![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
45 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is research? |
A systematic/methodological way to understand phenomena and to answer questions. |
|
|
What is ontology? |
Distinct assumptions about the nature of reality |
|
|
What is epistemology? |
How we can come to know that reality |
|
|
What is methodology? |
How we can systematically assess what can be known about that reality |
|
|
What is a research design? |
Structure of scientific project |
|
|
What is a method? |
An instrument of acquiring the knowledge about the reality (data collection and analysis) |
|
|
What belongs to what in methodological fit according to Edmondson & McManus (2007)? |
Quantitative vs. mature hybrid vs. intermediate Qualitative vs. nascent |
|
|
What is the difference between quantitative and qualitative? |
Quantitative is fixed, qualitative is flexible. |
|
|
What are two essential things when discussing fixed designs? |
- pilot studies always necessary - the golden standard |
|
|
What is the golden standard at fixed designs? (3) |
randomized controlled trials (medicines) - Random assignment of participants to different conditions / manipulation of one or more variables (IV) - Measurement of effects of this manipulation on one or more variables (DV) - Control of other variables |
|
|
What are problems of experimental studies? (4) |
- random assignment - external validity - ethical issues - control of other variables (and no other group to check for influence) |
|
|
What are quasi-experimental studies? |
Compromised true experimental studies (e.g. no lab, no pre-test, no random assignment. |
|
|
What should be avoided in quasi-experimental studies? (3) |
- One group, post-test only (much survey research!) - Non-equivalent groups, post-test only - Pre-test post-test single group (some panel studies) |
|
|
What is common-method bias? |
common-method bias is the spurious "variance that is attributable to the measurement method rather than to the constructs the measures are assumed to represent. |
|
|
What are demands of the researcher in qualitative research? (7) |
- Question asking - Good listening - Adaptiveness & flexibility - Lack of bias - Writing skills - Theory-development skills - Rigor |
|
|
What is a common assumption in qualitative research concerning ontology? |
Empirical world of lived experiences The world is: complex, pluralistic, changing, subjective & interpreted |
|
|
What is a common assumption in qualitative research concerning epistemology? (5) |
- Unarticulated - Contextual - Temporal / process - Spatial Taken for granted - Tacit |
|
|
What are the 6 implications for qualitative research design? |
- researcher is involved - small samples - generating theories - fieldwork methods - falsification - looking for differences |
|
|
What are the 6 implications for quantitative research design? |
- researcher is independent - larger samples - testing theories - experimental design - verification - looking for similarities |
|
|
Why qualitative research in entrepreneurship? (4) |
- It’s a young field - With heterogeneous phenomena - Sometimes infrequent, accidental and extraordinary phenomena - The process character of entrepreneurship |
|
|
What are the five official judgment criteria? |
• Internal validity: is there really a relationship between A and B (or is there a factor C)? • Construct validity: do I measure what I think I’m measuring? • External validity: Is it also valid in other settings and over time? • Reliability: Is my measurement consistent over time (e.g., test-retest). • RQ fit • Theory-status (nascent, intermediate, mature) |
|
|
What are the unofficial (underbelly) judgment criteria? (6) |
- Time consumption of a method - Experience with a particular method - Writing abilities - (Perceived) journal preferences - Personal preferences (of your supervisor) - Opportunism |
|
|
What should you do when you know you cannot construct a flawless design? |
Do multiple studies which are complementary (so not redundant) to each other |
|
|
Which options exist for multi-method designs? (5) |
• Sequential explanatory: Quant --> qual • Sequential exploratory: Qual --> quant • Concurrent triangulation design • Concurrent nested • Sequential/concurrent transformative design (theoretical framework requiring both qual & quant measures) |
|
|
What are advantages of multi-method designs? (7) |
• Triangulation (vs. common method) • Offsetting weaknesses • Answering multiple questions • Dealing with complexity • Explaining not only describing • Illustration of data • Instrument development (sequential exploratory) |
|
|
What are disadvantages of multi-method designs? (4) |
• Skills and training • Timing • Limits: what’s the added value • Lack of integration of data |
|
|
What are the classic sampling steps? (6) |
1. Define relevant population 2. Determine parameters of interest 3. Define unit of analysis (individual, team, firm, industry, spatial unit) 4. Choose sampling frame 5. Determine type of sample (probability vs. non-probability) 6. Determine sample size |
