![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
11 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is erosion? |
This is the process by which theland is worn away by forces such as water (rivers, ocean waves or glacial ice)or wind. osion is the process by which cliffs areturned into boulders, boulders are turned into pebbles, then further reduced tosand. In a coastal environment, the force of nature doing most of this work iswaves. |
|
|
What is transportation? |
TRANSPORTATION isthe process by which eroded material such as sand is moved to a new place. Inthe coastal environment this is usually done by ocean waves causing longshore drift- a natural process by which sand is transported along a shoreline in aparticular direction. |
|
|
What is deposition? |
When the sea loses energy, it drops the sand, rock particles and pebbles it has been carrying. This is called deposition. Deposition happens when the swash is stronger than the backwash and is associated with constructive waves.Thisis the process by which material is dropped in a new place having been erodedand then transported from somewhere else. There, deposited material such assand will accumulate gradually forming new landform features such as beaches, lagoons, mangroves. |
|
|
What is abrasion action? |
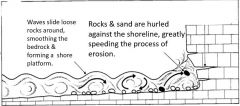
Waves sometimes also have ‘tools’ tospeed the process or erosion. Abrasion is when waves also pick up sand and small rocks and smash them against therocks of the shoreline. This is like turning clear water into sandpaper and itgreatly speeds erosion between high and low tide levels. The process is calledabrasion. |
|
|
What is hydraulic action? |
erosion occurs when pressures exerted by breaking waves as air trapped in cracks in the cliff is compressed by water. This sudden compression and sudden release gradually forces the cracks apart. |
|
|
What causes waves? |
Waves are generated by the wind;therefore, in windy, exposed areas waves have more energy and are moredestructive (erosional waves) while in more protected areas with less wind,waves tend to have less energy and are constructive (depositional waves). |
|
|
Explain the role waves play in coastal erosion? |
Anyonewho has been ‘dumped’ by a big wave will know how much power a wave can have.As they relentlessly pound a shoreline over thousands or years, even thehardest rocks can be worn away. There are two critical factors: time, and thenature of the shoreline geology (specifically, how hard the rocks are).Obviously, some shorelines can be eroded far more quickly than others.d |
|
|
Define these terms: Wave crest Trough Wave length fetch |
WAVECREST - Top of the wave TROUGH - Lowest point between two crestsWAVEHEIGHT - Height between the trough & the crest WAVELENGTH-The distance between two crests WAVEFREQUENCY - The number of waves in any given timeframe BREAKER - Where the top of the wave topples overor breaks Fetch:Fetch, area of ocean or lake surface over which the wind blows in an essentially constant direction, thus generating waves. The term also is used as a synonym for fetch length, which is the horizontal distance over which wave-generating winds blow. |
|
|
What is swash and backwash? |
s |
|
|
What is wave refraction and diffraction? |
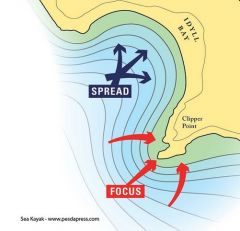
When waves move into shallow water asthey approach the shore they begin to drag on the bottom, rise up, and slowdown. This causes the waves to bend and to take on the approximate shape of theshoreline. Also, when waves approach a headland they wrap around the headlandwhich concentrates the wave energy onto the headland and this is why erosionalfeatures tend to be formed on headlands. In between headlands in sandy bays,the opposite happens as wave energy is spread out (Diffraction). Therefore,deposition is far more likely to occur and a sandy beach might be built |
|
|
What is erosional coastlines? Give example of landform and Victorian coastal region. |
Victoria’s Great Ocean Road is anexample of a predominantly erosionalcoastal environment. Some land forms common are stacks, arches, rock platforms and sea-cliffes |

