![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
9 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
The difference between positive and negative work |
|
|
|
What type of product of vectors is work? |
|
|
|
What is the work done by a variable force? |
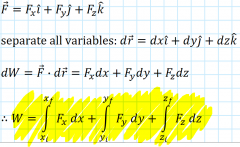
|
|
|
What is the work-and-kinetic-energy theorem for a variable force? |

|
|
|
Power |
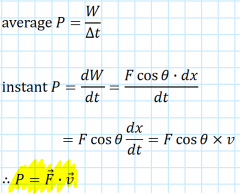
The rate at which work is done
|
|
|
How is potential energy related to work? |
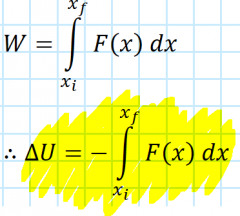
ΔU = −W |
|
|
What is the gradient of a potential energy curve? |
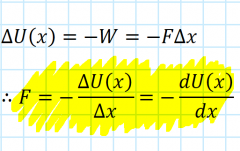
Force |
|
|
What are the 3 equilibrium points? |
|
|
|
What does the conservation of energy state? |
|

