![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
8 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Glycoprotein-containing envelope, and therefore susceptible to drying, acid, solvents, and detergents. Space between capsid and envelope contain enzymes and viral proteins that initiate replication and this space is called a tegument. The envelope of Herpes comes from the nucleus of the Golgi membrane. Can be transmitted at time of birth
|
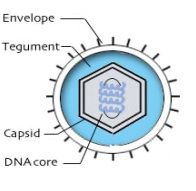
Herpes Simplex Type 1
General notes |
|
|
Herpes Simplex Type 1
Areas of body affected |
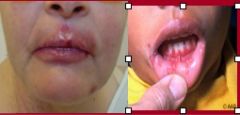
Type 1 - Usually oral, latent in trigeminal ganlia
|
|
|
Herpex Simplex Type 1
Genome and Replication |
Double-stranded DNA envelope virus.LYSOGENIC...1-Latency (asymptomatic) is initiated by transcription by host polymerase in the cytoplasm (not integrated) ON EXAM!. Infection initiated in mucous membrane, virus infects cells at site, and virus moves to innervating neurons, traveling to ganglion. Tissue damage is caused by virus infection and host response. Lesions heal with scarring. 2-Lytic cycle is when the genome has completed transcription performed by viral-encoded polymerase. 3-Regulated by viral-encoded and cellular nuclear factors 4-Scavenger enzymes provide DNA substrates to viral polymerase. 5-Recurrence activated by stress, virus travels down nerve and initiates another lesion at the same site. Recurrent infections are generally less severe, more localized, and heal more quickly.
|
|
|
Herpes Simplex type 1
Epidemiology |
Infected individuals remain infected (and infectious) for life. HSV is labile (enveloped). Transmitted sexually via vesicle fluid (kissing), saliva. 90% of third-wolrd invididuals have HSV 1 and antibody by age 2. Nearly half of adults in US have been infected with HSV 2???. If transmitted during birth, HSV 2 can cause disseminated and neurologic infection. Both types of herpes simplex cause the lesions in either the oral or genital regions, and can not be differentiated by look.
|
|
|
Herpes Simplex Type 1
Virulence Factors |
Infection initiated in mucous membrane (virus infects cells at site, and vius moves to innervating neurons, traveling to ganglion. Infection returns to the original site and produces vesicles (but may be inapparent). Herpes simplex has clever mechanisms to avoid antibody-mediated inactivation. Glycoprotein C (gC) binds and depletes complement. gE/gl complex binds Fc portion of antibody = camouflage ON EXAM. Infection is controlled by TH1-associated delayed-type hypersensitivity and cytotoxic killer T-cell (culprit = CD8 ON EXAM). Humoral immunity (i.e. antibodies) is ineffective. Cell mediated immunity is responsible for many of the symptoms. In immunocompromised pateints (weak or absent CMI) HSV can disseminate to vital organs and brain. (hides during latency and spreads cell-to-cell). Tissue damage is caused by virus infection and host reponse and lesions heal without scaring. Encodes a protein which blocks TAP channel, thus can't get viral antigen thru TAP channel in order to be presented on MHC I which prevents recognition by CD8 cells.
|
|
|
Herpes Simplex Type 1
Signs and symptoms |
Oral herpes - in kids (50% teenagers), usually type 1. In adults, mostly type 1 (89-90%), some type 2 (22%). Clear vescicle on an erythematous base. Becomes pustular, crusted, and PAINFUL! Recurrence via "cold sores." Reactivates from trigeminal nerve.
Herpetic keratitis - eye infection which can lead to scarring and blindness. Herpetic whitlow - infection on finger (thumb-suckers). Herpetic gladitorum - on body, frequently seen in wrestlers. Eczema herpeticum - seen in kids with eczema, may disseminate. Herpes pharyngitis - presents like Group A strep (ON EXAM). |
|
|
Herpes simplex Type 1
Laboratory Diagnostics |
Serology is not useful because it is cell mediated. Tzanck Smear - scrape the base of a lesion, Pap stain shows giant cells and inclusions. Culture - sensitive and rapid (2-3 days), lab will usually tell you if it is type 1 or 2. Biopsy of brain - herpes can be seen by a good pathologist.
|
|
|
Herpes Simplex Type 1
Treatment |
The scavenger enzymes are targeted by some antiviral agents because they are different from host cell enzymes. Most drugs are nucleotide analogues and inhibitors of DNA polymerase. Acyclovir is activated by viral thymidine kinase (ON EXAM - acyclovir mechanism of action); incorporated by polymerase into viral DNA instead of tymidine; prevents elongation of DNA molecules; Resistance mechanism = inactivated viral thymidine kinase. Treatment may shorten symptoms but doesn't eliminate latent infection.
|

