![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
42 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Health --> ______ --> ______ --> death and disability
|
risk factors
disease |
|
|
name the upstream determinants of the evans and stoddart model
|
behavioral factors
social environment built environment genetic makeup |
|
|
Describe population health science
|
body of scientific disciplines interested in the study of the distribution, determinants, and means for the control of health and disease states in the population. Includes medicine, nursing, pharmacy, clinical reserach, health services research, etc etc
|
|
|
what is health as defined by the WHO
|
state of complete physical, mental, and social well being and not merely the absence of disease or infirmity
|
|
|
draw the disease causation continuum
|
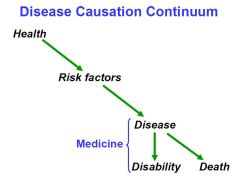
|
|
|
draw the disease causation continuum for CVD
|

|
|
|
draw an example of the disease causation continuum from smoking to lung cancer
|
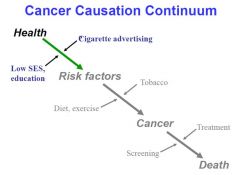
|
|
|
draw the wisconsin model
|

|
|
|
The epidemiologic triad includes host, agent, and environment. Give examples of each of these categories.
|
host- age, sex, marital status, previous disease, cultural habits, job
Agents-- biologic, chemical, physical, nutritional Environment-- temperature, humidity, altitude, housing, crowding, water, radiation, air pollution, noise, advertising, marketing! |
|
|
Definition. study of how disease is distributed in population and the factors that influence or determine this distribution
|
epidemiology
|
|
|
Describe the natural history of disease.
|
state of pathological onset
presymptomatic stage clinical manifest of disease outcome |
|
|
What do you call the time period between the pathological onset and the first symptom?
|
incubation period
|
|
|
what is an epidemic?
|
occurrence in a community or region of cases of an illness, health related behavior, or health related event clearly in EXCESS of normal expectancy
|
|
|
Name the determinants of disease etiology and natural history
|
causes (risk factors)
prognostic factors evaluating treatment |
|
|
define incidence
|
The number of NEW cases of a disease in a population during a specified period of time
|
|
|
define mortality
|
incidence of death
|
|
|
define prevalence
|
number of existing cases of disease in a population at some point in time
|
|
|
define endemic
|
constant presence of a disease or infectious agent within a given geographic area of a population group
|
|
|
define pandemic
|
epidemic occurring over a very wide area, usually affecting a large proportion of a population
|
|
|
define epidemic
|
occurrence in community or region of cases of an illness, health related behavior, or health related event clearly in excess of normal expectancy
|
|
|
Draw the 2x2 table
|
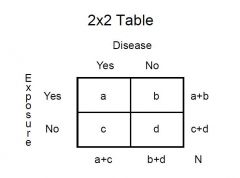
|
|
|
draw the epidemiologic triad
|
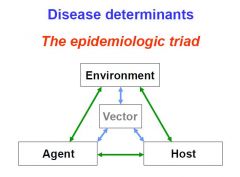
|
|
|
what is an epidemic curve?
|
histogram representing times of clinical disease onset in individuals
|
|
|
who is the father of epidemiology
|
john snow
|
|
|
incidence =
|

|
|
|
prevalence =
|

|
|
|
What are the main purposes of controlled trials
|
to balance the groups according to measurable and unmeasurable factors and probable confoudning features. To avoid bias from stass. To provide basis for statistical testing.
|
|
|
name the main features of controlled trials
|
randomization
blinding placebo |
|
|
when is blinding really important
|
for subjective outcomes
|
|
|
What are three types of controlled trials?
|
FDA therapeutic trials
according to type of intervention according to patient allocation |
|
|
What are some examples of controlled trials according to patient allocation
|
parallel
crossover-- one group begins with therapy A and then moves to therapy B Factorial -- when more than one drug is tested |
|
|
what are the benefits of a crossover controlled trial?
|
each patient is his or her own control
|
|
|
what is case fatality rate?
|
incidence of death among people with the disease
|
|
|
state the steps of kaplan meier approach.
|
1. Sort the survival times from longest to shortest
2. For each time of occurrence of an event, compute the conditional survival time 3. For each time of occurrence of an event, compute the cumulative survival. **Multiply all prior conditional probabilities of survival at each time point. |
|
|
what does 210.2 per person year mean?
|
1 person will have this occurrence 210 times per year
|
|
|
Odds =
|
prob/(1-prob)
|
|
|
true or ralse. You can use incidence, mortaility, or prevalance to calculate the odds
|
true!
|
|
|
end lecture 4
|
lecture 4
|
|
|
If the probability of an event is 50%, what are the odds?
|
33%
|
|
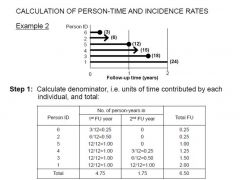
explain what is going on.
|
Person years-- conditional probability of kaplain meier.
|
|
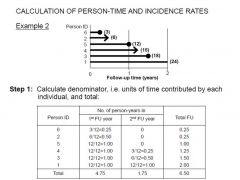
calculate the person years for one year.
|

|
|
|
what are the odds?
|

|

