![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
51 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back

Matter |
°Occupies space and has weight(mass) °composed of atoms |
|
|
Solid (Characteristic of Matter) |
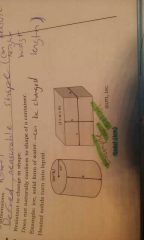
°3 dimensions °Resistant to change in shape °Does not naturally conform to shape of container *Heated solids turn into liquids |
|

Liquid (Characteristic of matter) |
°No clearly defined shape. °FILLS BOTTOM AND SHAPE OF CONTAINER ° Can be atomized(liquid drops suspended in air). *Flammable liquids must be vaporized(turned into a gas) before they will burn |
|

Gas (Characteristic of Matter) |
°No clearly defined shape. *EXPANDS TO FILL THE SHAPE OF CONTAINER ° Highly compressible
|
|
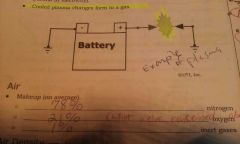
Plasma (Characteristic of Matter)
|
°No clearly defined shape °Does not fill a container like a gas or water(amorphous). *SUPER HEATED GAS *Cooled plasma changes form to a gas.
|
|
|
Air |
°78% Nitrogen °21% Oxygen °1% inert (not able to move) gases |
|
|
Air pressure |
°Mean Sea Level Pressure (MSLP) is normal,everyday atmospheric pressure=14.7psi °⬇when altitude⬆ °pressure differences between two points results in air movement °Can move matter ex:weather. °AN ENGINE'S INTAKE EVENT |
|

Air Density |

|
|
|
Boyle's Law |
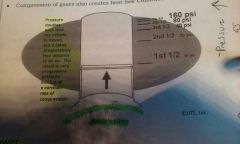
A trapped gas doubles its pressure each time it's volume (space) is halved (compressed,lessened) |
|
|
Power |
°Is the production of EFFORT, WORK OR FORCE *FORMULA: Power=Amount of work÷ period of time |
|
|
Motion |
Change of position over time |
|
|
Velocity |
°INDICATES SPEED OR DESTINATION of an object's movement °constant velocity is the speed of an object from point A to point B |
|
|
Acceleration |
°rate of velocity over time. *How fast you can reach a certain SPEED (ex: Mario Kart) |
|
|
Mass |
°Resistance of an object to acceleration *considered weight by motorcycle standards |
|
|
Inertia |
Resistance to change in motion or direction |
|
|
Law of Inertia |
A body in motion wants to stay in motion ( short version) |
|
|
Momentum |

°The ENERGY WITHIN a moving object *FORMULA: =mass x velocity Or =weight x speed |
|
|
Energy |
°is the ABILITY TO DO WORK *Thermal= light and warmth emitted by 🔥 *Electrical= spinning an electric motor with power *Gravitational= dropping an object and watching it fall *Magnetic= push two + magnets together and fuel the resistance |
|
|
Newton's Law |
°Energy cannot be CREATED OR DESTROYED ° Can be converted or changed from one form to another *conversion is not 100% efficient ➡EXAMPLE: Drop a ball and it will not bounce up to the same level |
|
|
Potential Energy |
°latent or NOT CONVERTED FROM ONE FORM TO ANOTHER ➡EXAMPLE: Holding ball in the air |
|
|
Kinetic Energy |
°energy required to create movement is stored in a moving object
|
|
|
Active energy |

°energy that has been CONVERTED FROM ONE FORM TO ANOTHER *EXAMPLE: Energy converted to light |
|
|
Force |
°The amount of PRESSURE used to create work (weight, pressure, voltage) °Brake Mean Effective Pressure (BMEP)...indicates the average pressure of all power STROKES ➡FORMULA: 2-stroke BMEP = 75.4 psi × Torque (ft - lb.) ÷ Displacement (CI) ➡ FORMULA: 4-stroke BMEP = 150.8 psi × Torque (ft.- lb.) ÷ Displacement (CI) |
|
|
Work |
°The application of FORCE TO MOVE AN OBJECT ➡FORMULA: force × distance **EXAMPLE: 50 lb. pushing on 1 ft. long lever = 50 ft.- lb. torque ** movement of the piston in a cylinder is work |
|
|
Leverage |
°Ability of a pivoting bar to use distance to gain mechanical advantage. |
|
|
Leverage |
°ability of a pivoting bar to use distance to gain mechanical advantage
|
|
|
Torque |

°ability to create TWISTING OR ROTATIONAL WORK ➡EXAMPLE: combustion FORCE applied to crankshaft leverage |
|
|
Horsepower |

°Is the rate at which work is performed ➡FORMULA: (force×distance) ÷ time = power *HORSEPOWER RESULTS FROM TORQUE (COMBUSTION FORCE) AND RPM (COMBUSTION FREQUENCY) |
|
|
Oxidation (Combustion) |

°COMBINING OXYGEN TO ANOTHER MATERIAL |
|
|
Internal Combustion (Gasoline Engine) |
°Compresses air and fuel then used a spark to initiate combustion |
|
|
Internal Combustion ( Deisel Engine) |

