![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
44 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is an enzyme? |
A biological catalyst which speeds up the rate of reaction without altering the final equilibrium between reactants and products |
|
|
What shape is the velocity v substrate conc graph? |
Rectangular hyperbola |
|
|
How do enzymes work? |
They lower the activation energy of the reaction by providing an alternate route |
|
|
What are the consequences of enzyme specificity? |
A group of enzymes present in one compartment of a cell can give rise to a complex and coordinated patheway |
|
|
How are enzymes classified? |
Divided into 6 main classes according to type of reaction they catalyse Further divided into subgroups according to their substrate Each enzyme has its own 4 digit number |
|
|
What is an example of an enzymes classification? |
catalase= E.C.I.II.I.6 |
|
|
What do oxidoreductases catalyse? |
the transfer of hydrogen atoms and electrons |
|
|
What do transferases catalyse? |
The transfer of functional groups from donors to acceptors |
|
|
What do lyases catalyse? |
the cleavage of C-C, C-O or C-N bonds to form double bonds |
|
|
What do hydrolases catalyse? |
the cleavage of bonds by addition of water |
|
|
What do isomerases catalyse? |
the transfer of functional groups within the same molecule |
|
|
What do ligases catalyse? |
use ATP to catalyse the formatione of new covalent bonds |
|
|
Why are enzymes so sensitive to changes in the environment? |
The tertitary and quatenary structure are stabilised by weak bonds which are easily broken |
|
|
what does the lock and key model suggest? |
Only one substrate can fit in one enzyme |
|
|
What does the induced fit model suggest? |
The enzyme slightly changes shape to fit the substrate |
|
|
Effect of temperature on enzyme reactions |
Enzymes have an optimal temperature at which their rate is fastest At extreme temp they will denature |
|
|
What are cofactors? |
Inorganic ions which can change their electric charge to handle electrons in enzyme reactions to help them |
|
|
What are isoenzymes? |
Enzymes with different protein structures which catalyse the same reaction Isoenzymes will be coded for by different genes |
|
|
What is enzyme kinetics? |
The study of the rate of an enzyme catalysed reaction and how the rate varies with differing environment |
|
|
How does reatcion rate change with increasing substrate concentration? |
At low substrate conc, the reaction rate is directly proportional to the substrate conc. At high substrate conc, the reaction rate is independent of substrate conc. |
|
|
What is the Michaelis-Menton reaction model? |
E+S<--->ES----> E+P S= substrate E= enzyme P= product |
|
|
What are the three asumptions of the Michaelis Menton reaction model? |
[S]>[E] so that the amount of product bound by the enzyme at any one point is small [ES] does not change with time- formation is equal to breakdown Initial velocities used, concentration of product small and back reaction of P to S ignored |
|
|
What is the Micahaelis Menton equation? |
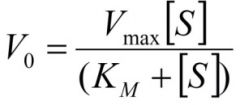
|
|
|
What is Vo? |
the initial reaction velocity, measured as soon as enzyme and substrate are mixed |
|
|
What is Vmax? |
maximal velocity of an enzyme catalysed reation i.e. when all the active sites are full |
|
|
What is Km? |
The Michealis constant The substrate concentration at which the initial velocity is half the maximal velocity |
|
|
The michaelis menton plot |
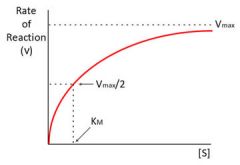
|
|
|
Does Km represent the affinty of the enzyme for its substrate? |
No- unless K2 is rate limiting |
|
|
Equation for Km |
Km= K2+K(-1)/K1 |
|
|
What is Kcat turnover numbers? |
The number of substrate molecules converted to product in a given time on single enzyme molecule whne the enzyme is saturated with substrate |
|
|
The Lineweaver- Burke plot |
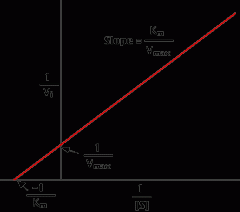
|
|
|
What is a competitive inhibitor? |
Blocks the enzyme active site |
|
|
What is a non- competitve inhibitor? |
Can be reversible or irreversible and will interfer in some way with the catalytic mechanism |
|
|
How do competitve inhibitors effect Km and Vmax? |
alter the Km but not the Vmax |
|
|
How do non-competitve inhibitors effect Km and Vmax? |
lower the Vmax but no effect on Km |
|
|
How is angiotensin production controlled? |
Reduced glomerular filtration means less Na in distal tubule Causes Renin to be released Renin cleaves angiotensinogen to angiotensin I Angiotensin converting enzyme produces angiotensin II which causes peripheral vasoconstriction and Aldosterone secretion |
|
|
What is the effect of angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors? |
Stop formation of angiotensin II so no release of aldosterone causing Na and water retention |
|
|
How is enzyme activity metabolicaly regulated? |
Allosteric binding Covalent modification by other enzymes Induction or repression of enzyme synthesis |
|
|
What are the two types of allosteric enzymes? |
Homotropic and heterotropic |
|
|
How do homotropic allosteric enzymes work? |
They are multisubunit enzymes which have the same binding site on each subunit which funcions as an active site and a regulatory site The substrate acts as an activator to change the enzymes conformation so enhances the binding of subsequenct substances |
|
|
What is an example of a negative allosteric effector? |
ATP |
|
|
What is an example of a positive allosteric effector? |
Fructose 1,6 bisphosphate or pyruvate kinase |
|
|
How does covalent modification regulate enzymes? |
Typically addition or removalof phosphate groups This will either increase or decrease the enzymes activity |
|
|
What is prolytic activation? |
some enzymes are synthesised as larger inactive precursor forms called zymogens which are activated by hydrolysis of peptide bonds |

