![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
49 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Homeostasis
|
Maintaining an internal balance
|
|
|
Endocrine system
|
Maintains homeostasis
|
|
|
Endocrine glands
|
Secrete hormones
|
|
|
Hormones
|
Essential chemicals for proper functioning of body processes
|
|
|
Feedback mechanism
|
The body sends a signal for a certain hormone. Shen the need is completed, the signal stops and the hormone secretion stops.
|
|
|
Glands in the Endocrine System
|
Hypothalamus
Pituitary Thyroid Parathyroids Adrenals Pineal Pancreas Secrete hormones for delivery to a target organ through the bloodstream No ducts (except Pancreas) |
|
|
Exocrine glands
|
Sweat Glands
Has ducts Secrete chemicals into ducts, which deliver the secretion to the target site. |
|
|
Categories of Endocrine glands
|
Central
Peripheral |
|
|
Central glands
|
Two adjacent glands in the brain
Hypothalamus Pituitary Coordinate to regulate body functions such as water and sale balance Growth Reproduction Metabolism |
|
|
Peripheral Glands
|
Thyroid
Parathyroids Adrenals Pineal Pancreas All produce hormones Pancreas also has important digestive functions |
|
|
Endocrine glands - overview
|
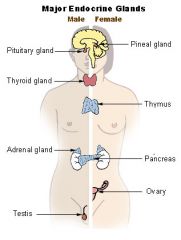
|
|
|
Pancreas
|
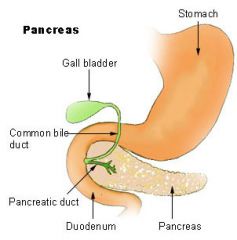
|
|
|
Testis
|
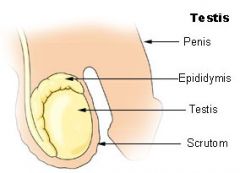
|
|
|
Ovary
|
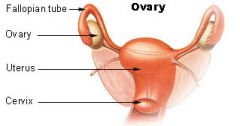
|
|
|
Adrenal Gland
|
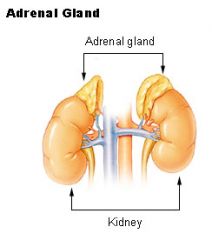
|
|
|
Parathyroid
|
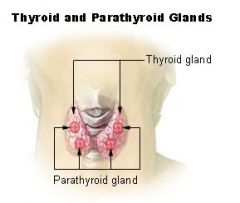
|
|
|
Pituitary and Pineal
|
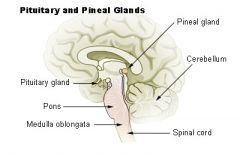
|
|
|
Hypothalamus
|
Central Endocrine gland
Works in tandem with pituitary Produces and secretes neurohormones Produces tropic hormones which effects pituitary activity Produces antidiuretic hormone and Oxytocin |
|
|
-tropic
-tropin |
Substances that stimulate other organs to secrete hormones
|
|
|
Pituitary Gland
|
Hangs from the Hypothalamus by the infundibulum
Pea sized Divided into Anterior and Posterior lobes |
|
|
Hormones secreted by the Anterior Pituitary
|
Secrets 7 hormones
5 are tropic (stimulating) 2 induce other glands to release hormones Adrenocorticotropic (ACTH) Growth Hormone (GH) Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) Folicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) Luteinizing hormone (LH) Prolactin (PRL) Melanocyte-stimulating hormone (MSH) |
|
|
PRL
|
Prolactin
Stimulates breast milk production |
|
|
MSH
|
Melanocyte-stimulating hormone
Stimulates melanocyte production in skin |
|
|
ACTH
|
Adrenocorticotropic hormone
Stimulates adrenal cortex to produce/secrete Cortisol, Aldosterone and sex hormones |
|
|
GH
|
Growth hormone - somatotropin
Stimulates growth in all body cells Controls the release of the hormone somatomedin from the liver |
|
|
TSH
|
Thyroid stimulating hormone
stimulates the thyroid gland to produce and secrete its own hormones Thyroxine (T₄) Triiodothyronine (T₃) |
|
|
FSH
|
Follicle stimulating hormone - a gonadotrophin
Stimulates growth of gonads (ovaries and testes) Males - promotes sperm formation Females - monthly development of the ovum (egg) and secretion of estrogen and progesterone |
|
|
LH
|
Luteinizing hormone - a gonadotrophin
females - triggers ovulation Males - regulates testosterone secretion and is called interstitial cell-stimulating hormone (ICSH) |
|
|
Posterior Pituitary
|
Stores and secrets 2 neurohormones produced by the hypothalamus
Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) - AKA Vasopressin Oxytocin (OT) |
|
|
ADH
|
Antidiuretic hormone
Prevents excessive loss of water |
|
|
OT
|
Oxytocin
Stimulates uterine contractions to assist childbirth Regulates the flow of milk from mammary glands |
|
|
Thyroid Gland
|
Below the Larynx
2 lobes - Right and Left connected by the Isthmus Produces, stores and secretes 2 hormones T₃ - triiodothyronine T₄ - thyroxine Regulate metabolic rate and increase production of energy from food Also produces Calcitonin - which regulates blood calcium levels |
|
|
Parathyroid Glands
|
Four of them - located on the thyroid (2 each side)
Egg shaped glands Secrete parathormone (PTH) Contributes to the regulation of calcium and phosphorus |
|
|
Adrenal Glands
|
Sit on top of each Kidney
Functionally/Structurally, there are 2 parts Adrenal Cortex Adrenal Medulla |
|
|
Adrenal Cortex
|
Secretes 3 hormones
Mineralocorticoids Glucocorticoids Sex Hormones |
|
|
Adrenal Medulla
|
Produces
Adrenaline or Epinephrine Noradrenaline or Norepinephrine These are "Fight or Flight" hormones |
|
|
Mineralocorticoids
|
Adrenal Cortex
Most important secretion - Aldosterone Central role in regulation of sodium and potassium levels |
|
|
Glucocorticoids
|
Adrenal Cortex
Most Important secretion - Cortisol Necessary for antibody production Key role in response to stress Necessary for utilization of carbohydrates, fats and proteins |
|
|
Sex Hormones
|
Adrenal Complex
Includes estrogen and androgens Secondary to secretions by the ovaries and testes Role in development of secondary sex characteristics - pubic and facial hair and breast development |
|
|
Pineal Gland
|
Located deep within the brain
Role in waking and sleeping cycle Secretes melatonin Receives stimulation from the eye Melatonin is also connected to mood |
|
|
Pancreas
|
Located behind the stomach
Secretes pancreatic juice (exocrine function) Secretes Insulin and Glucagon (endocrine functions) |
|
|
Insulin
|
Secreted by the Pancreas
Lowers blood sugar by stimulating sugar absorbtion by the body cells Converts Glucose into Glycogen - how sugar is stored in the liver |
|
|
Glucagon
|
Increases blood sugar by converting glycogen back to glucose for use by the body when blood sugar is low
|
|
|
immun/o
|
safe
|
|
|
radi/o
|
radioactive
|
|
|
-genesis
|
production
|
|
|
-gen
|
producing
|
|
|
eu-
|
Normal
Good |
|
|
acr/o
|
Extremity
Top |

