![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
51 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back

Atmosphere |
The layer of gases that surround earth |
|

Biosphere |
A relatively thin layer of earth that has conditions suitable for supporting life as we know it |
|

Hydrosphere |
All the water on earth whether present as liquid, vapor or ice |
|

Lithosphere |
Solid portion of earth composed of minerals, rocks and elements |
|

Thermosphere |
Furthest atmospheric layer from earth's surface |
|
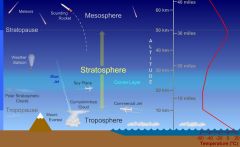
Stratosphere |
Second farthest layer from earth's surface |
|
Climate |
Average weather conditions that occur within a area over a long period of time, usually around 30 ish years |
|

Weather |
Conditions of temp, air pressure, cloud cover, precipitation, and humidity at a particular place at a particular time |
|
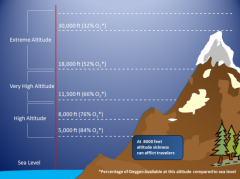
Altitude |
The distance above earth's surface, measured at sea level |
|

Troposphere |
First layer of earth's atmosphere |
|

Mesosphere |
Third layer of earth's atmosphere, and the most boring |
|
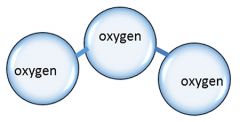
Ozone |
A molecule made up of three atoms of oxygen |
|
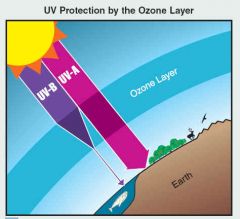
Ozone layer |
A layer within the atmosphere containing high amounts of ozone gas |
|

Climate change |
Change that occurs within the climate in a 30 year or longer time span |
|

Adaptation |
Any change in the structure or function of an organism that makes it more suited to its environment |
|
Scientific Evidence |
Evidence based on facts and tests made using the scientific method |
|
|
Net radiation budget |
The difference between the amount of incoming radiation and outgoing radiation from earth's surface and atmosphere |
|
|
Solar Energy Output |
The amount of energy generated from the sun |
|
|
Terrestrial Energy Output |
Amount of energy generated using Earth's resources |
|
|
Net Radiant Energy |
The amount of energy we make compared to the amount we use |
|
|
EMR Spectrum |
Electromagnetic Spectrum, all known light waves and their lengths |
|
|
Greenhouse Gas |
Gases that contribute to the greenhouse effect |
|
|
Angle of Inclination |
The degree by which Earth's poles are tilted from the perpendicular of the plane of its orbit |
|
|
Angle of incidence |
The angle at which light reflects off of a surface relative to the normal line |
|
|
Latitude |
Imaginary lines that run parallel to Earth's equator with the equator having a latitude of 0 and the poles having a latitude of 90N and 90S |
|
|
Insolation |
The amount of solar energy received by the earth's surface |
|
|
Albedo |
Amount of solar radiation a surface reflects |
|
|
Atmospheric Pressure |
The pressure exerted by the mass of air above any point of earth's surface |
|
|
Conduction |
Transfer of thermal energy by direct contact between the particles if a substance without moving the particles to a new location |
|
|
Coriolis Effect |
The deflection of any object from a straight line path, caused by the rotation of Earth |
|
|
Current |
Flow from one place to another in one direction |
|
|
Jet Stream |
A band of fast moving air in the stratosphere |
|
|
Convection |
Transfer of thermal by the movement of particles from one place to another |
|
|
Radiation |
Emission of energy as particles or waves |
|
|
Heat of Fusion |
The amount of energy absorbed when 1 mol of a substance changes from solid phase to liquid phase without a change in temperature |
|
|
Heat of Vaporization |
The amount of energy absorbed when 1 mol of a substance changes from vapor phase to gas phase without a change in temperature |
|
|
Heat of Condensation |
The amount of energy released when 1 mol of a substance changes from vapor phase to liquid phase without a change in temperature |
|
|
Heat of Solidification |
The amount of energy released when 1 mol of a substance changes from liquid phase to solid phase without a change in temperature |
|
|
Hydrologic Cycle |
The process by which water molecules move from earths surface into the atmosphere and then back again |
|
|
Phase |
State of a substance (solid, liquid, gas) |
|
|
Quantity of Thermal Energy |
The amount of thermal energy absorbed or released when the temperature of a substance changes by a certain number of degrees given the equation: Q = mc^(triangle??)t |
|
|
Specific Heat Capacity |
Amount of energy required to raise temp of specific substance by 1 degree celsius |
|
|
Biome |
A large geographical region with a particular range of temperature and precipitation levels, and the plants and animals are adapted to those climate conditions |
|
|
Closed System |
Any system that exchanges energy with its surroundings without exchanging matter |
|
|
Open System |
System that exchanges both energy and matter with its surroundings |
|
|
Climatograph |
Average of temperature and precipitation of an area for each month of the year for a given location, presented as a graph |
|
|
Carbon Sink |
And process that removes carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, such as photosynthesis |
|
|
Carbon Source |
Any process that releases carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, such as burning of fossil fuels |
|
|
Fossil Fuel |
Carbon-based fuels formed from the remains of living organisms |
|
|
Extrapolation |
Estimating or concluding based on a mindset that the way things are going now will continue |
|
|
Enhanced Greenhouse Effect |
The change in Earth's net radiation budget, caused by the increase in human-generated greenhouse gases |

