sheets of cells that cover all cavities and surfaces of the body.
|
|
|
What are the general characteristics of Epithelium?
|
1. Sheets or layers of cells held together by cell surface specializations
2. Polarized- Have a base, apex, and lateral surfaces 3. The cells are supported at the base by a basement membrane (basal lamina) and a layer of connective tissue 4. Constantly renewed- epithelia are constantly being replaced by new epithelial cells. |
|
|
What are the functions of epithelial tissues? And provide examples. (Total of 7)
|
1. Covering and lining surfaces (skin, intestine)
2. Protection (skin) 3. Secretion (Glands) 4. Absorption (intestines) 5. Sensation (olfactory neuroepithelium) 6. Contraction (Myoepithelial cells) 7. Transcellular transport/selective permeability |
|
|
What are the 4 various layers of Epithelium?
|
A. Simple - 1 cell layer
B. Stratified- 2 or more layers C. Pseudostratified - 1 layer - all cells contact basal lamina, but not all contact the surface D. Transitional: Can be 1 or more layers. Domelike cells found in organs that STRETCH! ~Contracted = several layers ~Distended = few layers |
|
|
What are the 3 CELL FORMS of epithelial cells? (Shape of Epithelial Cells)
|
Squamous -flat
Cuboidal-height=width Columnar-height>width |
|
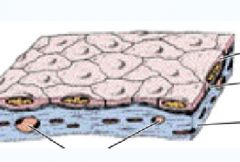
|
Squamous - Flat
Epithelium Basement Membrane Lamina Propia |
|
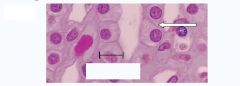
|
Example of squamous flat epithelial cells:
Blood Vessel |
|
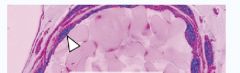
|
Example of Cuboidal Epithelium Cell
In the white box: Epithelium |
|
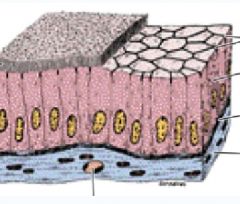
|
Columnar Epithelial cells
|
|
|
What are Transitional Cells?
What does Contracted vs. Distended mean? |
Domelike cells found in organs that stretch
Contracted: Several layers Distended: Few layers |
|
|
Name 3 Modifications of Apical Cell Surface
|
1. Microvilli
2. Cilia 3. Endocytosis |
|
|
Microvilli:
a. what do they look like? where are they found? b. what do they do? c. what are they covered by? d what is the core of the microvilli? |
a. finger like projections that line many absorptive cells
b. increase surface area, usually to aid in absorption c. covered by protein coat called GLYCOCALYX d. a filamentous core made up of actin microfilaments crossed linked together. |
|
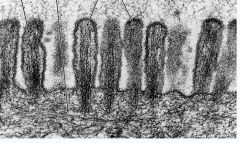
|
Microvilli with the microfilaments in the core and the cell coat on the outside.
|
|
|
Cilia:
a. Structure? b. Internal structure? c. Where are cilias' inserted? d. How does it move? e. Function? |
a. Active cylindrical motile structure
b. Internally they contain 2 central microtubules surrounded by 9 pairs of microtubules. c. cilia are inserted into a basal body at the apical pole below the membrane. d. Back and forth motion, frequently coordinated, to create a flow of fluid in one direction...move with a "whip like action" using ATP as energy source. e. Function is to move surface layers such as mucus or cells such as ova. |
|
|
Break down the 3 main differences between Microvilli and Cillia
|
a. Microvilli are made of actin
Cillia are made of Tubulin b. Microvilli are shorter than cillia c. Microvilli are not motile Cillia move with the use of ATP |
|
|
What did Double 07 have.....
