![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
57 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is an episode of abnormally synchronized and high frequency firing of neurons resulting in abnormal behavior or experience?
What is a chronic brain disorder of various etiologies characterized by recurrent, unprovoked seizures? |

|
|
|
What are groupings of similar epileptic patients according to seizure type, EEG age of onset, prognosis, and clinical signs? |

|
|
|
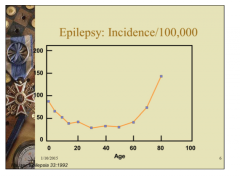
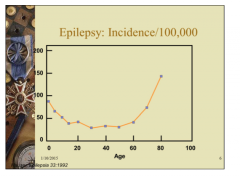
What is the increase of incidence in patients over 60 due to? |
Strokes |
|
|
|
|

What are these all causes of? |
Adult-onset epileptic seizures |
|
|
What are seizures with no focal onset, thought to emanate from the brainstem structures; with spread to both hemispheres at the same time?
What are focal onset seizures that emanate from a specific cortical head region, and may sometimes spread to become secondarily generalized? |

|
|
|
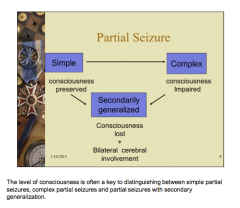
Partial seizures:
Differences between simple, complex, and secondarily generalized? |
|
|
|
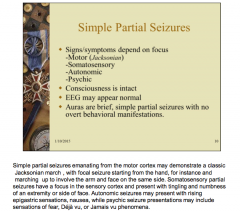
Simple partial seizures: What do signs/symptoms depend on? Is consciousness intact? EEG normal or abnormal? Any auras?
What type of movement if emanating from motor cortex? How will somatosensory seizure present? How will autonomic present? How will psychic seizure present? |
|
|
|
Complex partial seizures: How is consciousness affected? How long does it last? Where do they emanate from? How will it physically present? |
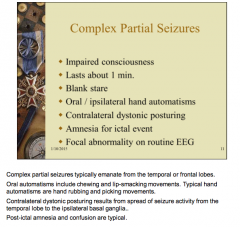
|
|

What are these all components of? |
Primary generalized seizures |
|

What are all of these? |
Absence seizure features |
|

What are these features of?
Also called what? |
Tonic-clonic seizure
Grand Mal seizure |
|

What type of seizure? What condition commonly presents with this? |
Myoclonic seizure
Juvenile myoclonic epilepsy |
|

What type of seizure? |
Atonic seizure |
|
|
Drugs levels of what that the patient may be taking helps detect non-compliance or inadequate dosing? |
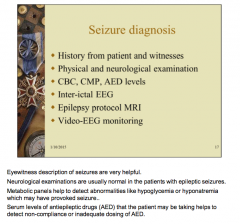
|
|
|
Should you do multiple EEGs in seizure patient? |
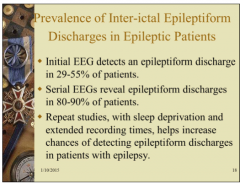
|
|
|
What are examples of epileptiform abnormalities seen in EEGs of patients with epileptic seizures? |
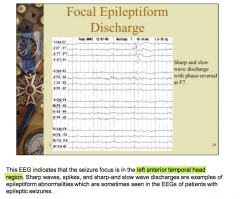
Sharp waves, spikes, and sharp-and slow wave discharges |
|
|
What pattern is typical for primary generalized seizures such as juvenile myoclonic epilepsy?
Where does the discharge occur? |
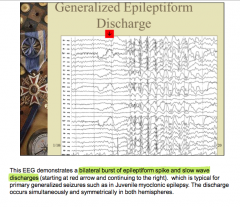
|
|
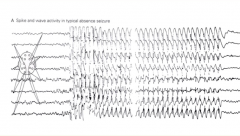
What seizure type? |
Bilateral and symmetrical spike and wave activity occurring at a frequency of 3 per second (3 Hz) is classic for petit mal absence seizure, a primary generalized seizure type..
EEG in ABSENCE SEIZURE |
|
|
Recent-onset epilepsy requires what imaging in adults? |
|
|
|
What MRI type should be done through the whole brain?
Which type do detect hippocampal sclerosis? |
|
|
|
What is useful in differentiating epileptic seizures from non-epileptic seizures? |

