![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
146 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Number of bones in the body
|
206
|
|
|
Bone Function
|
Determine height, width and basic shape of the body
Make movement possible Act as levers Provide protection and support for organs Produce blood cells Regulate essential minerals |
|
|
Minerals regulated by bones
|
Calcium
Phosphorus Release when needed into the bloodstream |
|
|
Skull protects...
|
the brain
|
|
|
Ribs protect...
|
the heart and lungs
|
|
|
Blood cells
|
produced by red bone marrow
|
|
|
Mature bone cells...
|
Osteocytes
Limitedlife span Broken down by Osteoclasts |
|
|
New bone cells...
|
Osteoblasts or
Osteogenesis |
|
|
Remodeling
|
constant breakdown and renewal of bone tissue
Insures that bones remain strong |
|
|
True or False
Bones change shape in response to stresses on them |
True
|
|
|
Bone formation
|
ossification
|
|
|
Axial skeleton
|
Head
Vertebral column Thoracic cage Hyoid bone |
|
|
Skull
|
Frontal
Temporal Zygoma Maxilla Nasal bone Temporomandibular joint Parietal Occipital Mandible Part of the Axial Skeleton |
|
|
Thorax
|
Sternum
Ribs |
|
|
Collar bone
|
Clavicle
|
|
|
Shoulder Blade
|
Scapula
|
|
|
Upper arm bone
|
Humerus
|
|
|
Forearm bones
|
Radius (thumb side)
Ulna (pinkie side) |
|
|
Spinal column
|
Vertebral column
Part of the Axial skeleton |
|
|
Wrist and Hands
|
Carpals
Metacarpals Phalanges |
|
|
Hip
|
Ilium
|
|
|
Tailbone
|
Sacrum
|
|
|
Upper thigh bone
|
Femur
|
|
|
Lower leg bones
|
Tibia (inner) thicker bone
Fibula (outer) |
|
|
Knee bone
|
Patella
|
|
|
Ankle and foot
|
medial malleolus
lateral malleolus Tarsals Metatarsals Calcaneus (heel bone) Phalanges |
|
|
elbow joint
|
Olecranon process
|
|
|
Appendicular skeleton
|
pectoral girdle - connects arms to thoracic cage
pelvic girdle - connects legs to axial skeleton Arms and legs (themselves) |
|
|
Axial skeleton
Cranial Bones |
Frontal bone - forehead
Parietal bones (pair that make up the crown) Temporal bones - one on either side of the cranium Occipital bone - back of the head Sphenoid bone Ethmoid bone |
|
|
Axial Skeleton
Facial bones |
Nasal bones
Zygomatic bones Vomer Maxilla Mandible - lower Jaw bone Nasal Conchae (or turbinates) Lacrimal Bones - |
|
|
Mandible unites with the temporal bone of the skull
|
at the Temporomandibular joint (TMJ)
Only movable bone of the skull |
|
|
Vertebral Column
|
33 bones - vertebral
Named by location Made up of invertebral discs |
|
|
Sequence down the vertebral column
|
Cervical - 7
Thoracic (or Dorsal) - 12 Lumbar - 5 Sacrum - 5 fused bones Cocyx or tailbone- 4 fused bones Referred to by letter C 1 - 7 T 1 - 12 L 1 - 5 S 1-5 |
|
|
Between the vertebrae
|
intervertebral discs
Shock absorbers Made of cartilage 2 layers |
|
|
Intervertebral discs
|
Annulus fibrosus - tough, outer layer
Nucleus pulposus - soft, gel-like inner portion |
|
|
Slipped or herniated disc
|
common and painful
gel material pushes the outer layer out of its normal position. Nerves are then pinched. Creates a back spasm. |
|
|
33 Vertebrae
|
Number of vertebrae in each group -
Breakfast at 7am Lunch at 12 noon Dinner at 5 pm |
|
|
Thoracic Cage
|
Breastbone - Sternum
Ribs - 12 pair Costal cartilage Thoracic vertebrae |
|
|
12 ribs
|
Posteriorly, they attach to the 12 thoracic vertebrae
Anteriorly, the top 10 ribs connect to the costal cartilage then to the sternum. the other 2 are floating ribs (in front) |
|
|
Appendicular Skeleton
|
Pectoral girdle
Collar bones OR Clavicles PLUS Shoulder blades or Scapulae |
|
|
Pelvic Girdle
|
Protects pelvic organs
2 hip or coxal bones |
|
|
Hip bones
|
three segments that become fused
ilium ischium pubis |
|
|
Hip socket
|
Acetabulum
allows the head of the femur to fit into it forming the hip joint |
|
|
Right & left hip joints
|
form a circle anteriorly at the
symphysis pubis and Posteriorly with the sacrum to for the Sacroiliac joint. |
|
|
Female sacroiliac
|
Stretches slightly to allow for birth of a baby.
|
|
|
Upper Extremity
|
Hand and arm bones
|
|
|
Prepare to name anterior skeleton parts
|

