![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
93 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
|
|
|
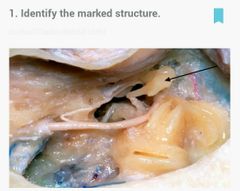
Blood supply of labyrinth |
Labyrinthine artery. Br. Of AICA |
|
|

|
|
|
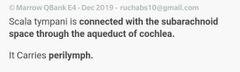
|
|

|
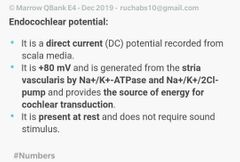
|
|

|

|
|
|
Parts of vestibule are |
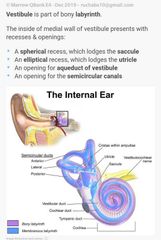
|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|
|

|
|

|
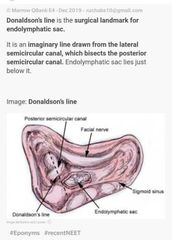
|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|
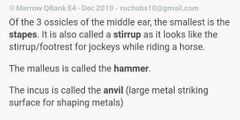
|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|
|

|
|

|
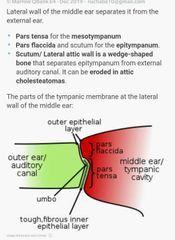
|
|

|

|
|

|
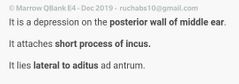
|
|

|
|
|

|

|
|

|
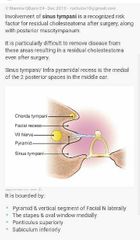
|
|

|
|
|
|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

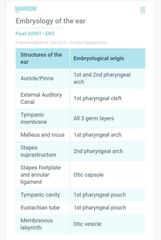
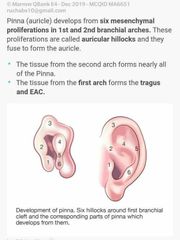
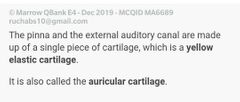
Embryological Derivatives of ear |
|
|

|

|
|

|
|
|

|
|
|

|

|
|

|
|
|

|

|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|

|
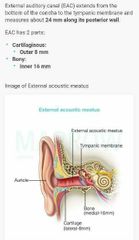
|
|
|
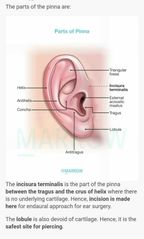
Furuncles are seen in |

|
|

|

|
|

|
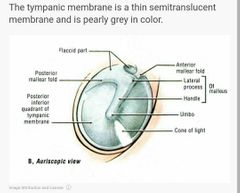
|
|
|
Dimensions of tympanic membrane: thickness, length, width, Area, angle with horizontal |
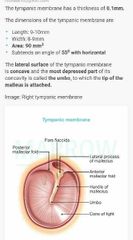
|
|

|
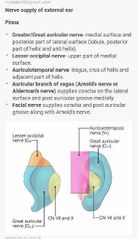
|
|
|
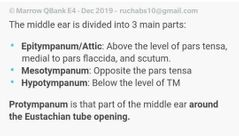
Relations of middle ear walls |
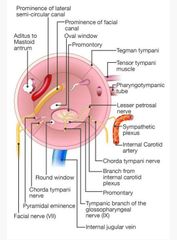
|
|

|
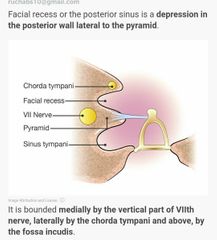
|
|
|
Which structure forms the promontory |

|
|

|
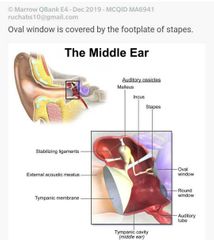
|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|
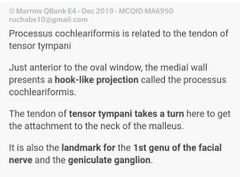
|
|

|

|
|

|
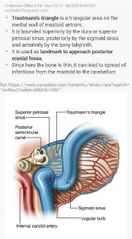
|
|

|
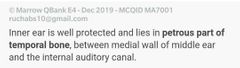
|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