|
|

What does GABA activate? How are inhibitive effects generated through this?
This slide is review |

|
|
|
What is overcome during the development of a focal seizure? |

|
|
|
What are the two types of remission? What is the major goal of AED therapy? What type of therapy may result in disease remission? |

|
|
|
What is the drug of choice for primary generalized seizures and syndromes such as JME?
Which are only indicated for partial onset seizures with or without secondary generalization?
Which two drugs can result in weight loss as a side effect?
Which is approved for migraine prophylaxis?
Which is effective in depression and mood disorders?
Which is effective in bipolar disorder?
|

|
|
|
Enhances activity of GABA receptor, depresses glutamate activity, reduces sodium/potassium conductance |
Phenobarbital |
|
|
Blockade of sodium channels and inhibitory action on calcium and chloride conductance |
Phenytoin |
|
|
Blockade of neuronal sodium channel conductance |
Carbamazepine |
|
|
Affects GABA glutamatergic activity and reduce threshold of calcium and potassium conductance |
Valproate |
|
|
Inhibits calcium T-channel conductance |
Ethosuximide |
|
|
Blockage of voltage-dependent sodium conductance |
Lamotrigine |
|
|
Sodium channel blocker |
Oxcarbazepine |
|
|
Blockage of sodium channels, enhancement of GABA mediated chloride influx |
Topiramate |
|
|
Blockage of sodium, potassium and calcium channels, inhibits glutamate excitation |
Zonisamide |
|
|
Modulation of N-type calcium channel |
Gabapentin |
|
|
Which four drugs are all effective in partial and tonic-clonic seizures?
Which two are effective for absence seizures? |

|
|
|
Which two drugs are effective for partial seizures?
Which four drugs are broad spectrum for partial and generalized seizures? |

|
|
|
Aplastic anemia, hepatotoxicity, SJS, lupus-like syndrome |
Carbamazepine |
|
|
Bone marrow depression, hepatotoxicity |
Ethosuximide |
|
|
SJS or toxic epidermal necrolysis |
Lamotrigine |
|
|
Aplastic anemia, hepatic failure, SJS, lupus |
Phenytoin |
|
|
Hyponatremia, rash |
Oxcarbazepine |
|
|
Renal calculi, hypohidrosis |
Topiramate and zonisamide |
|
|
Hepatotoxicity, connective tissue disorder, SJS |
Phenobarbital |
|
|
Hepatotoxicity, hyperammonemia, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, pancreatitis |
Valproate |
|

What do these drugs have in common? |
Hepatic cytochrome p450 inducers |
|

What are all of these effects of? |
Cytochrome P450 inducers |
|

What should you be cautious of in these populations? |
Enzyme induction |
|
|
What pregnancy class are the newer AEDs? |
Category C |
|
|
True or false:
Most patients who respond to AEDs do so with the first AED used in mono therapy. |
True |
|
|
What is intractable epilepsy?
What is the treatment?
What percent of epilepsy patients are intractable? |

20-30% |
|
|
What is the therapy of refractory epilepsy? |

|
|
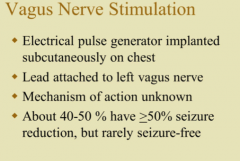
|
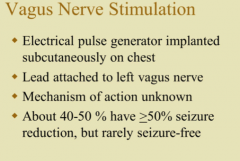
|
|

What is the first point defining? |
Generalized convulsive status epilepticus |
|

What is this the management of? |
GCSE |
|
|
When is GCSE considered to be refractory? What should you do if convulsive seizures persist? |

|