° Compresse air and fuel until the temperature increases to the point of combustion (Boyle's law) |
|
|
External Combustion |
°combustion occurs outside the engine ➡EXAMPLE: steam engine |
|
|
1st stage of COMBUSTION |

COMBUSTION LAG is the time it takes after ignition for combustion to reach peak pressure (low pressure to peak pressure) |
|
|
2nd stage of COMBUSTION |
°ACTIVE COMBUSTION is the working pressure. |
|
|
3rd stage of COMBUSTION |
°POST-COMBUSTION activity. °no power production °The piston continues moving due to crankshaft momentum. |
|
|
Abnormal Combustion (Pre-ignition) |
°Is an untimed burn event (valves) with normal combustion speeds. °Occurs BEFORE normal ignition. * Will not cause a ping or knock. **Caused by hot spots in the cylinder such as too hot of a SPARK PLUG, PROTRUDING GASKETS, METAL BURRS,AND CARBON DEPOSITS HEATED from previous combustion cycles. |
|
|
Abnormal Combustion (Detonation) |

°Untimed explosive event with rapid combustion speeds. *usually happens just after spark ignition *Usually happens just after spark ignition °Can be caused by POOR QUALITY FUEL, TOO LOW OCTANE,TOO HIGH OF COMPTESSION RATIOS,HIGH ENGINE LOAD, PRE-IGNITION AND POOR STATE OF TUNE. |
|
|
result of Combustion (physical) |
°a low thumping sound °normal pressures may peak over 1000 PSI °normal temperatures can reach 4000°F (1/3=exhaust,1/3=cooled, 1/3=heat nitrous) |
|
|
Result of Combustion (Chemical) |
➡carbon monoxide CO is a colorless, odorless, and lethal gas °partially burned fuel ➡hydrocarbons HC are chains of multiple hydrogen and carbon atoms. °unburned fuel *lean mixtures,lean misfires, and low compression can cause high HCs.
|
|
|
Result of Combustion (Chemical) |
➡✅Carbon Dioxide CO2 is the ideal product of HC combustion where two oxygen molecules bind to a carbon molecule and split off from the hydrocarbon chain °result of complete combustion |
|
|
Result of Combustion (Chemical) |
➡⚠Oxides of nitrogen NO× or Acid ☔ rain °NO× is toxic to animals and plants in higher levels *in low doses NO× is safe for our environment and acts as a fertilizer for plants *High combustion temperatures cause nitrogen to bond to two or three oxygen molecules |
|
|
Result of Combustion (Chemical) |
➡✅ water H2O is an ideal by-product of Combustion where the hydrogen molecules bind to oxygen |
|
|
Emissions Standards (CAA) Clean Air Act |
°1970 Clean Air Act (CAA) was created by Congress to regulate the emission of airborne pollutants. |
|
|
Emission Standards (EPA) Environmental Protection Agency |
°1970 ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION AGENCY (EPA) established to protect the environment and human health and govern the CAA. *the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regulates motorcycle emissions from new Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) *Exhaust emissions of CO,HC,NO× and particulate matter. |
|
|
Department of Transportation (DOT) |
°responsible for safe,secure, and quick transportation to support our nation's growth. * established the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) to govern safety related items on new automobiles and motorcycles |
|
|
Emission Controls |
➡CHARCOAL CANISTERS or carbon containers are used to trap fuel which has evaporated from the fuel system or if the fuel tank is overfilled. *California Air Resource Board (CARB) required emissions item ➡AIR INJECTION allows air to be introduced to exhaust gases. ➡CATALYTIC CONVERTER converts toxic gases to safer gases through oxidation. *Rich mixtures can cause temperatures to rise and can clog and damage CATALYTIC converters |
|
|
Volumetric Efficiency (Engine) |
°HOW FULL THE CYLINDER GETS. *Affected by: ➡Valve timing ➡Intake and exhaust tuning ➡Intake Velocity ➡Naturally aspirated ➡Supercharging or turbocharging can increase volumetric efficency over ambient pressures
|
|
|
Combustion efficiency (engine) |
°HOW COMPLETELY THE CYLINDERS CONTENTS BURN. Affected by: ➡Combustion chamber design,intake velocity. ➡Anything that affects mixture |
|
|
Thermal efficency (Engine) |
°HOW MUCH OF COMBUSTION'S HEAT ENDS UP PUSHING ON THE PISTON. *Heat Distribution ➡30-35% pushes piston ➡30-35% leaves with exhaust gases ➡30-35% radiated away |
|
|
Stroke efficiency (engine) |
°HOW FAR DOWN THW COMBUSTION STROKE THE PISTON IS MOVED BY THE COMBUSTION PRESSURE Affected by: ➡ignition timing= when spark plug sparks ➡rod/stroke ratio |
|
|
Mechanical efficiency |
°HOW MUCH POWER IS LOST TO FRICTION, PARTS FLEX, AND OTHER ENERGY ABSORBING FACTORS, SUCH AS ALTERNATOR DRAG. Affected by: ➡number of cylinders, number of bearings ➡fit of parts ➡Rigidity of parts |