|
|
|
Prepare to identify the posterior skeleton parts
|
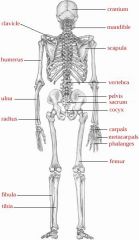
|
|
|
Prepare to list hand bones
|

|
|
|
Lower Extremity
|
Bones of the left leg and foot.
Bones include Thighbone - Femur, The knee - patella, The shin or tibia and the fibula which is the lateral bone of the lower leg. A protrusion (bump) on the distal tibia is called the lateral malleolus. The projection of the distal fibula is called a laterla malleolus. |
|
|
Name the bones of the Shoulder and Arm
|

|
|
|
Name the bones of the fooot
|

|
|
|
Name the bones in the leg an knee joint
|

|
|
|
Name the bones of the Pelvis
|

|
|
|
Describe the Rib Cage
|

First 7 - True ribs
Next 3 - False ribs Final 2 - Floating ribs |
|
|
Skull - Anterior view
|
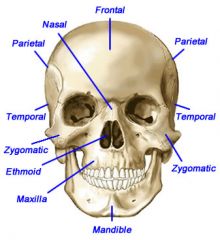
|
|
|
Skull - Lateral view
|
|
|
|
Spine - side and back view
|

|
|
|
Slipped disc is a
|
herniated disc
|
|
|
Forehead
|
Frontal bone
|
|
|
Temples
|
Temporal bones
|
|
|
Cheek
|
Zygoma
|
|
|
Upper jaw
|
Maxilla
|
|
|
Lower Jaw
|
Mandible
|
|
|
Breastbone
|
Sternum
|
|
|
Hip
|
iliac
|
|
|
Olecranon
|
Elbow
|
|
|
Wrist
|
Carpals
|
|
|
Heel
|
Calcaneus
|
|
|
Supporting Structures
|
Ligaments
Bursae |
|
|
Ligaments
|
attach bone to bone
|
|
|
Bursae
|
Tiny, purselike sacs
Lined with synovial membrane Filled with synovial fluid Prevents friction between 2 structures that need to glide past each other when moving - like bone and skin. |
|
|
Bursitis
|
Inflammation of the Bursae
|
|
|
Joint
|
Union between 2 bones - 5 parts
Articular cartilage Joint cavity Synovial membrane Synovial fluid Joint Capsule Named after the bones they join |
|
|
Supporting Structures
|
Ligaments
Bursae |
|
|
Ligaments
|
attach bone to bone
|
|
|
Bursae
|
Tiny, purselike sacs
Lined with synovial membrane Filled with synovial fluid Prevents friction between 2 structures that need to glide past each other when moving - like bone and skin. |
|
|
Bursitis
|
Inflammation of the Bursae
|
|
|
Joint
|
Union between 2 bones - 5 parts
Articular cartilage Joint cavity Synovial membrane Synovial fluid Joint Capsule Named after the bones they join |
|
|
Synovial Joint
|
|
|
|
Supporting Structures
|
Ligaments
Bursae |
|
|
Ligaments
|
attach bone to bone
|
|
|
Bursae
|
Tiny, purselike sacs
Lined with synovial membrane Filled with synovial fluid Prevents friction between 2 structures that need to glide past each other when moving - like bone and skin. |
|
|
Bursitis
|
Inflammation of the Bursae
|
|
|
Joint
|
Union between 2 bones - 5 parts
Articular cartilage Joint cavity Synovial membrane Synovial fluid Joint Capsule Named after the bones they join |
|
|
Synovial Joint
|
|
|
|
Supporting Structures
|
Ligaments
Bursae |
|
|
Ligaments
|
attach bone to bone
|
|
|
Bursae
|
Tiny, purselike sacs
Lined with synovial membrane Filled with synovial fluid Prevents friction between 2 structures that need to glide past each other when moving - like bone and skin. |
|
|
Bursitis
|
Inflammation of the Bursae
|
|
|
Joint
|
Union between 2 bones - 5 parts
Articular cartilage Joint cavity Synovial membrane Synovial fluid Joint Capsule Named after the bones they join |
|
|
Synovial Joint
|
|
|
|
Synovial Joint
|