LOL! |
Primary Cilia Diskenisia
|
|
|
Modifications of Lateral Cell Surfaces: Name 4
|
1. Zonula Occludens
2. Zonula Adherens 3. Macula Adherens = Desmosome 4. Gap Junctions |
|
|
Zona Occludens
-where is it located? -function? -what does it constitute? |
Tight Junctions
-most apical of the junctions -forms continuous band around the cell -fuse neighboring cells together, creating a seal that prevents the flow of material between cells -constitutes a permeability barrier |
|
|
Zonula Adherens
|
-Encircles the cell and provides adhesion to neighboring cells
-can also sometimes be seen as spots of attachment called adhesion plaques |
|
|
Macula Adherens = Desmosomes
|
A complex of proteins in a disc like shape that match with an identical structure on neighboring cells
Provides strong cell to cell adhesions |
|
|
Gap Junctions
-what is each unit of the gap junction called? -how many connexins are in a connexon? -what kind of pore does it create? -what does it permit? |
Each unit of the gap junction is called a connexon
10-100 connexon in a gap junction each connexon is made of 6 connexins that form a hydrophilic pore, creating a channel between two cells. -this permits electrical coupling between cells for cell communication |
|
|
Difference between:
Tight Junction vs Desmosomes & Zonula Adherens? And what is the function of Gap Junction? |
Tight Junctions = Seal the epithelium; for example the intestines
Desmosomes and Zonula Adherens provide structural support Gap Junctions allow ion exchange between neighboring epithelia. |
|
|
Modifications of the Basal Surface/ Infolding of Basal Membrane
-Function? -Where is it found? -Give 2 examples -Where is the energy for the pumps coming from? |
-Increases Surface Area
-Found in ion-transporting cells to increase area for ion pumps or in tissues subject to stress, such as the tongue and the skin -Neighboring mitochondria provides ATP for the pumps. |
|
|
How are epithelial cells renewed by new epithelial cells?
|
1. Within the epithelium are cells that retain proliferative ability called stem cells
2. Stem cells divide and give rise to new differentiated cells that replace those that are lost 3. Rates of renewal differ markedly between tissues. |
|
|
From which layer are the olfactory epithelium cells renewed?
|
From the Basal Layer
|
|
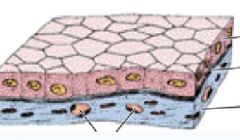
|
Cuboidal Simple Epithelial Cells
(notice the equal of the epithelium) |
|
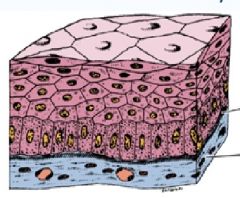
|
stratified = 2 or more layers
|
|
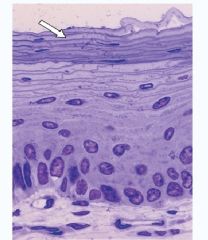
|
The arrow is pointing at the stratified epithelium
|
|
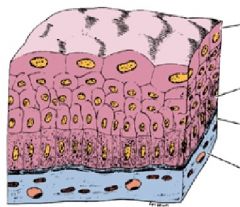
|
Transitional Cell layers
(notice the dome like cells that "stretch") |
|
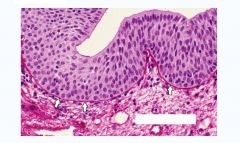
|
Pseudostratified cell layer
Notice the huge Goblet Cell.. |
|
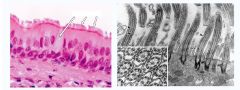
|
Transitional Cell Layer
do you see the "stretchy" cells? |
|
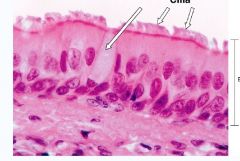
|
Cilia
In the pink picture, the cilia is the TOP arrow |
|
|
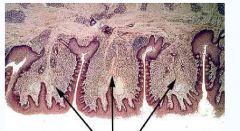
Modification of the Basal Lamina
The arrows are pointing to the "folliate papillae of the tongue" |
|

|
Cross section of Microvilli
|
|
|
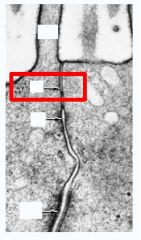
Zonula Occluden
Zonula Adherens Macula Adherens = Desmosomes |

