![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
45 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Main features of case control study?
|
Compares diseased with non-diseased patients; looking for difference in exposures
|
|
|
Main features of cohort?
|
Compares exposed with non-exposed; looking for difference in outcomes
|
|
|
What does prevalence measure?
|
Probability that a person in a defined population has a disease at a point (or period) in time.
|
|
|
What measure do you use to estimate burden of disease?
|
Prevalence
|
|
|
What defines an "at risk" individual?
|
Do not have disease at start of follow up period AND are capable of developing disease
|
|
|
What does cumulative incidence tell you?
|
Probability that an individual in a given population will develop the disease over a specified time period
|
|
|
What measure do you use to estimate disease risk?
|
Cumulative incidence
|
|
|
What is major difference between cumulative incidence and incidence rate?
|
Cumulative incidence does not reflect effect of differing lengths of follow-up between individuals in study
|
|
|
What does incidence rate measure?
|
Average rate at which a disease develops in a population over a specified time period
|
|
|
What measurement has units and what are they?
|
Incidence rate; "per unit time"
|
|
|
What type of study can study a number of outcomes from a single exposure?
|
Cohort
|
|
|
What types of bias do you have to be concerned about in a cohort study?
|
Bias in measuring outcome
|
|
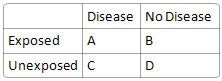
What is incidence in exposed group?
|
A / (A+B)
|
|
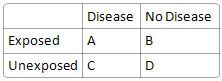
What is incidence in unexposed group?
|
C / (C+D)
|
|
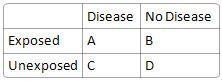
What is relative risk?
|
A / (A+B)
------------- C / (C+D) |
|
|
How is relative risk rate different from relative risk?
|
Uses person-years (instead of persons) in the denominator
(this allows it to take into account loss to follow-up) |
|
|
What is attributable risk? Formula?
|
Measure of the absolute risk of exposure; difference between incidence in exposed and unexposed groups
(Incidence in Exposed) - (Incidence in Unexposed) |
|
|
What is "number needed to treat"? Formula?
|
Simple measure of absolute benefit resulting from treatment
Reciprocal of attributable risk 1/(attributable risk) |
|
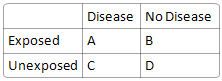
What is attributable risk?
|
[A/(A+B)] - [C/(C+D)]
|
|
|
What measurement do you use for a case control study?
|
Odds Ratio
|
|
|
What is a major source of bias in case-control studies?
|
Recall bias
|
|
|
What can you NOT measure in a case-control study?
|
Incidence
|
|
|
When would you NOT use a case-control study?
|
Studying rare exposures
|
|
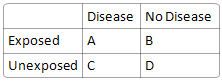
What is odds ratio?
|
(AD)/(BC)
|
|
|
What type of study selects subjects based on presence or absence of disease?
|
Case control
|
|
|
What are the three concerns when thinking of internal validity?
|
Bias, confounding, chance
|
|
|
What is symbol for false positive rate?
|
alpha
|
|
|
What is symbol for false negative rate?
|
beta
|
|
|
What is type I error?
|
False positives
|
|
|
What is a type II error?
|
False negatives
|
|
|
What does the p value estimate?
|
False positive rate (type I or alpha error)
|
|
|
What does the study power estimate?
|
False negative rate (type II or beta error)
|
|
|
What does a p value of .05 mean?
|
If the null hypothesis were true, there is a 5% chance of observing the study result or one more extreme
|
|
|
What does width of confidence interval reflect?
|
Sample size
|
|
|
What is the formula for power?
|
1 - beta
(beta is probability of making a type II error) |
|
|
Differential recall is an example of what kind of bias?
|
Information bias
|
|
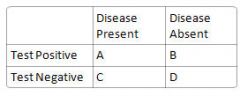
What is sensitivity?
|
A/(A+C)
|
|
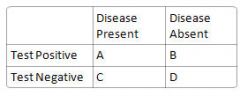
What is specificity?
|
D/(B+D)
|
|
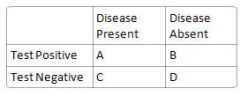
What is PPV?
|
A/(A+B)
|
|
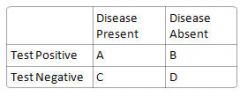
What is NPV?
|
D/(C+D)
|
|
|
What does sensitivity of a diagnostic test tell you?
|
Probability of a positive test if you have the disease
|
|
|
What does the specificity of a diagnostic test tell you?
|
Probability of a negative test if you do not have the disease.
|
|
|
Which measures of a diagnostic test are intrinsic?
|
Sensitivity and specificity
|
|
|
As disease prevalence in population increases, what statistics regarding a diagnostic test change?
|
PPV increases
|
|
|
If you have a 100% specific diagnostic test, what does that mean?
|
You have NO false positives
|