Frequencies at different parts |

|
|

|
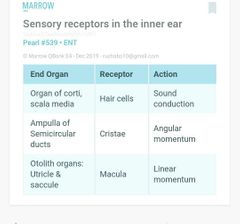
|
|

|

|
|
|
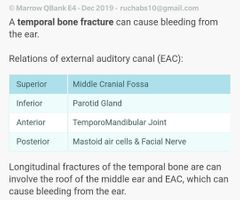
Skin lining the bonny EAC is |
Stratified squamous epithelium without appendages |
|
|
Forman of Huschke |
Deficiency medial to isthmus. Communicates with base of skull and parotid. Closes by 5-6 years of age |
|
|
Sharpnells membrane |
Also called pars flacida |
|
|
Aditus |
Opening on the posterior superior part of the middle ear. Use- ventilation for mastoid and spread of infection |
|
|
Sound threshold for stapedial reflex |
90-100 decibal above normal |
|
|
Stapedial reflex afferent and different and their palsy. Use. |
Afferent- 8th nerve. Palsy results in loss of reflex in both ears.
Efferent - 7th nerve. Pasly results in loss of reflex in that ear
Use - detect malingering |
|
|
Carotid wall of middle ear? |
Anterior wall |
|
|
Anterior middle ear wall opening for cord tympani |
Canal of Huguier |
|
|
Membranes in the cochlea Separating , 1. scala vestibule & media. 2. Scala media & tympani |
1. Reissner's membrane 2. Basilar membrane |
|
|
Ototoxic drugs |
A3 - Aminoglycosides Ototoxic ( K - Kanamycin. A - Amikacin. N - Neomycin ( MOST OT) Vestibulotoxic ( G - Gentamycin. S - Streptomycin. ) - Antimalarials - Analgesics V - Vancomycin - Vancomycin C - Cyclosporin D - Loop Diuretics A and V are irreversible. |
|
|
Shearing force moving Basilar Membrane |
Transduction |
|
|
Auditory parhway |

|
|
|
Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo |
Calcium Carbonate crystals ( Otolith) from Macula dislodge into semicircular canals ( MC- posterior) cause vertigo. |
|
|
Bill's bar |
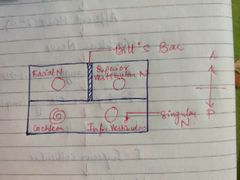
In Internal acoustic meatus |
|
|
MC benign Tumor of Cerbropontine angle |
Acoustic neuroma |
|
|
Rinne's and webber Algorithm |
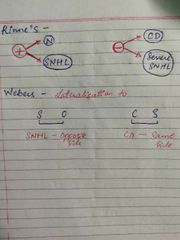
|
|
|
Absolute Bone Conduction Test and Schwabach Test Algorithm |
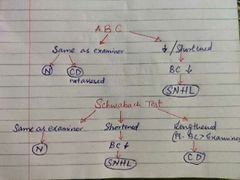
|
|
|
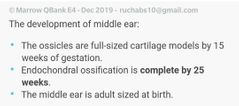
Bony Labyrinth embryological formation |
From Mesenchymal origin. Undergoes enchondral ossification |
|
|
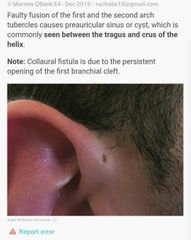
Fistula Ante Fenestrum |
Fixes footplate of stapes --> Otosclerosis. ( MC middle ear pathology) |
|
|
Michel Aplasia, Alexander Aplasia, Mondini A. , Scheibie A |
M - the complete absence of cochlea and nerve. Is a Contraindication for implant A - absence of basilar turn. High frequency affected Mo - Only 1.5 turn of the cochlea S - vestibular dysplasia along with cochlea MC type |