|
|
What are the three different strategies in qualitative research? |
- Sampling comparable cases that differ on the (theoretical) variables of interest. - Search for a representative sample. - Single case sampling. |
|
|
What are the main difficulties of sampling individuals in entrepreneurship? (4) |
1. What is an entrepreneur? 2. Who becomes an entrepreneur and for how long? (Half the population) 3. Compare with non-entrepreneurs? 4. Focus on what they are doing instead of what they are? |
|
|
How should you sample nascent entrepreneurs? (3) |
- Use informants such as incubators; but biased - Use the first visible trace; but 1) incomparable across sectors and regions and 2) often too late in the process. - Snowball sampling: biased as better networked individuals are more represented (and networking is an important variable of interest) - Best method currently: two step approach of PSED (1: screening sample; 2: select NE’s) - Country and culture differences in definitions of entrepreneurs and ventures |
|
|
How should you sample internal venture projects? |
1. Create a sample of larger firms (how?, where?) 2. Select internal projects (how many and how?) |
|
|
How should you sample firms? (Most frequent unit of analysis) (4) |
1. What is a firm? What are the firm boundaries? 2. What about characteristics such as industry and start date, if the firm is active in multiple sectors and different departments started over time? 3. Can you use a single informant for big firms? 4. Random sampling of firms results in oversampling small firms. |
|
|
How should you sample industries? (2) INDUSTRIES ALWAYS MATTER! |
- Heterogeneity: Is the theory applicable to all industries (or only to manufacturing)? Are the industries comparable? - Size distribution: is size an attribute of the industry? |
|
|
What is a spatial unit? |
The spatial unit by which geographic data is organized, subdivided, and stored in a map library. Tiles subdivide the area covered by a map library and organize the library data by location (e.g., counties might be the tiles in a statewide database). |
|
|
What are issues of sampling spatial units? (2) |
- Who is the informant for the region or cluster? - Can you compare the clusters/regions? |
|
|
What entails a hybrid strategy when doing research? |
Hybrid strategies allow researchers to test associations between variables with quantitative data and to explain and illuminate novel constructs and relationships with qualitative data. |
|
|
What are two difficulties when doing quantitative research in areas of nascent theory? |
- it is difficult to create measures of acceptable external validity or reliability when phenomena are poorly understood - Researchers need to go through the process of building new ideas iteratively (with repetition) , with extensive exposure to the phenomenon and an open mind, before becoming captivated by potentially chance associations. |
|
|
What are two difficulties when doing quantitative research in areas of intermediate theory? |
- research in an area of intermediate theory that combines new and established measures without supporting qualitative data data is likely to suffer from the uneven status of empirical measures - in contrast, a purely qualitative study in an intermediate theory area encounters the problem of lost opportunity for preliminary statistical support for its hypotheses. |
|
|
What are two difficulties when doing quantitative research in areas of mature theory? |
- there is a problem of reinventing the wheel - when integrating both quali and quanti in a single paper faces the uneven status of evidence. the challenge lies in assessing whether qualitative data in all its richness is of value to or unnecessary. |
|
|
What are the three distinct meanings of quantitative according to davidsson? |
- using many cases - applying formal measurement - the use of statistical or mathematical data analysis techniques |
|
|
What is a reason for conducting laboratory research in entrepreneurship instead of real-life settings? (3) |
- The process nature of entrepreneurship - Real-world entrepreneurs or intrapreneurs don't always provide us with all the right answers. - laboratory research makes it possible to compress time data without having to wait before any analysis is done. |
|
|
What is a general shortcoming of laboratory research |
The external validity of the findings can always be questioned |
|
|
What are the possible options for research design? (poor visibality, check p. 127 of Blumberg/cooper) |
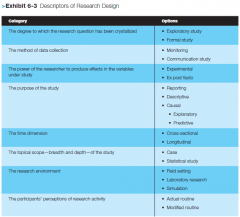
|
|
|
What is business research? |
A systematic inquiry that provides information to guide managerial decisions |
|
|
What is good research according to Blumberg/cooper? |
1. purpose clearly defined 2. research process detailed 3. research design thoroughly planned 4. high ethical standards applied 5. limitations frankly revealed 6. adequate analysis for decision maker's needs 7. findings presented unambiguously 8. conclusions justified 9. researcher's experience reflected |