|
|
|
kyph/o
|
humpback
|
|
|
lord/o
|
swayback
|
|
|
ped/o
|
chile
|
|
|
scoli/o
|
curved
|
|
|
tempor/o
|
temporal bone
|
|
|
-porosis
|
porous
|
|
|
Myel/o
|
bone marrow; spinal cord
|
|
|
osse/o; oste/o
|
bone
|
|
|
mandibul/o
|
mandible; lower jaw
|
|
|
maxillo/o
|
upper jaw; maxilla
|
|
|
Stern/o
|
sternum; breastbone
|
|
|
xiph/o
|
sword
Distal portion of the sternum; literally means "resembling a sword" |
|
|
cervic/o
|
neck
|
|
|
coccyg/o
|
coccyx; tailbone
|
|
|
lumb/o
|
lower back; loins
|
|
|
lumbosacral joint
|
pertaining to the joint between L5 and the sacrum
|
|
|
scar/o
|
sacrum
|
|
|
sacrococcygeal joint
|
pertaining to the joint between the sacrum and the coccyx
|
|
|
Difference between
Spondyl/o and vertebr/o |
Spondyl/o - used referring to condition of the vertebrae
vertebr/o - used in words to describe structure |
|
|
clavicul/o
|
clavicle; colarbone
|
|
|
brachi/o
|
arm
|
|
|
carp/o
|
wrist
|
|
|
olecran/o
|
elbow; olecranon
|
|
|
phalang/o
|
phalanx;
one of the bones making up the fingers and toes |
|
|
radi/o
|
radius
|
|
|
uln/o
|
ulnar
|
|
|
acetabul/o
|
acetabulum; hip socket
|
|
|
ili/o
|
hip
ili and hip both have an "I" in them |
|
|
pelv/i
pelv/o |
pelvis
|
|
|
calcane/o
|
heel
|
|
|
femor/o
|
femur
Thigh bone |
|
|
fibul/o
|
fibula
|
|
|
patell/a
patell/o |
patella
kneecapo |
|
|
tibi/o
|
tibia
shin |
|
|
arthr/o
articul/o |
joint
|
|
|
Osteoarthritis
|
OA
degeneration of the articular cartilage due to overuse results in painful movement of the joint |
|
|
Rheumatoid arthritis
|
RA
Autoimmune disease where the immune system fails to recognize its own tissue and attacks. Results in degeneration of the joint. |
|
|
-blast
|
immature
|
|
|
-clasis
|
surgical fracture or refracture
|
|
|
-clast
|
breakdown
|
|
|
-physis
|
to grow
|
|
|
-sarcoma
|
malignant tumor of connective tissue
|
|
|
ortho-
|
straight
|
|
|
Bone Cancer
|
Pain and swelling are symptoms, but fractures usually lead to diagnosis
Primary bone tumors - originates from bone tissue Osteosarcoma - most common bone cancer Ewing's tumor - occurs in children Chondroscaroma |
|
|
Treatment for Bone Cancer
|
Excision of the tumor
Amputation Chemotherapy Radiotherapy |
|
|
Most common bone cancers
|
Metastatic or secondary tumors
Result from spreading cancer to bone from other locations such as breast and lungs |
|
|
Fractures
|
Break or crack in a bone
|
|
|
Open fracture
|
broken bone with a open cut in the skin
|
|
|
Closed fracture
|
Broken bone with NO open cut in skin
|
|
|
Pathological fracture
|
Bone break due to being weak from disease
|
|
|
Names for fractures
|
Comminuted - splinter bone
green stick - partially broken on one side and bent on the other side Colles' fracture - of the distal radius bone near the wrist Intra-articular fracture - on the joint surfaces of the bone |
|
|
Treatment for broken bones
|
Reduction - placing bones back together
Immobilization - placing a cast of the break to prevent movement |
|
|
Types of reduction
|
Open - bone repair under direct visualization
Closed reduction - no direct visual contact required Open reduction internal fixation - uses screws, nails, or pins - severe fractures |

